Separations. Voted shoots: rhizome, tuber, bulb, their structure, biological and economic importance
Instruction
The stem creates a frame frame, makes leaves to light and conducts water, mineral and organic matter. In it can be laid in stocks of nutrients. On the stem, not only leaves, but also flowers, as well as fruits with seeds are developing. The main functions of the leaves are photosynthesis, water evaporation and gas exchange with the environment.
Valid shoots Additional functions are performed in the life of the plant. A number of perennials herbatous plants Have peculiar storehouses underground. They are modified underground shoots - rhizomes, bulbs, tubers. The above-mentioned parts are dying annually by autumn.
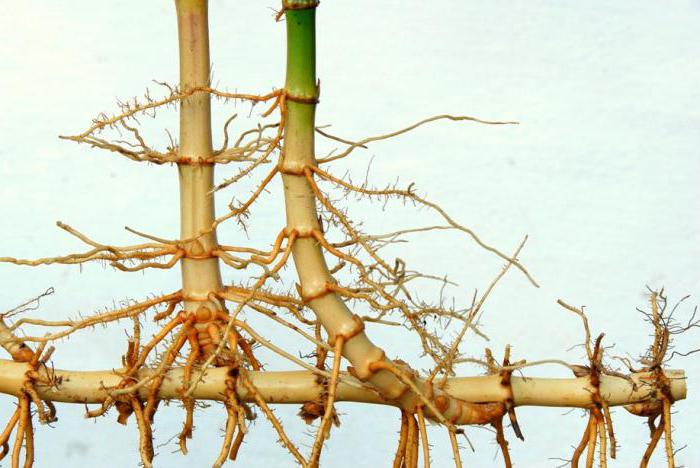
In rhizomes, bulbs and tubers are postponed for winter spare nutrients. Rhizome is present at nettle, valley, iris, dusty, aspidistra. Outwardly, it looks like a root, but he has the top and stubborn kidneys, and the role of modified leaves is played by film scales. The peel roots are growing from the rhizomes, and the top and stuffed kidneys give rise to young above-ground shoots. At the same time, the plant uses substances stored in the fall.
With the help of rhizomes, as well as other modified shoots, vegetative reproduction of plants can be carried out. Soldering part of the rhizomes with the kidney and roots into the soil, you can get a new, independent plant organism. Some decorative plants Protect fragmentation of rhizomes.
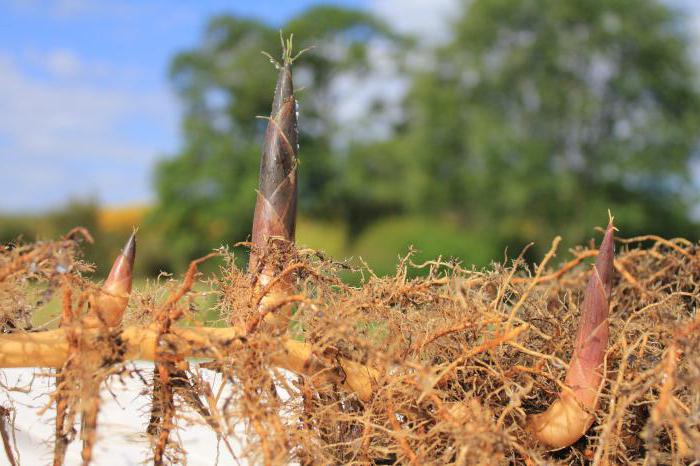
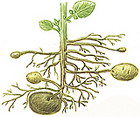
Tubers can be observed in potatoes, Topinambur (earthlings), haggard. From the bases of the above-ground stems, underground shoots are brought, called columns. The top thickening of the latter and are tubers.
On the upper surface of the tuber you can see the eyes - these are modified kidneys. The bottom side of the tuber is connected to underground escape. As with the stem, the tuber on the cross section can be distinguished by several characteristic layers: a plug, lob, wood and core. All these signs prove that the tuber is a modified escape.
Nutrients from leaves continuously leak to tubers through stems and collines. Thus, these tops of underground shoots are saturated with starch and increase in size.
The bulbs are characteristic of tulips, lilies, on Luka, wild goose bow, daffodils. The lower part of them is represented by a flattened modified stem - the Donets on which scales grow ( modified leaves). Outside, scales are usually leathery and dry, and inside meat and juicy. Water, sugar and other valuables are inhibited in them. In the sinuses, scales on the bottom are kidneys. When planting to the ground from the bulbs, the urine is growing root system, and kidneys develop children - young bulbs.
"Biology. Bacteria, mushrooms, plants. Grade 6." V.V. Beekeeper
Overhead I. underground modifications Escapes
Question 1. What kind of modified underground shoots do you know? Name plants having rhizome, tuber, bulb.
Tubers are formed as terminal thickening of underground shoots - collines. Strokes are growing from the base of the aboveground stems. Tubers develop as a result of thickening of the top kidney kidney (potatoes, hooker, earthwood pear). They are located kidney groups that are called eyes. Tubers serve for vegetative reproduction.
The bulb is an underground shortened modified escape. The bulb stem forms a don. Leaves, or scales are attached to the Don. Exterior scales are usually dry, they perform a protective function. They cover the compound scales, in which nutrients and water are laid. At the bottom there is a top kidney, which develops overhead leaves and a color-based arrow. At the bottom of the Donets develop additive roots. The bulbs are characteristic of perennial plants (lilies, tulips, bows, garlic, daffodil, wild onions, etc.). With the help of bulbs, plants can grow vegetatively.
Rhizome is also underground escape, outwardly similar to the root. Rhizome carries the scratched leaves, in the sinuses of which are stubborn kidneys. Pressure roots are formed on the rhizer, and side buses of rhizomes and above-ground shoots are developing from the sinus kidneys. Rhizomes are found in perennial herbaceous plants (horsetails, ferns, nettle, valley, cereals, etc.). Rhizome is the organ of vegetative reproduction.
Question 2. How to distinguish rhizome from the root?
By appearance Rhizome is reminiscent of the root, but differs from it the presence of crystal leaves, leaf traces (scars from fallen leaves), kidneys, as well as the lack of root case.
Question 3. How does the potato tuber develop?
From the leaf of potatoes through the stalks to underground shoots (collisions), organic substances constantly express and are deposited in the form of starch. The tops of the columns grow, thicken and turn into large tubers by autumn.
Question 4. Why does the potato tube should be considered escape?
The potato tuber should be considered escape because it, like the escape, is formed by a stem that performs a sparkling function, has a kidney (eyes) and scratched leaves.
Question 5. What building has a bulb?
In the lower part of the bulbs, such as the onions, there is almost a flat stem-dona. Applying roots and modified leaves (scales) are departed from the Donets. External leaves - scales - dry and leathery, they perform a protective function; Internal - fleshy and juicy, nutrients are laid in them. In the sinuses of scales there are stubborn kidneys.
Question 6. How to prove that rhizome and bulb are modified shoots?
Externally, rhizome is reminiscent of the root, but he, like ground escape, there are uphety and stubborn kidneys, as well as film scales - modified leaves. Thus, the rhizoma has a stem (axial part of the rhizomes, kidneys and leaves (film scales), i.e., what is characteristic of escape. At the bulb we can also see all parts of the escape: Stem (Lukovitsy Donets), leaves (dry and juicy scales) and kidneys (between scales). This confirms that rhizome and bulb are modified shoots.
The modifications are associated with the performance of singular functions (these are sharp, hereditary changes). The most common modifiable shoots are rhizome, tubers, bulbs growing in the ground. Spare nutrients needed to transfer adverse conditions and serving for natural vegetative reproduction to be transferred to the transfer of adverse conditions.
Rhizome
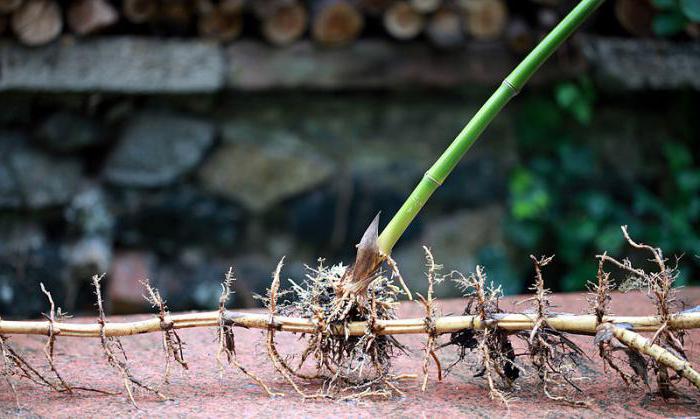
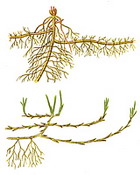
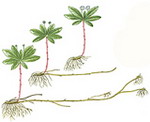
In the soil occupy a horizontal position. It is usually scratched leaves and kidneys. Candar roots depart from him. Spare nutrients are deposited in the stem part of the root. It looks like a root, but differs from it underdeveloped leaves and the lack of root cavity. It contains reduced leaves in the form of brown or colorless scales, and the kidneys are located in their sinuses, of which overhead shoots grow. They have nodes and interstices, prescript roots are formed from the nodes. At the top there is a top kidney, at the expense of which rhizome grows in length. Plants with branching rhizomes quickly grow (drinking creeping, valley, iris, bitch, etc.). The duration of the life of rhizomes ranges from 2-3 to several decades. Thin, elongated underground shoots carrying on the top of the tuber or bulb, called columns.Tuber
- This is an escape with a strong thickened stem, in which spare nutrients are laid. Tubers can be underground and overhead: underground - develop on the columns (potatoes, earthwood pear). Overhead - developing Kohlrabi cabbage, some orchids. On the club there are eyes - the deepening, in which the kidneys are located. They are located on the club on the spiral (like leaves on the stem) and give rise to aboveground shoots. Outside, the tuber is covered with epidermum, which is subsequently replaced by a plug. The potato cells of the pulp of the tuber are filled with starch, and earthwood pear - inulin (complex carbohydrate). Tubers develop from the top agony kidney.Bulb
- Underground Escape with a shortened stem. Applying roots are depressed from the bottom down, and up - closely pinned juicy leaves (bulbic scales), in which spare nutrients are deposited. In the sinuses of the bulbous scales are kidneys, of which the above-ground shoots and new bulbs are formed. The outer dry scales protect the internal fleshy from drying and dropping. The bulbs are formed at Luka, garlic, lilies, etc. At the top of the Donets there is a top kidney, which gives rise to the above-ground run - a colorless "arrow" and leaves. Bulbs help the plant survive in adverse conditions And are the organ of vegetative reproduction.Output:
1. Tuber, bulb, rhizome is a modified shoots, because They have kidneys, shortened interstices, big reserve organic substances, no chlorophyll, i.e. With its structure, they repeat the structure of overhead shoots.The modified shoots are a kind of storeroom, where nutrients containing starch, sugar, mineral substances, phytoncides (substances that kill microbes) are accumulated. They are widely used in food by man and are used on animal feed. In addition, they have and large biological significance - all are organs of natural vegetative reproduction, which is occurring in nature without human intervention.
How to distinguish rhizome from the root? We are confident if you ask such a question, very many will be surprised, because they believe that this is the same. But root and rhizome - absolutely different concepts. Why? Let's figure it out together.
Weight modifications
The above-ground part of the plant is called escape. It consists of two parts: stem and leaves. These plants serve for air power, gas exchange and vegetative reproduction. But under certain conditions this is not enough. Therefore, the modifications of various organs of plants, including escapes, arise. Rhizomes are one of them. To the modifications of the above-ground part of the plant also belong to the Topinambur, the bulbs of the tulip and garlic, the mustache strawberries and vintage mustache. All of them perform additional features. For example, with the help of the grapes, the grapes are attached to the support, which allows it to take the most favorable location for the implementation of the photosynthesis process. But in the bulb and underground, water is preserved with nutrients, which allows the plant without difficulty to experience an unfavorable period. With the help of the mustache, strawberries breedingly multiplies, as well as potatoes with its underground modifies - tubers.
The structure of root
Rhizome, being an underground modification of escape, has all the features of its structure. But they are somewhat modified. Rhizomes are a fluttering stem with elongated interstices, in which all the substance necessary for the plant are reserved. The beams of the apparent roots depart from it. And on the surface of the Earth are visible leaves that grow from the nodes of the elongated escape. They are simple. Their sheet plates are narrow, as a rule, with

How to distinguish rhizome from the root

What plants have rhizomes
Rhizomes are modifications characteristic of many plants. Most of them are a representative of one-bedroom class. Surely, many gardeners tried to get rid of malicious weed, which is called drinking. It is not easy to do this due to the presence of rhizomes in this plant. Tearing the leaves and part of the underground escape, a person does not recognize that his big part remains underground. From the kidneys of the preserved part of the escape, new leaves grow again. As a result, the weed grows again. Rhizome have a valley, mint, asparagus, peonies, irises, phloxes, gravity, blueberries. What advantages have plants that have modified data?

Functions root
First of all, the rhizomes ensure that making it more efficient. For example, to send irises, it is not necessary to take their large part of escape with leaves and flowers. It is enough to use a small element of rhizomes with kidneys and apparent roots. Since this selection of escape is located underground, it has a reliable shelter from all unfavorable conditions. ambient. He is not terrible drought. In conditions of severe heat, only leaves will die. But the underground part, which is directly by the escape of the plant, will remain viable. At the occurrence of well-war conditions from the kidneys, green leaves will again grow. Rhizomes is a valuable underground supply of water, mineral and organic substances, which plants formed during the presence of a sufficient amount of moisture and the implementation of photosynthesis. Thanks to this important feature, all plants with these modifications are perennial. Their underground part remains viable since the beginning of autumn until spring precisely due to the stock of all necessary substances that are in this modification.
So, rhizome is an underground modified vigorous shoot. Its main parts are elongated interstices, kidneys, simple leaves and apparent roots. Rhizome performs important functions, thanks to which a plant can easily tolerate any adverse periods and quickly spreads. This is the supply of water with nutrients and the implementation of vegetative reproduction.
Victims of escapes
Surprisingly how many shoots. Sometimes this body is even impossible to know. It's hard to see the escape in the bar hawthorn or mustache grapes. Why do such "transformations" happen to him?
Removing overhead shoots. We are called such shoots that perform some additional features: protection, climbing, supply of nutrients, etc. To the modified shoots belongspines, mustaches, tubers, juicy shoots, collishes, feces of insectivorous plants .
Spinys - Sewaged formations that protect the plant from eating animals. Spines can be formed from a sheet ( barberry ), Highlights ( yellow Acacia), escapes (sea buckthorn, hawthorn ).
Mustache
- Fit-shaped stuffing shoots (grapes, cucumber
) that perform a reference function. The pea in the mustache turns the part of the sheet.
Tuber - thickened escape that performs the function of the supply of nutrients (cabbage Kohlrabi. ).
Counters (Household name - "mustache") - horizontal creeping shoots that promote the reproduction of the plant. Each pole is located with apparent roots. After rooting the outlet, the horizontal escape is devoted (strawberry, lounge creeping ).
Juicy shoots - Plant adaptation to a hot and dry climate. Their function is to store moisture. Water can accumulate in the leaves (coid, Moldo, Aloe ) or in the stem ( mokha, cactus ).
Mexican cacti have fleshy stems of the most diverse shape: ribbed balls, columns, cylinders, even candelabra and cylinder. Cacti does not have green leaves: they turned into barbants. The photosynthesis function is performed by stalks.
Underground modified shoots. Stalls and tubers can be both overhead and underground. In addition to them, the underground shoots include rhizome and bulbs.
Underground collines
Perform the same functions as overhead - resettlement and reproduction of the plant. This explains the similarity in their structure.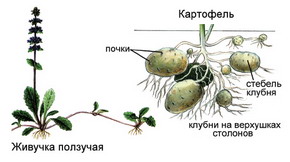
Tuber. This escape stem is short and thick. The leaf-scales quickly die and scars remain in their place (the potatoes in the people they call them "brovings"). In their sinuses are the kidney "eyes". The tuber performs the function of the supply of nutrients (for example, starch), the experiences of the unfavorable time of the year and reproduction. Tubers are not only potatoes but and also topinambura, Hochlaktka . They appear on underground columns.
Rhizome Externally, it often looks like a root, but the rhizomes have and scaly leaves, and in their sinuses - side kidneys, on the top - the top kidneys. Pressure roots are formed on the rhizer. Unlike alarm, rhizome - a long-term escape that allows the plant to survive unfavorable conditions. This underground escape is peculiar to many plants and can perform a variety of functions. In thick short rhizomes iris, Pouches Nutrients are soaked. W.sloppy, Mouse Peas, Lily of May Rhizomes are long and thin. They are capable not only to store nutrients, but also to capture new territories.
Rhizome not only increases rapidly (y white blond For suitable 1.5 meters, metcher - per meter), but also branches. As a result, the parent plant can be filled with several subsidiaries. Rural residents are known how difficult it is to fight with long-hall weeds: dressing, sick, mother-and-stepmother
. Quickly grow up
Make signatures to the drawing "The structure of the valve of the valley. (Interactive task)
Bulb
- Strongly shortened modified escape with a flat stem - "Donets", with leaves in the form of scales. Czechs can be juicy (in stockboring) or dry lining), can be narrow and only slightly cover each other ( lily) or grab each other almost completely (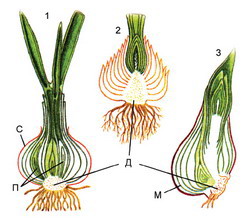
When we are talking about adverse conditions, it does not mean that it is necessary to go about winter. Many wild bulbous plants (ryabik, onions, tulip ) Grow in steppes, semi-deserts, mountains. Others -prolessa, goose bow, as well as tube (cyclamen) - in large forests. As a rule, these plants bloom in spring. Then, after the beginning of the roast summer, the entire above-ground part of the plant is devouted, the juicy scales of the bulbs retain moisture and in the arid period, which makes it possible to resume growth in the next season.
| Modifying underground escapes
|
|||
| Rhizome - the long-term underground escape, has scaly leaves and grows horizontally under the ground, forms apparent roots and kidneys ( lily of the Lily, Mint, Dress, Iris, Cuff ). | Stone - the stem that grows horizontally at the base of some plants is short-lived. The column forms the apparent roots in the nodes and new plants grow from these nodes ( nickname, Sedmichnik, Potatoes ). | Tuber - short, bored underground escape, which contains spawned nutrients. The kidneys are formed on it, of which a new plant will grow ( potatoes, Crested, Cyclamen ). | Bulb - short thick stem, surrounded by scaped leaves. They contain nutrients ( lilies, tulips, daffodils, hyacinths, amaryllis ). |
 |  |  | |