How to cook humus in the garden, dacha using accelerated technology. When and how organic fertilizers are applied. The effect of organic matter on a plant
Manure is considered the most convenient and readily available fertilizer. It is also used in small beds where various crops are grown - from vegetables to flowers. What kind of manure to choose for your site and why?
Manure application for plant nutrition - good tradition, which is more than two thousand years old. In a broad sense, it is a natural fertilizer of animal origin, excrement of farm animals (cows, horses, pigs, chickens and sheep) or mixtures thereof in different proportions. The manure contains a large number of active microflora, which is a source of trace elements and serves to enrich the soil. Manure also has a number of others advantages:
- acting as a complex fertilizer, manure gradually and evenly feeds plants with nutrients;
- decomposing in the soil, it saturates the root system with carbon dioxide and promotes photosynthesis;
- with the help of manure, you can adjust the composition of the soil, increase its looseness and permeability (for heavy clay soils) or increase the viscosity and ability to retain moisture (for light and heavy sandy soils);
- the effect of feeding with manure lasts up to 5-6 years on clay soils, and 3-4 years on sandy soils.
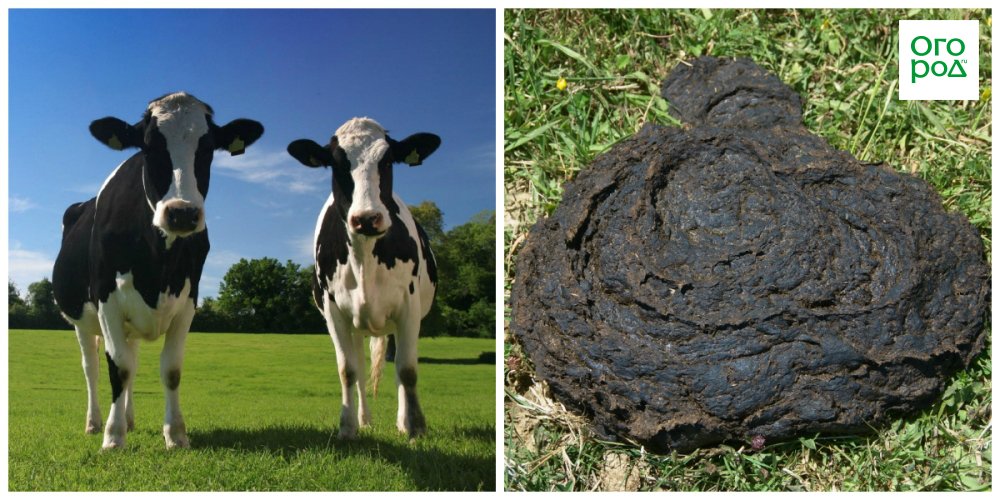
Feeding plants with cow dung
Many summer residents believe that cow dung is best fertilizer... It is actually one of the most popular and versatile organic fertilizers with maximum nitrogen content.
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
|
|
Cow dung is used to feed the following crops:
- cucumbers;
- tomatoes;
- cabbage;
- pepper;
- potatoes;
- fruit trees and shrubs;
- roses and other perennials.
Fresh mullein is not brought into the beds with root crops (turnips, carrots, radishes), kohlrabi and Chinese cabbage, garlic, onions and legumes.
Depending on the degree of decomposition, several types of cow dung are distinguished:
- fresh manure(the litter is unchanged and is applied immediately);
- semi-rotten manure(the litter has begun to decompose, has a low tensile strength);
- rotted manure(strongly darkened, litter is easily destroyed);
- humus(the fertilizer was caked and became homogeneous);
- dry dung(the basis for the preparation of infusions and foliar feeding).



The best time to apply cow dung is autumn... With podzimny top dressing, the manure gradually decomposes during the winter months and evenly feeds the soil and plant roots. For this purpose, manure is evenly scattered over the site at the rate 6 kg per 1 sq. M soil and dig up the soil.
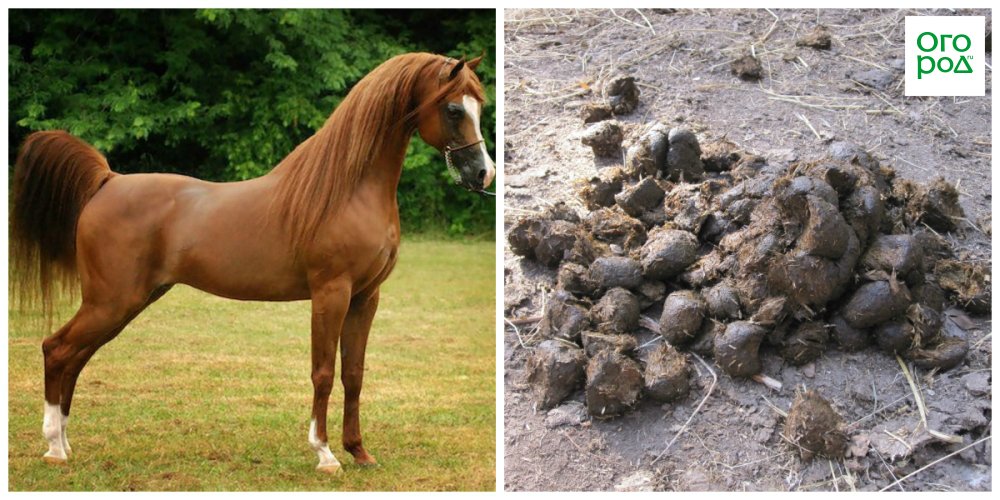
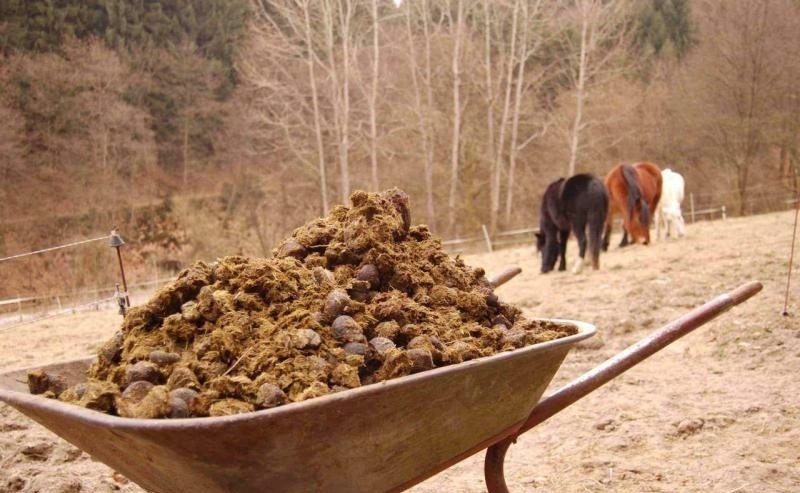
Feeding plants with horse manure
In a correspondence dispute about which manure is better, the horse sometimes "outperforms" its cow "fellow".
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
|
|
Horse manure is mainly applied for the same crops as cow... Litter can vary in composition and degree of decomposition (similar to cow dung):
- combined composition (the best - filled with peat, straw or sawdust) or "clean" manure;
- fresh, semi-rotted, rotted manure or humus.



The "older" the composition, the darker the organic looks. The components of the "young" manure are clearly visible.
Horse manure is applied in the spring or in the fall... Usually, fresh fertilizer is tried because it contains the maximum amount of nitrogen and energy to heat the soil. It is fresh manure that is used to fill greenhouses and warm beds. But manure, which is 3-4 years old, is also quite suitable. It loses its acrid odor, is saturated with beneficial microorganisms, acquires an optimal structure and moisture content.
In order for horse manure to "work" as efficiently as possible, the following must be observed introduction rules:
- lay it with a layer of 30-40 cm for the spring organization of the greenhouse and with a layer of 50 cm for the autumn formation of beds;
- cover evenly with straw on top;
- cover with a 30-35 cm layer of earth.
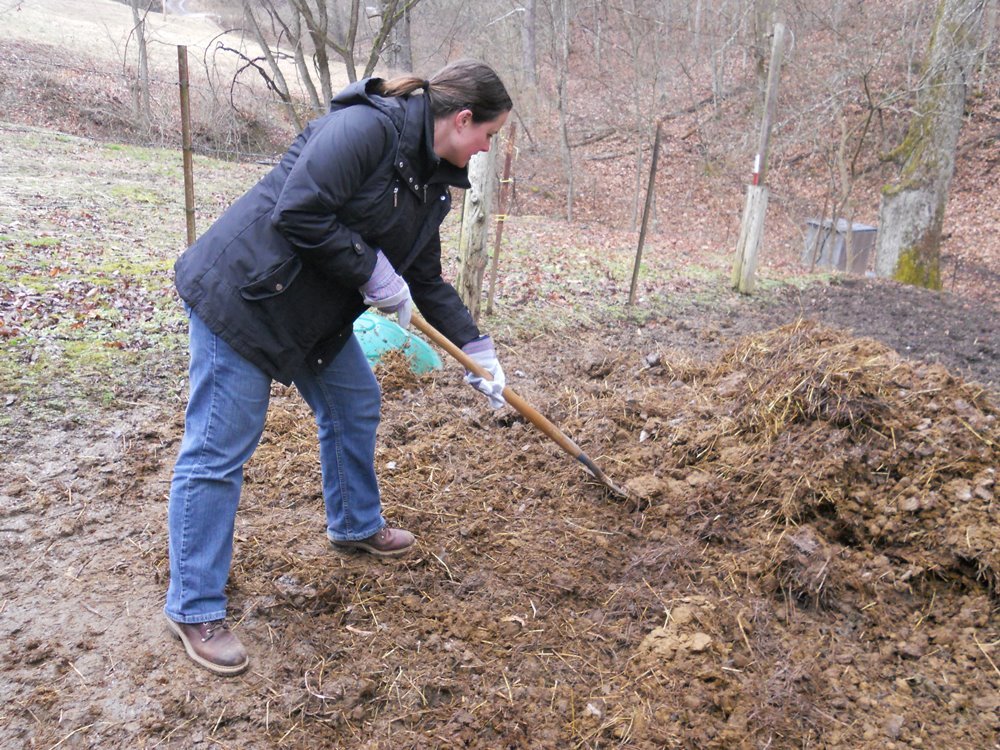



On 1 sq.m make no more than 6 kg horse manure, and immediately plow it up to avoid the loss of useful properties of the fertilizer.
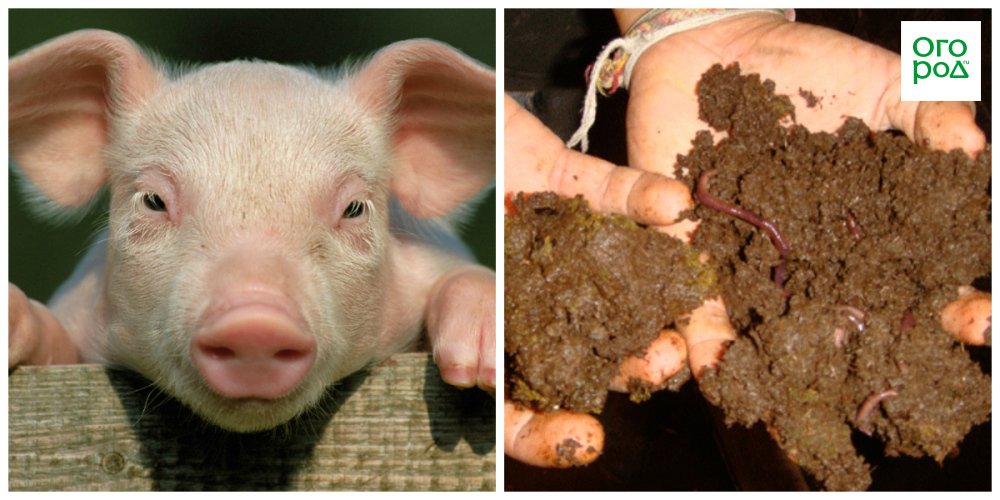
Pig manure as fertilizer
A distinctive feature of this type of manure is its composition. As you know, pigs eat food of plant and animal origin, which creates an original "cocktail".
You can neutralize the high pH level of swine manure by using dolomite flour or lime.
Basically, pig manure is used to fertilize vegetable crops, necessarily neutralizing its increased acidity. Moreover, he must rotate within 1 year. It is best to apply such manure to feed plants. in the fall, then by spring its effect will be maximum.



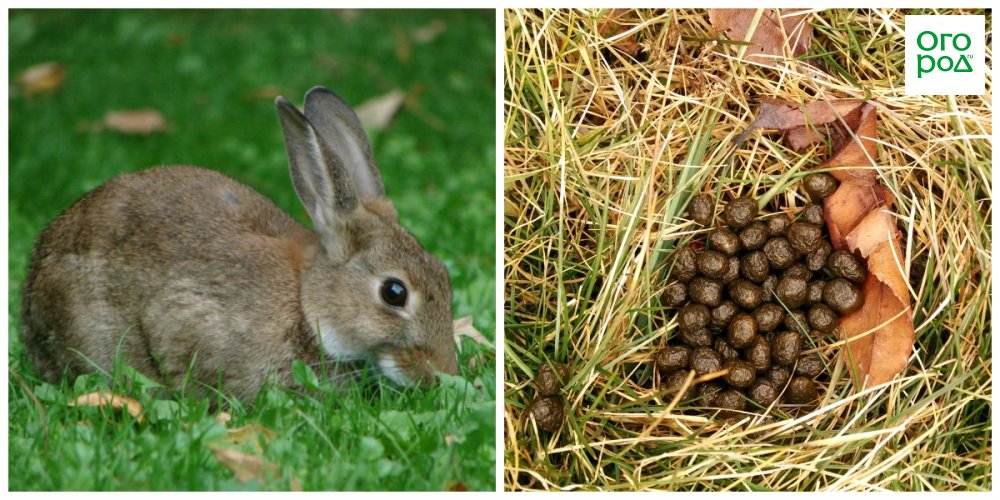
Rabbit dung as fertilizer
It turns out that these animals are valuable not only meat and skins, but also waste products. Rabbit manure is sometimes jokingly called a real "gold mine" - it contains many useful and necessary trace elements for plants.
Apply rabbit manure it can be done in different ways: in liquid form and in the form of a dry powder. You can do this as in the fall and in the spring... In liquid form, manure is introduced into the holes during plowing or before sowing. To do this, 1 kg of manure is diluted in 10 liters of water and insisted for a day, stirring occasionally. For 1 sq. M. contribute no more than 2 l composition.



To make dry powder, rabbit manure is first dried in the sun and then ground to a powdery state. Dosage of dried manure - 1 tsp powder for 1.5 kg of soil.
And you can make an incredibly useful fertilizer from rabbit manure:
- mix manure with plant and food waste;
- transfer the mixture to the compost heap (rabbit droppings should be no more than 10% of the total mass of materials in the compost heap) and put some earthworms there;
- after 40-45 days, stir the pile, removing the worms from the bottom layer. You will get high quality humus that can be used to feed all plants without exception.
Feeding plants with chicken droppings
It is an excellent alternative to complex additives and complex mineral fertilizers. The nutrients contained in organic matter are less washed out of the soil and do not create a high concentration of salts.
|
Advantages: |
Disadvantages: |
|
|
Adding chicken manure to the soil favorably affects the growth and development of crops such as cabbage, eggplants, tomatoes, and other vegetables. Also, this fertilizer is suitable for berry and fruit plants.
Feeding with chicken droppings of onions, garlic and other green crops should be carried out only at the beginning of their growing season (late spring - early summer), since fertilizing during the active growth of spicy plants will spoil their taste
- it is recommended to apply chicken manure to wet soil, after watering or rain, as in a humid environment its decomposition and assimilation takes place faster;
- in the garden for the autumn digging of the soil, 2 kg of fresh droppings are introduced per 1 square meter;
- trees and shrubs are fed with fresh chicken droppings diluted with water in a ratio of 1:15. The solution is poured away from the center of the trunk circle so as not to burn the roots. For one tree, you will need a bucket of top dressing, and for a bush, a little less.
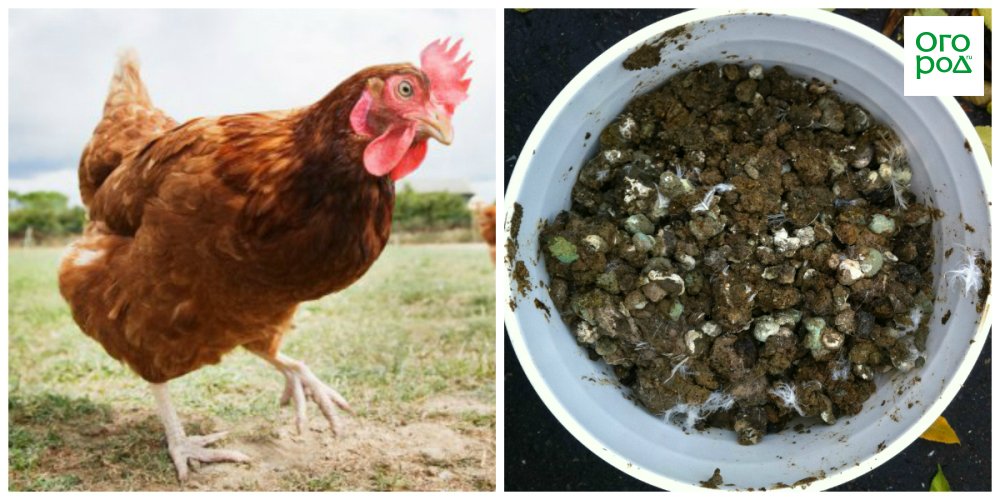



Dry chicken manure and compost based on it should be applied exclusively in the fall. Feeding plants in spring can slow down fruiting. Spring feeding allowed only on sandy soils.
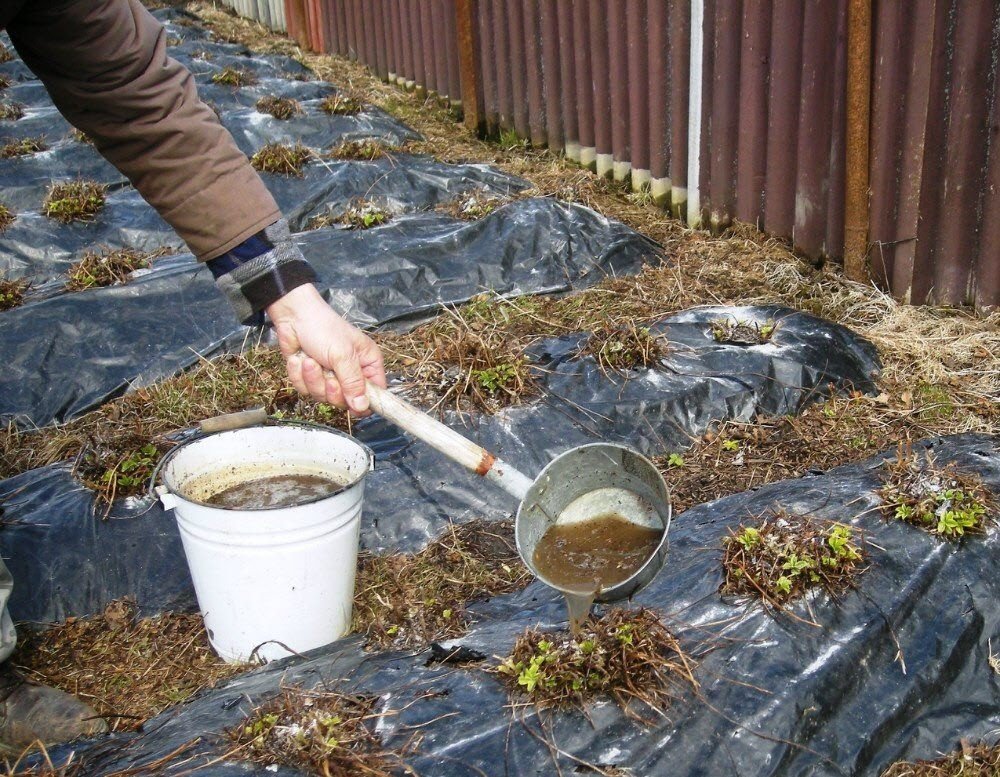
Top dressing with slurry
Slurry stands apart from the family of natural fertilizers. This is a "quick" fertilizer used during the growing season rather than before boarding. The main elements of fertilizer are nitrogen and potassium.
Do not confuse slurry and mullein. Slurry is the liquid or semi-liquid part of the manure, and mullein is an infusion made from fresh manure.
The slurry is especially helpful during the period of intensive tops growing and the formation of green mass. Fertilizer is used practically for any plants, there are no serious restrictions on its use. During the setting, formation and ripening of fruits, feeding is reduced, and then completely stopped.
In its pure form, slurry is not used. It is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 5-7 and superphosphate is added (50-60 g for every 10 liters of solution). Top dressing is applied in the aisles, in pre-prepared grooves to a depth of 10-15 cm and then covered with earth.
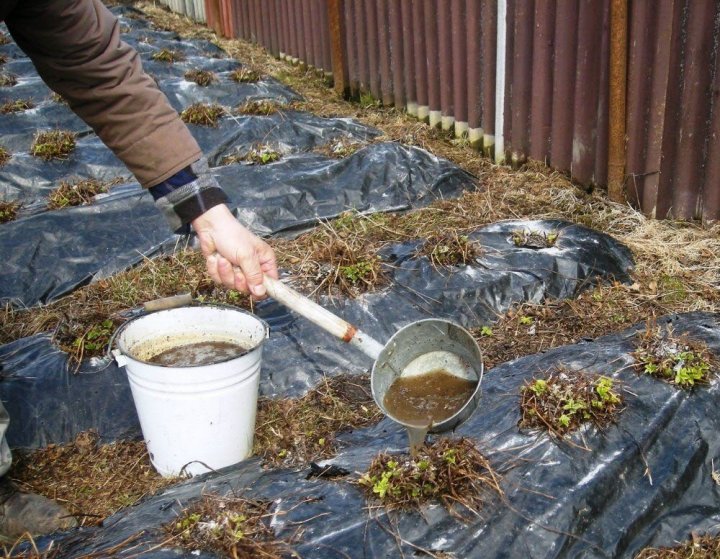



How to dilute manure for feeding
Manure watering sometimes it is considered more effective way fertilization than spreading fresh or dry material. That is why manure is often diluted with water. But in what proportions should this be done?
- Cow dung. Fresh fertilizer is placed in a container and diluted with water in a 1: 5 ratio. Withstand for 10 days, stirring the solution every 2-3 days. Received mullein before application, dilute again with water 1: 2 (if the soil is wet) or 1: 4 (if the soil is dry).
- Horse dung. Fresh fertilizer is mixed with water in a ratio of 1:10 and infused for 10-14 days, only after that the plants are watered. Liquid "express feeding" is prepared differently - the manure is poured with water in a 1: 1 ratio and insisted for 2-3 days in an enamel or plastic container. Before fertilization, the composition is filtered and again diluted with water in a 1: 1 ratio.
- Pig manure. This is one of the most caustic species manure. It is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:15.
- Rabbit dung. For feeding tomatoes, peppers and cucumbers during the flowering period, rabbit manure is diluted in a ratio of 1: 5, and during fruiting - 1:10.
- Chicken droppings... Initially, the container or barrel is half-filled with droppings and then filled with water to the brim. The mixture is infused for 14 days, and before addition, it is again diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10.
It remains only to find out how much manure of one kind or another fits in a standard 10 liter bucket.
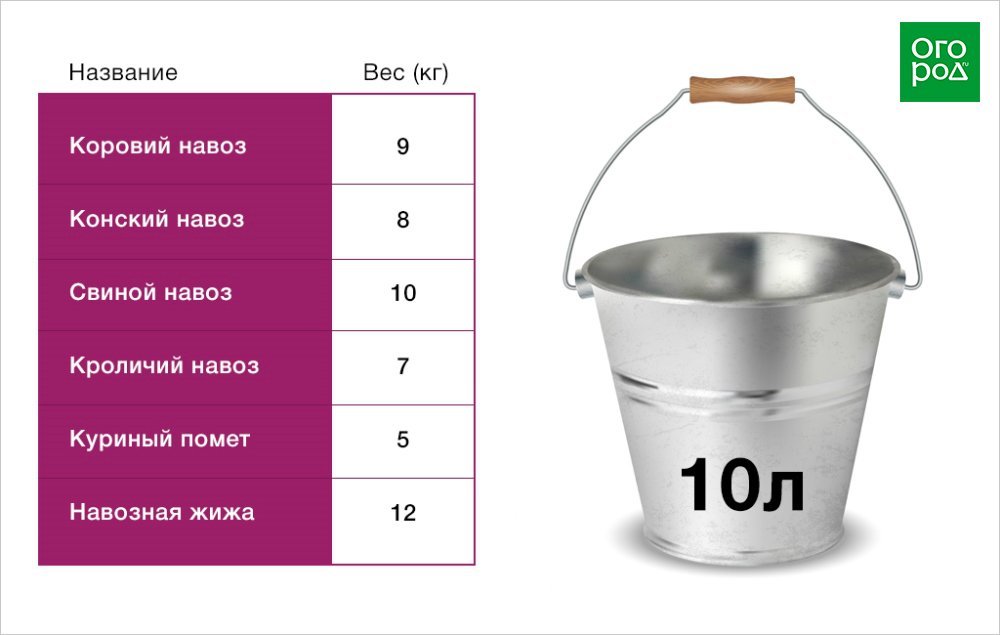
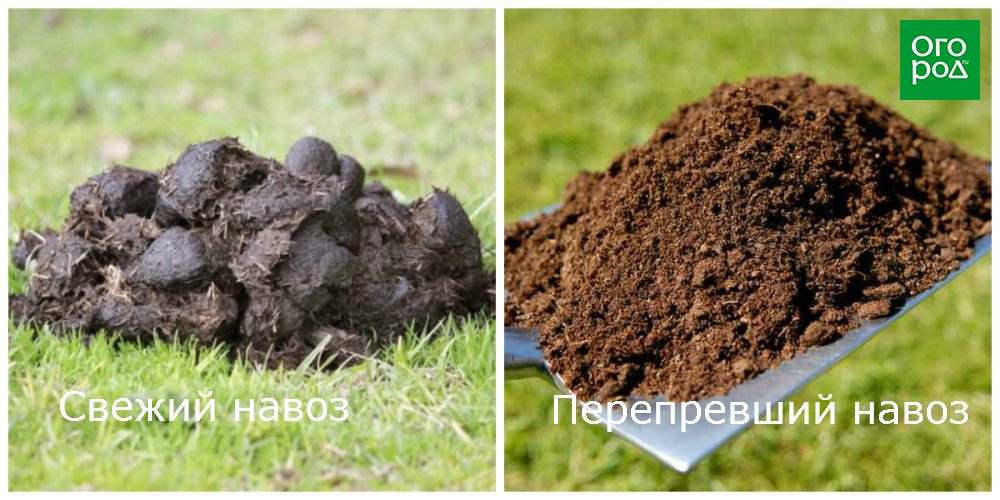
Humus is produced by the complete decomposition of manure, peat, straw, sawdust and grass. Outwardly, it looks like a homogeneous, loose mass of dark color with an earthy structure. Why exactly this " dry manure"Do summer residents appreciate so much?
- Humus is a versatile and "soft" type of fertilizer. It can be applied to any crop - trees and shrubs, vegetables, herbs and flowers. All nutrients are collected in the substrate and, in addition to the traditional ones (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium), manganese, zinc, copper and sulfur also accumulate there, without which no summer cottage culture can develop.
- Rotted manure improves the structure of any soil. Most often it is used as a soil mixture in a greenhouse or greenhouse, as well as as a nutrient substrate for seedlings.
- When planting and replanting seedlings of fruit trees and berry bushes humus is added to the planting pits.
- Humus is the most popular and efficient view fertilizers, which are applied during autumn and spring digging. 2-3 kg of this fertilizer are applied to 1 square meter of the garden. And since humus is considered more "long-lasting" than fresh manure, it needs to be applied much less frequently.



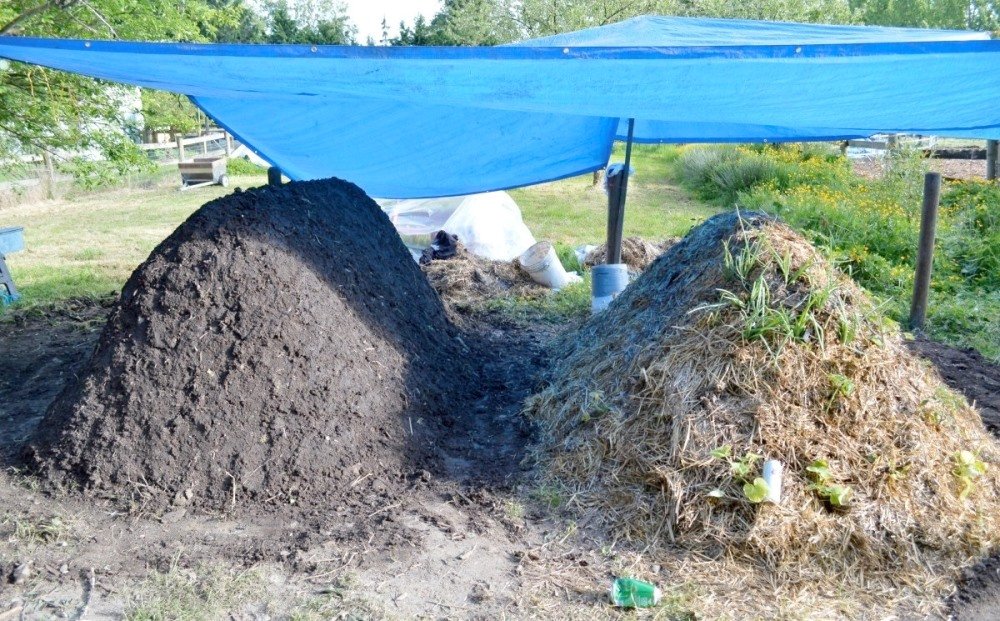
How to properly store manure
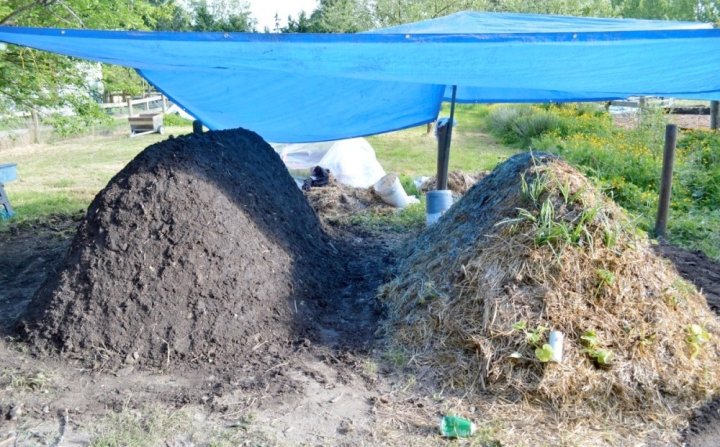
It is not always possible to use all the manure at once or get it quickly. Many summer residents do not have time to use manure during the season and therefore leave it for storage. But, unfortunately, they do it wrong. For example, small piles are simply left outdoors. But in this case, the nitrogen is washed out by the rain, and the heap itself erodes. But there is at least three ways to store manure.
- Hot (loose) Krantz storage method- with this method, loose and unripe manure is placed in insulated piles up to 3 m wide and up to 1 m high and left in this form for several days. When the manure is compacted, the next layer is laid on top. In cold weather, manure is covered with plywood or straw to avoid heat loss. After 3-4 months, a pile of manure with a height of 3 m turns into a neat and odorless humus.
- Hot-pressed method... The manure is laid in layers of 80-100 cm, sequentially compacting each layer and maintaining the temperature in the stack at 55-60 ° C. The total number of layers should be about three to four, and the height of the pressed material should exceed 2 m.
- Cold method... When using this method, the moistened manure is daily densely stacked in piles at least 5 m wide and up to 2 m high. In no case should it dry out, since then, instead of bacteria, fungi that absorb nitrogen develop.



Now you know everything about manure, you know how to choose the type that is most suitable for different purposes, properly breed and apply it, as well as lay it for storage. Despite the fact that the use of manure is considered the most "ancient" way to feed plants, a better and more natural fertilizer has not yet been invented.
It seems that in the wild, no one digs the soil on a schedule, does not add manure to the soil and mineral fertilizers... However, trees and grasses delight with vigorous growth, abundant flowering and generous gifts of fruit. For millions of years, nature has been able to create a very harmonious, self-regulating system in which everyone clearly knows their place and tasks. And only a reasonable person, who imagines himself the master of the world, destroys harmony, creating a bunch of problems for himself and nature. So now he has to, drenching in sweat, fertilize the depleted soil with manure.
Why does the soil need manure and other organic fertilizers
Our country is amazing. With its vast expanses and the presence of fertile land for mere mortals at all times, if land plots were allocated, then they were always problematic soils, in which a lot of work had to be invested in order to get a decent harvest.To improve the structure of clay or sandy soil, on which little grows, a person is forced to add manure or other organic fertilizers to them. Fertilizers loosen the clay soil, and glue the sandy soil together.
Microscopic fungi and bacteria in humus decompose organic matter into chemical elements available for assimilation by plants.
Even in soils with good structure, organic fertilizers improve gas exchange, create an optimal ratio between air, water and solid particles contained in the soil. The soil becomes loose and does not form a waterproof crust after rain or irrigation.
The effect of organic matter on a plant
In order for a plant to develop, it, like a person, needs micro- and macroelements. But in sandy soil, these elements have nothing to catch on, and they are washed out by streams of water, leaving the plant no chance to feed. The introduction of organic matter into such soils leads to the adhesion of soil particles, on which the chemicals necessary for nutrition are retained.For the normal development of plants on sandy soils, mineral fertilizing is also required. But with frequent mineral dressings in the soil solution, the concentration of salts increases, suppressing the activity of microorganisms, for which we introduced manure. This leads to a cessation of plant growth or the death of their root system. Therefore, it is necessary to very accurately calculate the concentration of mineral dressings and combine them with irrigation.
When and how to apply organic fertilizers
Fresh manure is applied to the soil in the fall. It should not be embedded very deeply into the soil, since at depth its decomposition will be very slow due to the weak development of soil bacteria there. A depth of 10-12 centimeters is enough.Humus and semi-rotten manure can be applied in the spring. Unlike fresh manure, they are scattered over the soil surface, and not buried deep.
Similarly, peat is scattered over the soil surface, followed by loosening of its upper layer. Vegetable plants successfully and quickly create an extensive root system in such a layer, which helps them grow more actively.
Organic fertilizers applied to the soil once every 2-3 years.
What vegetables are manure under
Manure introduced in the fall will help grow vegetables such as: cucumbers, lettuce, cabbage, rutabagas, leaf celery.Fresh manure is contraindicated for the following vegetables: carrots, beets, turnips, radishes, onions, tomatoes, beans, peas, radishes, horseradish. For them, plots where manure was applied a year earlier are more favorable.
Manure and weeds
It would seem that they fertilized the soil with manure and are waiting good harvest... But it was not there. Intrusive weeds grow in the garden bed, giving no respite to the gardener and taking away precious food from the plants. Only tore out some, and new ones are already appearing. Where does this invasion come from?And the manure introduced is to blame, which was not properly prepared in advance. The fact is that not all plant seeds are digested by the digestive system of cows and again enter the soil along with manure. And the grass bedding for cows, as it wears out, is also sent to the manure along with the seeds.
So that instead of an assistant, the manure does not turn into a disaster, you have to wait until it is overwhelmed, and the seeds preserved in it will lose their germination. As for the compost, it must be constantly loosened while the accumulation process is in progress. In addition, in order to deprive the seeds of the ability to germinate in the garden, you need to cover the compost with black film, tar paper, sheets of iron, roofing material, in general, with what is available on your farm. Then the seeds will germinate in the compost, but under cover they will quickly die.
Humus belongs to the class of organic fertilizers, and is an earthy loose substance. In other words, these are substrates at the last stage of reheating, during which the loss of the initial mass occurs up to 75%. It does not smell of rot and ammonia, therefore it is widely used by many gardeners and gardeners.
The basis of humus is manure, leaves, plant stems and much more.
1 Humus, its beneficial properties and value
The answer to the question of what is humus has already been received. Let's move on to examining its qualities. The organic component is rich in nutrients that any plant needs for healthy growth and development, improved yield and fertility, has the ability to absorb and retain moisture for a long time.
It ennobles the land, improves the soil composition, feeding the sandy soil, and "fluffing up" heavy clay soil. Makes it airy and loose. It is worth noting that black soil is the richest soil in humus.
The overripe form of manure is universal in application: composition for mulching, soil base for diving seedlings, for seed sowing. It is a valuable nutrient suitable for all crops. It is obtained by long-term decomposition of components of animal and plant origin. Therefore, in ecological farming there is the concept of leaf humus. This fertilizer includes every vital mineral element: nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus and others. It allows you to replace the introduction of agrochemicals.
The uniqueness of such organics lies in the fact that humus is added without fear of harm to the root of the plant. Pork, cow or horse manure is taken as a basis. Leaf humus is prepared from grass, leaves, tree bark. The latter, by the way, can be introduced into the soil in unlimited quantities.
The best effect is achieved when using rotted manure material as mulch. The soil is given a favorable environment for the settlement of earthworms, the beneficial bacteria that have arisen contribute to the effective work of the roots. The temperature changes smoothly, which allows the thermophilic flora to acclimate. This substrate is necessary for the cultivation of cucumbers, eggplants and other pumpkin seeds; hibiscus, begonia, pelargonium.
1.1 Organic fertilizer from leaf humus, manufacturing methods
Leaf humus replenishes and balances the water regime of soils, effectively acidifies acidophiles, saves human resources while helping plants survive drought in the summer.
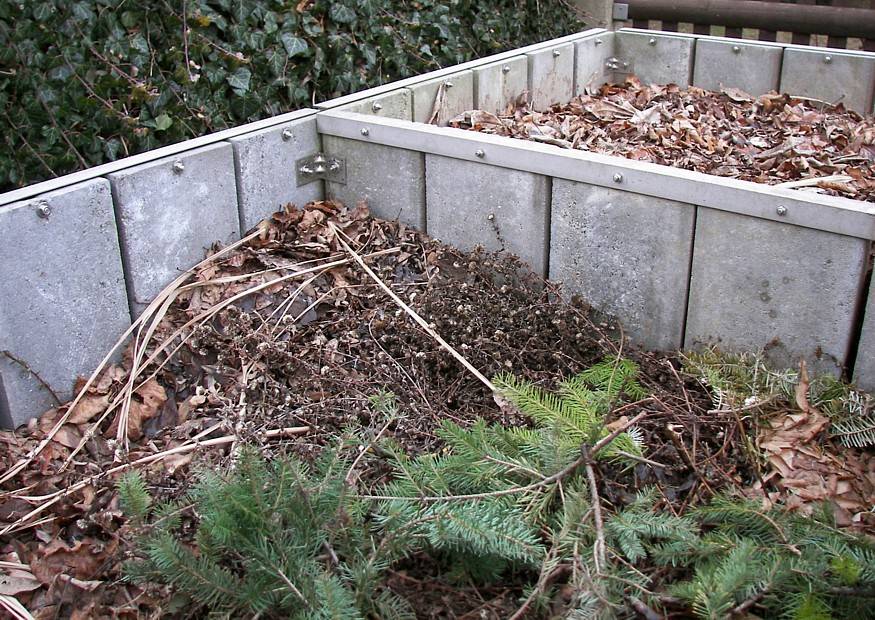

Leaf humus is often added to garden compost. Mineralizing bacteria and other microorganism helpers choose it as an excellent habitat. It is formed at home in the fall from fallen leaves, in summer and spring from weeds pulled out. It is better to make leafy humus in advance. To do this, the collected foliage is moistened, tightly laid and tamped. Where to store the leaves is up to you. It can be plastic bags, a plastic box, you can save in bags specially purchased in garden stores.
If you decide to store foliage in your own burlap, you should make several holes in it for oxygen circulation, do not tie a knot, twist it arbitrarily. The decomposition time depends on the tree species. Leaves of oak, birch, mountain ash, hazel, maple, hawthorn, hornbeam are enough for a year. Coniferous briquettes decompose within 2-3 years. The main feature in the production of humus from leaves is their constant wet content. To speed up the preparation process, it is recommended to add small pieces of green grass to the bag.
At the end of the laying of the external organs of plants, they need to be given time to rot. If the leaves are laid correctly, the product can be used in 1-2 years. Substrate made - good material for growing plants in residential premises. To indoor flower feed with the resulting mass, pre-mix leaf humus with sand or loam in a 1: 1 ratio.
1.2 Cooking leaf humus (video)
1.3 The role of microorganisms in the decomposition of humus and fertilization of the soil
Earlier in the article, it was said that bacteria and other representatives of microbiology choose plant and animal remains as their favorite habitats. Any microorganism is actively involved in the release of nutrients from humus. Nitrogen-fixing microbes and bacteria form food available to plants. As a result of their vital activity, the mineralization of soil organic matter is carried out.
The richer the decomposition product of animal or vegetable components by small living organisms, the more energetic their effect on overheating. Bacteria are able not only to mineralize the organic components necessary for the earth, they contribute to the proper growth of flora, perform a soil-forming and sanitary role.

The soil and fertilizing value of saprotrophic microorganisms of fermentation and decay is undeniable. It is thanks to them that humus or humus of the soil is created. By forming mineral salts, necessary for plants, they generate nodules on young roots.
2 Garden compost: composting materials
Gardening beginners confuse garden compost with humus, having no idea how to make it. Compost is a mixture of decomposed organic waste used to improve the structure of the soil. Some people think composting is a simple matter: put tree branches, leaves in a box, cover and wait for ripening. Others purchase concentrated EM preparations. But there is the possibility of cooking it at home. The more varied the content of the compost heap, the better the finished product will be.
Suitable materials for composting:
- cut grass;
- kitchen leftovers, tea residues;
- peat;
- animal feces;
- hemp and flax campfire;
- sunflower stalks, corn stalks;
- garden weeds, tops;
- eggshell;
- sewage sludge;
- unsuitable feed;
- straw, seed husks, sawdust, etc.
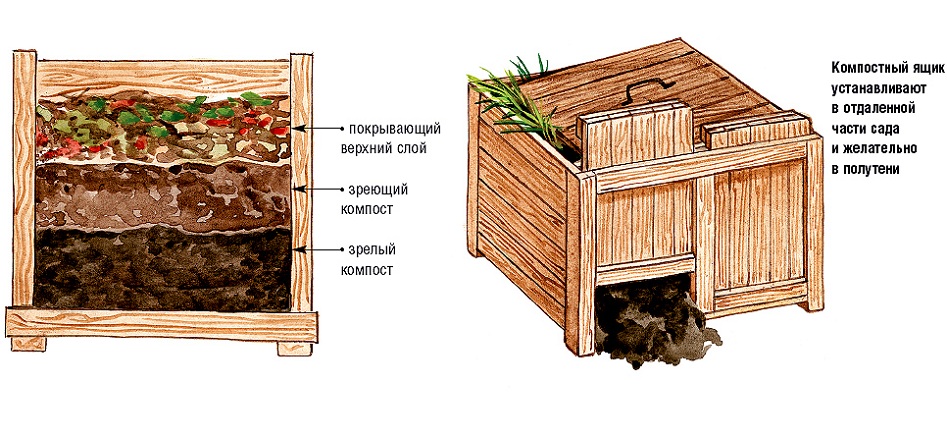
The question of where to produce fertilizer is not fundamental. A compost bin, any container, will do. Chips and branches are placed in it, protruding as drainage, then waste is laid in layers. Each layer should have a thickness of up to 50 cm, and an earth layer of up to 10 cm. An experienced agronomist allows the mixture to brew for several weeks in the open air, after which he periodically agitates. After a couple of years, when the product received dark color, wet but crumbly structure, we can talk about its readiness.
Suitable for all crops. The dosage is the same as for manure, about 20-40 t / ha. The resulting mass is scattered over a freshly plowed garden, used in the process of autumn plowing for spring crops, added to the holes when planting seedlings.
A sufficient proportion of compost is achieved through the formation of a compost heap, the area of which is equal to 1/10 of the size of the beds. If there is a lot of wood shavings in the mixture, additional sawdust must be added:
- ammonium sulfate or ammonium nitrate (300 g per 10 kg of compostable mass);
- 20-30 kg of superphosphate or phosphoric flour. Phosphate fertilization will improve the quality of the compost.
2.1 Technology of preparation and storage rules for perennial fertilizers
At home, the production of humus fertilizer depends on the material you choose. If we are talking about rotted manure, then the substrates of animals are placed in a box or bag, and a compost pit is often dug. Each layer is overlaid with peat or straw in order to preserve the maximum amount of nitrogen and other minerals. In winter, a pile of manure is covered with soil, under which the process of overheating takes place until the spring period.
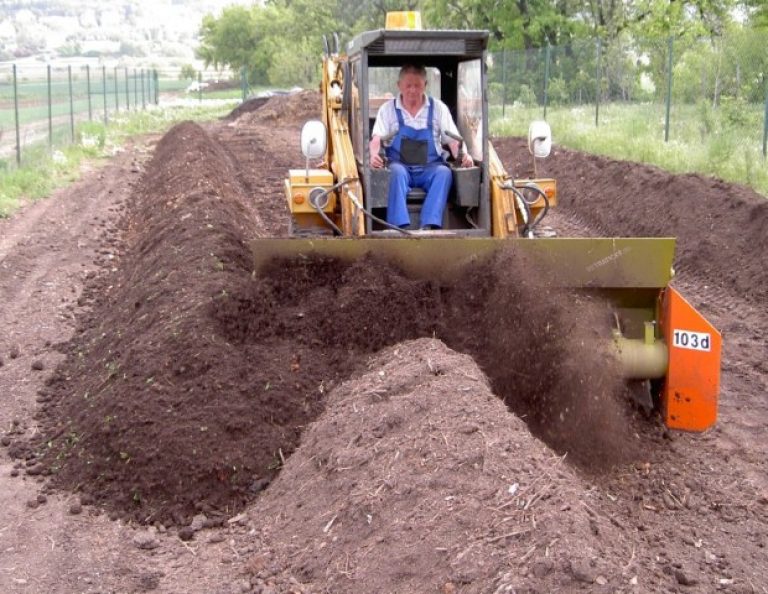

The combined cooking method is the most optimal. "Svezhak" is laid out in a box or other container in layers, at first it was loose. Within 5 days, the temperature in the stacks will rise to 60 degrees. Only after that do the layers begin to be compacted. This is how they do it with each new portion of animal excrement. The layer is brought up to 1.5 m, covered with peat (layer - 30 cm), mown grass. It is recommended to let the mass brew and brew for 5-6 months.
The storage of humus is carried out in two ways: cold and hot. Hot provides for a loose content of humus heap. In this case, the decomposition of manure is faster and more vigorous, but a lot of nitrogen is volatilized. For a cold one, a site of compacted soil is needed. Animal excrement is placed on it, covered with earth and dry leaves (30 cm) Covered will prevent the risk of freezing and getting wet from the rain. As with compost, it is stacked and replaced with low-lying peat, the layers of which are equal to the layers of manure.
The resulting mass is brought under the trees mainly in the autumn. A two-year-old seedling requires 15 kg of fertilizer. Top dressing is repeated after 2-3 years. Vegetable crops needs 5-8 kg. Dates of fattening - spring-autumn. Those who are interested in whether it is possible to add a decomposition product under the currants, a positive answer awaits. Gooseberries, currants and raspberries should be mulched in the autumn, moreover, annually.
The answer to the question of what compost is for regularly worries many farmers. It is impossible to say unequivocally what the composting of the earth affects, since it is a multifaceted biochemical and physical process that improves the overall structure of the fertile layer and enriches it with nutrients. In order to understand this issue thoroughly, we recommend that you read this material.
It is very favorable for seedlings when planting to add life-giving humus (dung or vegetable) to the holes - this is both a guarantee of better survival, and a supply of food for the first time for good growth.
Compost composition
Humus, obtained from plant debris from the decomposition of compost or just a heap of grass or leaves, has very beneficial properties for plants. The compost contains many different enzymes, vitamins, stimulating organic substances. Better this "food" for the roots does not exist, it is like green parsley for us or other living vitamins - nowhere without them. Humus literally empowers plants, heals them, stimulates them, nourishes them. Therefore, it is very pleasant to deal with him when working with plants, they are made noticeably "more obedient" and more durable. Humus is a welcome addition to any soil.
With the help of humus, you will be able to revive a "dohlik" bought or sent by mail - a seedling, a tuber, a bulb overdried on the road: plant it immediately in moist clean humus. All serious growers, as a rule, become permanent procurers of herbal or leaf humus, include it in the composition of soil mixtures.
Seeds not sprouting? Sow them in humid humus at a shallow depth and cover with glass - let them lie “stimulated” (humus substances pass through the seed coat), if they begin to sprout, this is normal.
Organic fertilization
The introduction of organic fertilizers will be needed for landing pit when planting fruit and decorative crops: they will take root better in the presence of humus in the hole. If a heated greenhouse, greenhouse, winter garden - compost is definitely needed for potted plants. Small volumes of soil are particularly demanding! A soil mixture based on clay with crumbly herbaceous humus is more nutritious and "long-lasting" than ordinary soil.
Any soil is made into soil by decomposed organic matter. Before it is shredded rock... It follows from this that with the help of humus, anyone can. Even if it is pure clay, or sand, or a mixture of them with vermiculite, perlite - with humus it immediately turns into fertile soil. It is advisable to let this mixture stand a little in a wet state for a couple of weeks, so that a chemical interaction occurs (creation of organomineral colloidal compounds, etc.), or you can immediately plant plants.
Composting technology
Composting technology provides that the final amount of the resulting humus will always be approximately two to three times less than the piled organic matter. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate the final volume, making an amendment not only for "shrinkage and shaking", but also for "burnout".
Use of organic fertilizers
It is known that with long aging, organic matter gradually decreases in volume by several times. This happens due to the release of carbon dioxide - CO2: here it is - C - "coal", carbon that imperceptibly leaks into the air! The bacteria "eat" the compost, while breathing - and carbon dioxide makes its way up through the thickness of organic matter. Like compost smolders invisibly and sags.
It is this notorious decrease in volume that haunts plant breeders, for whom the use of organic fertilizers plays a decisive role. Therefore, many are supporters of "fermentation", that they cannot accept losses, as they believe, and without that "rare". Volume is a secondary matter, and in the first place is the concentration of nutrients. Add nitrogen fertilizer to the compost - a couple of tablespoons of the same carbamide or half a bottle of humates - and the volume loss will cease to matter. Feel sorry for carbon? Add fire coal. But the technology will be simplified: you must admit that in everyday life the simplest and fastest is composting by the method of layering organic matter in a compost heap, without any fermentation.
There is no need to confuse farming for profit and summer cottage gardening for pleasure. For the farmer, everything rests on calculations and gaining "grains" for each operation. In the family garden, everything is freer, here no one bothers with weighing, here neither the total harvest nor the yield from each is counted. square meter, here no one will consider the profitability of flower beds and measure the volume of compost.
Pleasure reigns here. When applying fertilizers, we are limited only by safety reasons, so as not to introduce excess substances. Monitor the amount of fertilizer so that you do not exceed reasonable established rates, but not at all in order to consider profitability.
The lost volume, as already mentioned, is taken up with filler: turf, ordinary earth. This litter absorbs during composting nutrients and is loosened by earthworms. Then we mix everything thoroughly - and we get enough fertilizer.
Compost will increase the yield
Another garden axiom: compost is the center of attraction for all living creatures. Even dogs poke their noses in here, attracted by the delicious smell of freshly discarded food leftovers. Therefore, you can even be sure that compost will increase the yield on your summer cottage several times.
Compost is life itself! This is pure food. And one thing pulls the other: food chains arise. The activity of living organisms of all levels rages in the compost, starting with microbes: worms, snails, insects, toads, moles, mice. Everyone strives here because of the abundance of food. Moles sometimes tear up the compost pile up and down, looking for larvae and earthworms in it, but they will not overfill everyone even close, the worms, although they know about the proximity of the mole, still never leave the pile due to the abundance of food.
The compost will always be full of different animals - this is the law of nature. There are countless larvae here, here you can find all the soil fauna: centipedes, tardigrades, woodlice. By the way, I assure you, they are all harmless to plants, since they are all saprophytes, that is, they feed on already dead organic matter. Unreasonable fears of gardeners to bring any pests with compost into pots or beds. In these food chains, there is no link of a living plant, here no one encroaches on roots or seedlings, so everything actively sprouts on heaps of organic matter: seeds of tomatoes and melons, peeling potatoes. Here, no one touches them, everyone is busy actively eating organic matter and each other: all together turn into humus, as a result, a homogeneous crumbly mass will turn out. Here, even a pathogenic infection gradually fades away and disappears, mushrooms "eat" it: add the affected by late blight, scab or powdery mildew tops - and in a year it will become harmless. Self-purification mechanisms are too strong: there is a predator for each species, the life of microorganisms boils here - and these are their enzymes entering the environment in huge quantities (enzymes are catalytic substances that accelerate the rate of chemical reactions, the presence of enzymes leads to the decomposition of complex organic compounds, enzymes destroy the "hard" substances of peat and insect shells (lignin, chitin), pectin substances, etc.).
A big mistake a gardener makes is to disinfect the compost before using it. Instead of living earth, you get a sterile substrate, which you will surely get covered with mold.
You can solve this problem if you periodically apply fertilizers. Mineral complexes, undoubtedly, are quickly absorbed by plants, have an excellent effect on their growth and fruiting, but such fruits, along with vitamins, contain a large amount of nitrates, pesticides and other compounds harmful to health.
Unlike mineral fertilizers, organic fertilizers are quite harmless. They belong to long-term fertilizers, they need to be applied twice a year. All nutrients that make up this top dressing are contained in the most acceptable proportions required by the plants. However, they must be entered correctly, otherwise the effect will be the opposite. Almost all organic fertilizers can be combined with one term - humus. Humus is manure, grass, or bird droppings and other organic waste. It is also called compost, and some rules must be followed when applying it.
Types of humus
The most popular among gardeners is manure humus. Introduced in the fall, manure is better decomposed into trace elements, therefore, plants planted in spring will receive all the substances necessary for growth and development. It is strictly forbidden to apply fresh manure under most crops, because root system plants will simply burn out.
Bird humus is very strong. It must be introduced in a diluted state, at the rate of 100 g of dry chicken manure per bucket of water. In the same way as manure, poultry droppings must be composted, this will destroy all the eggs of flies and worms in it. This compost is rich in manganese, iron, zinc and cobalt. A significant disadvantage of this fertilizer is an unpleasant, pungent odor.