Modifying underground shoots. Underground shoots
Escape is one of the main vegetative organs of higher plants. It consists of a stem on which the kidneys and leaves are placed. Escape the most changeable appearance Structural element of the plant.
The elevated part of the plant is a shoot or a system of shoots.
Escape consists of a stem (axis) and the leaves and kidneys located on it. The location of the leaf attachment to the stalk is called a node, and the area between the two adjacent nodes is interstitial. The angle between the stem and the sheet is called the top of the sheet. Escape develops from the kidneys.
The kidney is a succession escape with very shortened interstices. The central part in the kidney occupies the primary stem, on the top of which there is a cone of an increase in the educational fabric. On the stem is the embossed leaves. Outside the kidney is covered with renal scales capable of protecting the incharpasses and the increasing cone from unfavorable conditions medium. To perform a protective function at renal scales, thick omens is formed, resinous substances are isolated, etc.
The modified escape is a plant organ, in which the shape and function of the stem, kidney and leaves are irreversibly changed in the process of evolutionary devices to certain conditions for the existence of the body. In cultural plants, the selection of escape is due to human intervention.
Eugene metamorphosis can be both insignificant and substantial - to highly changed plants. Metamorphoses are subjected to both the main and side shoots, as well as the kidneys and leaves.
The main types of green plants shoots are overhead and underground. Overhead (air) shoots are assimilant, on the axis of which the leaves are located. Assimilant shoots are very diverse by appearance. In many cases, in addition to the main function of photosynthesis, such shoots perform the role of a pointer and support organ of the plant, as well as the function of vegetative reproduction.
|
Victims of escapes |
||
|
Name |
Functions |
Plant |
| Rhizome (formed underground or when accuming escape into the soil) | Stock substances, reproduction, resettlement | Osay, anemone, scarecrow, Kaluzhnitsa, |
| CaudEx (thickened main escape, passing into a rod root. When aging the plant is devouted, I start from the center.) | Stock substance | Swimpse, Asparagus, Mednica, voroniye eyes Coupling, Nijnik, Pyrey, Kear, Violet Amazing, Strawberries, Cuff, Iris, Barberry, Gravel, Lung-Batun, Blueberry, Lily |
| Mustache (Thin shoots with scaped leaves and sockets in interstitial) | ||
| Tuber (formed at the ends of underground steps) | Reproduction and settlement | Strawberry, Papers, Goose, Sedmichnik, Kostyannik |
| Corm | Substance and reproduction | Gladiolus, Khokhlatka |
| Bulb | Substance and reproduction | Onions, Lily Saranka, Tulip, Narcissus, Ryabchik |
| Succulent shoots | Water supply | Cacti, Mokhokha |
| Spines (located in the sinuses of the leaves, and when they are dedicated over the sheet scar) | Protection | Hawthorn, apple tree |
| Fillocladium (sheet-like shoots) | Photosynthesis | Asparagus, iglitsa |
| Layout (flat photosynthetic shoots) | Photosynthesis | Phillocactus, chests, siegocactus, horsetails |
| Mustache | Attachment to the support | Pumpkin, cucumber, hops |
Modifications of overhead escapes
We are modified with such shoots that perform some additional features: protection, climbing, nutrient stuff, etc. To the modified shoots include spines, mustaches, tubers, juicy shoots, collishes, shoots of insectivore plants.
Spiky - needle-like formations that protect the plant from eating animals. Birthdays can be formed from sheet (barberry), stristers (yellow acacia), escapes (sea buckthorn, hawthorn).
A mustache - filamentous stuffing shoots (grapes, cucumber) that perform a reference function. The pea in the mustache turns the part of the sheet.
The tuber is a thickened escape that performs the function of the supply of nutrients (Kohlrabi cabbage - approx. Site).
Stokers (domestic name - "mustache") - horizontal creeping shoots that promote the reproduction of the plant. Each pole is located with apparent roots. After rooting the outlet, the horizontal escape is devoted (strawberries, the luggage creeping).
Strawberry. Photo: Gabriel.
Juicy shoots - plant adaptation to a hot and dry climate. Their function is to store moisture. Water can accumulate in the leaves (crawl, mounted, aloe) or in the stem (softener, cactus).
Mexican cacti have fleshy stems of the most diverse shape: ribbed balls, columns, cylinders, even candelabra and cylinder. Cacti does not have green leaves: they turned into barbants. The photosynthesis function is performed by stalks.
Underground modified shoots
Stalls and tubers can be both overhead and underground. In addition to them, the underground shoots include rhizome and bulbs.
Underground collines perform the same functions as overhead - resettlement and reproduction of the plant. This explains the similarity in their structure.
Tuber. This escape stem is short and thick. The leaf-scales quickly die and scars remain in their place (the potatoes in the people they call them "brovings"). In their sinuses are the kidney "eyes". The tuber performs the function of the supply of nutrients (for example, starch), the experiences of the unfavorable time of the year and reproduction. Tubers are not only in potatoes, but also to Topinambur, storks. They appear on underground columns.
The rhizome externally looks like a root, but the rhizomes have scaly leaves, and in their sneakers - side kidneys, on the top - the top kidneys. Pressure roots are formed on the rhizer. Unlike alarm, rhizome - a long-term escape that allows the plant to survive unfavorable conditions. This underground escape is peculiar to many plants and can perform a variety of functions. In thick short rhizomes of the iris, nutrients are reserved. In a crazy, mouse peas, Lily of the Major rhizoma long and thin. They are capable not only to store nutrients, but also capture new territories.
Rhizome not only increases rapidly (the blonde for suitable is 1.5 meters, and mother-and-stepmother - for meter - as a result, the parent plant can break down to several subsidiaries. Rural residents are known how difficult it is to fight long-term weeds. : Pyrem, sick, mother-and-stepmother. Fresh buckthorn, rosehip, raspberry quickly grow.
The bulb is a strongly shortened modified escape with a flat stem - "Donets", with leaves in the form of scales. The scales can be juicy (in stockboring) or dry lubricants), may be narrow and only slightly cover each other (lily) or bite each other almost completely (hyacinth, tulip, onions). The bulb allows the plant to survive the unfavorable period of the year. The stubble kidneys can turn into bulbs - kids. Consequently, the bulb is both breeding.
At a rampant, gladiolus, underground escape is called the clubnewukov. Outwardly, the clubnevukovitsa resembles a bulb, but differs from it a strongly broken Don, to which the scratched-shaped small leaves are attached, and serves as an organ of accumulation of spare nutrients. In the clubnelukovice, the top and stubborn kidneys, giving rise to color-saving escape and childcareball children, are well developed.
Embry of either from the stubborn or apparent (adventtive) kidney. Thus, the kidney is escaped. In the germination of the seed from the germinal kings, the first escape of the plant is formed - its main escape, or escape of first order.From the main escape form side shoots, or second order shoots, and when repetition of branching - third order, etc.
Applying shoots Formed from the apparent kidneys.
This is how the system of shoots is formed, presented by the main escape and side shoots of the second and subsequent orders. The shootout system increases the total area of \u200b\u200bcontact with the air environment.
Depending on the function being performed, the elevations of vegetative, vegetative and generative and generative are distinguished. Vegetative (invisible) shoots consisting of a stem, leaves and kidneys and vegetative-generative (partially modified), consisting additionally from a flower or inflorescences, perform aircraft functions and provide synthesis of organic and inorganic substances. In the generative (fully modified) shoots of photosynthesis, it does not occur most often, but there are processed sporangies, the task of which is reduced to ensuring the reproduction of the plant (there are flower to such shoots).
Escape on which flowers are formed, called flower escape, or coloros (Sometimes the term "floweros" is understood in a narrower sense - as a plot of a stem on which flowers are located).
The main bodies escape
Vegetative unbearable Escape is a single plant organ, consisting of a stem, leaves and kidneys, which is generated from the general massif of the meristem (escape cone) and possessing a single conductive system. Stems and leaves that are the main structural elements of escape - are often considered as its composite bodies, that is, the second order bodies. In addition, the obligatory affiliation of escape is the kidney. The main appearance, distinguishing the escape from the root - the presence of leaves.
Monopodial branching
Monopodial branching is the next stage of the evolution of the branching of shoots. In plants with the monopodial type of building, the tossekoy kidney is maintained throughout the life of escape. Monopodial type branching is often found among vote plants, also occurs in many coated bridges (for example, in many species of palm trees, as well as plants from the orchid family - gastroinoshilus, phalaenopsis and others). Some of them have the only vegetative escape (for example, Phalaenopsis is pleasant).
Monopodial plants - The term most frequently used in the description of plants of tropical and subtropical flora, as well as in popular science literature on room and greenhouse flower growing.
Monopodial plants can differ significantly externally. Among them there are sockets, with elongated escape, bush.
Sympodial branching
In plants with a symphodial type of building of the escape kidney, finishing the development dies or gives the beginning of the generative browse. After flowering, this escape is no longer growing, and a new one begins to develop a new one. The structure of escapes in plants with a symphodial type of branching is more difficult than in plants with; Sympodial branching is an evolutionary more advanced type of branch. The word "sympoidal" is formed from Greek. sym. ("Together" or "a lot") and pod. ("leg").
Sympodial branching is typical for many coated plants: for example, for Lip, Yves and many orchid.
In the orchid, in addition to the top, the side of sympodial orchids are formed and side inflorescences are formed, developing from the kidneys located at the base of escape (Grebena Pafin). Part of the escape, pressed against the substrate, is called the rhizome. It is usually horizontally and does not have real leaves, only the scratched. Reduced, almost indistinguishable risoma sometimes happens to many molding, dendrobiums and oncidiums; Well distinguishable and thickened - at Cattles and Lelia, elongated - in Bulbophilleumov and Zhaichin, reaching 10 or more centimeters. The vertical part of escape is often a thickened forming the so-called tuberidium, or pseudobulb. Pseudobulb can be of different shapes - from almost spherical to cylindrical, cone-shaped, male and elongated, reed stalks. Pseudobulbs are in stockborne bodies.
Sympodial plants - The term most commonly used in the description of plants of tropical and subtropical flora, as well as in popular science literature on room and greenhouse flower growing.
|
Bulbophyllum Grandiflorum |
Cirrhopetalum Macraei.. Curtis "S Botanical Magazine Vol. 127 Ser. 3 Nr. 57 Tab. 7787, 1901 |
Oncidium dasystyle. Curtis "S Botanical Magazine Vol. 127 Ser. 3 Nr. 57 Tab. 7787, 1901 |
Dendrobium Senile.. Curtis "S Botanical Magazine Vol. 127 Ser. 3 Nr. 57 Tab. 7787, 1901 |
Evolution of branch types
Seagility modifications (metamorphosis)
Escape is the most volatile plant on the appearance of the plant. This is due not only to the total multifunctionality of the vegetative organs arising in the process of evolution, but also with changes occurring in the process of ontogenesis of plants caused by adaptation to the diversity of conditions ambient, and u cultural plants - under the influence of man.
The main type of green plant escape is an overhead (air) assimilating escape, carrying green-based green formations on the axis. However, assimilant shoots are not the same. Often, along with the main function of photosynthesis, others serve others: the deposition of reserves and the reference function (mostly in perennial stems), vegetative reproduction (creeping shoots, whites).
Winding of underground escapes
The shoots living under the ground, under the influence of a complex of conditions, sharply different from the ground medium, almost completely lost the functions of photosynthesis and acquired other equally important life functions, such as organs transfer the adverse period, soaring nutrients, vegetative renewal and reproduction of plants. Underground modified shoots include: rhizome, cakex, underground column and tuber, bulb, clubnellukovitsa.
Kaodex. - a long-term body of shooting the origin of perennial herbs and semi-shops with a well-developed rod root, which remains throughout the life of the plant. Together with the root, it serves as a place of deposits of spares and bears a lot of renewal kidney, some of which can be sleeping. Caudek plants are a lot among umbrellas (fear, furul), legumes (alfalfa, lupines), complex (dandelion, wormwood, grouse vasileuk).
Underground counteus - Annual extended subtle underground escape with underdeveloped scratched leafy leaves. On the thickened ends of the collines of the plants can accumulate spare substances, forming tubers or bulbs (potatoes, saddumpp, adox).
Stem tuber - A modified escape with a pronounced pointer stem, the presence of crystal leaves, which quickly peel, and the kidneys that are forming in the sneakers of the leaves and called eyes (potatoes, Topinamburg).
Bulb - Underground (less often above ground) strongly shortened specialized escape, in which spare substances are postponed in the scales of the sheet nature, and the stem is converted to the bottom. The bulb is a typical organ of vegetative renewal and reproduction. The bulbs are characteristic of one-bedroom plants from the family of Lily (Lilia, Tulip, Bow), Amarillic (Amarillis, Narcissus, Hyacinth), etc. As an exception, they are also found in dicotomic - in some types of acidic and granolases.
Corm - a modified underground shortened escape with a thick stem, sparkling assimilants, apparent roots, growing from the lower side of the clubnelukovitsa, and the remaining dried bases of leaves (film scales), together constituting protective cover. Clubneelukovitsy have saffron, gladiolus, a lack of junk.
Modifications of overhead escapes
An unusual lifestyle and / or adaptation to the special conditions of the existence of plants leads to various modifications of shoots. At the same time, shoots can serve not only for storing nutrients, reproduction and reproduction of plants, but also perform other functions. There are often cases when not all the escape is modified, but only its leaves, and some of their metamorphoses externally and functionally gathering with escape metamorphoses (spines, mustlemen).
Kolyuk - a strongly decisive, a leafless shortened escape with a sharp top. Spines of shooting origin perform mainly a protective function. At the wild apple tree, wild pears, crazy laxatives ( Rhamnus Cathartica.) In the spines, shortened shoots are converted, having limited growth and ending the edge. Glootichia ( GLEDITSCHIA TRIACANTHOS.) Powerful branched spines are formed on siblings from sleeping kidneys. Many species of hawthorn have spines, forming from the stubble kidney of the leaves, which topographically corresponds to lateral shoots.
Pretodium - a modified lateral escape, which has the ability to long-term growth, with green flat long stems that perform the function of the sheet. As an organ of photosynthesis, prettle has a well-developed chlorophyllon fabric located under the epiderm. Plants with quarters include Mulenbekia placcoon ( Muhlenbekia Platyclada.), cactus-Decembrist ( Zygocactus Truncates.), Karmikhelia South ( Carmichaelia australis), college ( Colletia Cruciata.) and omitation ( Opuntia.).
Fillocladium - A modified leaf-shaped flattened side escape, which has limited growth and performing sheet functions. Filloclasia develops from side kidneys, therefore always in the sinus of a small film or scaled leaf. Performing the function of photosynthesis, the shoots of philocladium and externally acquire similarities with a sheet, which is manifested in a limited growth and complete loss of the metaireral structure. Philloclaadium phenomenon is characteristic of such plants like a needle, dare, types of childbirth asparagus ( Asparagus.), Fillantus ( Phyllanhtus.). Filloclands are found not only to coated, but also in some viced, in particular, coniferous plant From the family of nine-folding - Fillocladus.
Outlet shoots - abnormal shoots formed on pine due to harm caused by pine with some harmful insects, for example, a butterfly monastery, etc.; Such shoots are extremely short and have bundles of short and wide needles.
Escape is one of the main vegetative organs of higher plants. It consists of a stem on which the kidneys and leaves are placed. Escape the most variable in appearance structural element of the plant.
The elevated part of the plant is a shoot or a system of shoots.
Escape consists of a stem (axis) and the leaves and kidneys located on it. The location of the leaf attachment to the stalk is called a node, and the area between the two adjacent nodes is interstitial. The angle between the stem and the sheet is called the top of the sheet. Escape develops from the kidneys.
The kidney is a succession escape with very shortened interstices. The central part in the kidney occupies the primary stem, on the top of which there is a cone of an increase in the educational fabric. On the stem is the embossed leaves. Outside the kidney is covered with renal scales capable of protecting the infarded leaves and the increasing cone from unfavorable environmental conditions. To perform the protective function, the renal scales are formed thick omitous, resinous substances are isolated, etc. The modified escape is a plant organ that the shape and function of the stem, kidneys and leaves are irreversibly changed in the process of evolutionary devices to certain conditions for the existence of the body. In cultural plants, the selection of escape is due to human intervention.
Eugene metamorphosis can be both insignificant and substantial - to highly changed plants. Metamorphoses are subjected to both the main and side shoots, as well as the kidneys and leaves.
The main types of green plants shoots are overhead and underground. Overhead (air) shoots are assimilant, on the axis of which the leaves are located. Assimilant shoots are very diverse by appearance. In many cases, in addition to the main function of photosynthesis, such shoots perform the role of a pointer and support organ of the plant, as well as the function of vegetative reproduction.
|
Victims of escapes |
||
|
Name |
Functions |
Plant |
|
Rhizome (formed underground or when accuming escape into the soil) |
Stock substances, reproduction, resettlement |
Osay, anemone, scarecrow, Kaluzhnitsa, |
|
CaudEx (thickened main escape, passing into a rod root. When aging the plant is devouted, I start from the center.) |
Stock substance |
Swimpanica, Asparagus, Medicarus, Voroniy Eyes Puppet, Nijnik, Floor, Homemade, Camper, Iris, Landberry, Gravel, Lung-Batun, Bilberry, Lily |
|
Mustache (Thin shoots with scaped leaves and sockets in interstitial) | ||
|
Tuber (formed at the ends of underground steps) |
Reproduction and settlement |
Strawberry, Papers, Goose, Sedmichnik, Kostyannik |
|
Corm |
Substance and reproduction |
Gladiolus, Khokhlatka |
|
Bulb |
Substance and reproduction |
Onions, Lily Saranka, Tulip, Narcissus, Ryabchik |
|
Succulent shoots |
Water supply |
Cacti, Mokhokha |
|
Spines (located in the sinuses of the leaves, and when they are dedicated over the sheet scar) |
Hawthorn, apple tree |
|
|
Fillocladium (sheet-like shoots) |
Photosynthesis |
Asparagus, iglitsa |
|
Layout (flat photosynthetic shoots) |
Photosynthesis |
Phillocactus, chests, siegocactus, horsetails |
|
Attachment to the support |
Pumpkin, cucumber, hops |
|
Modifications of overhead escapes
We are modified with such shoots that perform some additional features: protection, climbing, nutrient stuff, etc. To the modified shoots include spines, mustaches, tubers, juicy shoots, collishes, shoots of insectivore plants. Spiky - needle-like formations that protect the plant from eating animals. Birthdays can be formed from sheet (barberry), stristers (yellow acacia), escapes (sea buckthorn, hawthorn). A mustache - filamentous stuffing shoots (grapes, cucumber) that perform a reference function. The pea in the mustache turns the part of the sheet. The tuber is a thickened escape that performs the function of the supply of nutrients (Kohlrab cabbage - approx. Biofile.ru). Stokers (domestic name - "mustache") - horizontal creeping shoots that promote the reproduction of the plant. Each pole is located with apparent roots. After rooting the outlet, the horizontal escape is devoted (strawberries, the luggage creeping).
Juicy shoots - plant adaptation to a hot and dry climate. Their function is to store moisture. Water can accumulate in the leaves (crawl, mounted, aloe) or in the stem (softener, cactus). Mexican cacti have fleshy stems of the most diverse shape: ribbed balls, columns, cylinders, even candelabra and cylinder. Cacti does not have green leaves: they turned into barbants. The photosynthesis function is performed by stalks.
Underground modified shoots.
Stalls and tubers can be both overhead and underground. In addition to them, the underground shoots include rhizome and bulbs. Underground collines perform the same functions as overhead - resettlement and reproduction of the plant. This explains the similarity in their structure. Tuber. This escape stem is short and thick. The leaf-scales quickly die and scars remain in their place (the potatoes in the people they call them "brovings"). In their sinuses are the kidney "eyes". The tuber performs the function of the supply of nutrients (for example, starch), the experiences of the unfavorable time of the year and reproduction. Tubers are not only in potatoes, but also to Topinambur, storks. They appear on underground columns. The rhizome externally looks like a root, but the rhizomes have scaly leaves, and in their sneakers - side kidneys, on the top - the top kidneys. Pressure roots are formed on the rhizer. Unlike alarm, rhizome - a long-term escape that allows the plant to survive unfavorable conditions. This underground escape is peculiar to many plants and can perform a variety of functions. In thick short rhizomes of the iris, nutrients are reserved. In a crazy, mouse peas, Lily of the Major rhizoma long and thin. They are capable not only to store nutrients, but also to capture new territories. Rhizome not only increases rapidly (the blonde for suitable is 1.5 meters, and both mother-and-stepmother have a meter - approx. Biofile.ru), but also branches. As a result, the parent plant can be filled with several subsidiaries. Rural inhabitants are known how difficult it is to fight with long-lung weeds: dyeing, sick, mother-and-stepmother. Getting around sea buckthorn, rosehip, raspberry. The bulb is a strongly shortened modified escape with a flat stem - "Donets", with leaves in the form of scales. The scales can be juicy (in stockboring) or dry lubricants), may be narrow and only slightly cover each other (lily) or bite each other almost completely (hyacinth, tulip, onions). The bulb allows the plant to survive the unfavorable period of the year. The stubble kidneys can turn into bulbs - kids. Consequently, the bulb is both breeding. At a rampant, gladiolus, underground escape is called the clubnewukov. Outwardly, the clubnevukovitsa resembles a bulb, but differs from it a strongly broken Don, to which the scratched-shaped small leaves are attached, and serves as an organ of accumulation of spare nutrients. In the clubnelukovice, the top and stubborn kidneys, giving rise to color-saving escape and childcareball children, are well developed.
Vegetative reproduction, the formation of a new organism from the part of the maternal; One of the methods of dust reproduction of multicellular organisms. At lower plants (for example, algae) is more often carried out by dividing, in mushrooms - killing (for example, in yeast, some basidial mushrooms) or parts of mycelium (for example, hawk fungi), in higher plants - parts of vegetative organs ( root, stem, sheet), but more often by their modified forms - rhizomes (drinking, swine, etc.), tubers (potatoes, dahlia, etc.), bulbs (onions, tulip, etc.), root offspring (raspberry, cherry, Plum et al.), Usami (strawberry, strawberries), etc. It is characteristic of almost all perennial plants (based on their ability to regenerate). Vegetative offspring of one individual is called clone. Artificial methods of vegetative reproduction include all natural, as well as reproduction cherenca (currants, sea buckthorn, grapes, aloe, begonias, etc.), vaccine cuttings and kidney (pear, apple tree, rose, lilac, etc.), digging(Currant, Hazelnut, etc.). Vegetative reproduction of cultivated plants is applied for many centuries. In modern practice, effective methods of tissue culture (microdomism) are used. Clonal microdalization is based on the preparation of the planting material from the cells of the top meristem (the tops of the shoots). This method allows from one plant during the year to obtain several thousand plants with signs of maternal and free from viral and other infection to the desired period. Thus, planting vegetable, fruit and ornamental plants are obtained. In animals, vegetative reproduction is carried out either by fragmentation - branches from the material body parts of the body, which then completing themselves to the whole body, or by bearing. When you kill on the motherboard, a grow (kidney) is formed, from which a new part develops. Vegetative reproduction is characteristic of some worms, sponges, intestinal, shells.
\u003e East and underground metamorphoses of escape and root in cultivated plants. Draw different types of metamorphosis
Metamorphosis - transformation of one organ in another with a complete change of shape and function, occurs in many herbatous plants (gradual dying of the above-ground escape and the transition to rhizome, bulb, clubnelaukovitsa for the time of an unfavorable period). In most cases, non-differentiated organs of an adult plant are subjected to metamorphosis, and their primitives, for example, when turning part of the shoots and leaves in spines, mustaches.
The root is an underground organ of the plant, which is a continuation of the escape axis. He strengthens the plant in the ground, sucks water and mineral salts, accumulates spare substances, sometimes serves for vegetative reproduction. There are two main root systems: rod and urine.
Sodle root system occurs u dichomotor plants. It consists of a powerful main root located vertically down, and weakly developed lateral roots growing from it, which can be repeatedly branched on the roots of the first, second and subsequent orders.
All endings of young roots are covered with root hairs, which form, the so-called suction area.
W. monocoan plants The main root dies sooner and in its place appear growing from the stem, appropriate roots forming, the so-called, urine root system.
There are a variety of radiation modifications, especially in twilight and perennial plants. Most often they become in stockborne bodies and acquire a wide variety of forms. Sometimes the whole roots become stocking, sometimes their parts.
The spindle-shaped root is formed in the case when the main root grows greatly, it grures and takes the type of spindle, from whose lateral side roots.
The beck-shaped root in the upper part is strongly expanded, will be offered, and in the bottom remains oblong.
The tuber root consists of lateral swollen roots, accumulating spare substances or has single, double or several tubers.
Escape is an overhead (sometimes underground) part of a plant consisting of stem and leaves. At the top of the escape there is an upheat kidney, differing from the rest: the side kidneys are laid in the sinuses of the leaves, between the stems and sheet. On the shoot, nodes are highlighted, that is, the places from which the leaves grow, and the interdosezium - segments of the stems lying between them.
The main escape in the trees is called the barrel, the side shoots of rolling plants, shrubs and semi-accounts - branches. The shoots can be elongated, with long or shortened interstices, with close-lying nodes lying apart, and finally short, with very close-limited interstices. The axial part of escape is stem; It can be raised, stealing, curly, angular, rounded, thick, dense, etc. A leafless stem, growing directly from the root or root, carries a flower or inflorescence and is called an arrow.
The stem may be simple or branched. Each plant seeks to increase the area of \u200b\u200bits contact with the medium, whether water, air or soil. For this it branches. Branching is a different kind.
Dichotomous (Wilic) branching - when two escapes develop from the top of growth.
This type of branching is found at Mukhov, Playanov, some ferns, lower plants, for example, in algae.
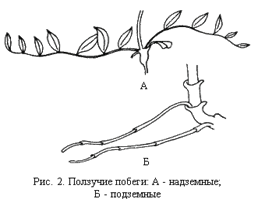
In seed plants there are monopodial, sympodial and fodderous types of branching. Monopodial (single-zone) branching takes place when the main escape develops from the top kidney, and thin side shoots grow out of the side kidneys. This type of branch is inherent in most conifers. But he has its drawbacks. If the top of the tree is damaged or strengthened in the process of growth in the branch of another tree, the entire growth of the tree can almost stop. Sympodial (multi-axis) branching have plants that have an elbow kidney, or the main escape is somewhat eliminated, and an escape is growing from a close side kidney, which continues the main escape axis. So branches most of the deciduous trees.
False-alone branching is observed in the case when the top kidney does not develop, or when the escape developing from it quickly devies, and two equal escapes grow up from the other two below the next side kidneys.
Overhead shoots have numerous modifications (metamorphosis). Some plants have such thin that they cannot climb up, and steals on the ground. This is the so-called, sharpening shoots. Plants thanks to such shoots can multiply vegetatively, since the nodes may occur the apparent roots. Sometimes pinching shoots have very long interstices, and in the nodes instead of assimilating leaves they grow unknown, scaly leaves, these are so-called creeping shoots or collisions that serve for vegetative reproduction. They form in the nodes of scaly kidney leaves and apparent roots, and after separating such a part of the collishes from the parent plant, they start the new organism.
W. curly plants Thin shoots climb up the backups. This is a curly stem. Among them, two types can be distinguished: wrapping and clinging. Stems spooking themselves around the backup (for example hop). Clinging do not possess such ability, they cling to the backup by special bodies, such as spikes, spines, clinging hairs, suckers, mustache, which are represented by valid shoots Or parts, apparent roots, leaves and even the top of the sheet.
In many plants, shortened shoots turn into pointed, often surrounded by kidney barrels, some short shoots can be flattened, they become similar to the leaves and perform the assimilation function. They are called philodiyev.
Underground shoots are found in perennial plants with green above-ground shoots. They perform the function of the inefficient organs in which the plant postpones summer period Spare substances. Underground shoots are also needed for vegetative renewal. In the spring of them grow overhead green shoots that feed on the nutrient reserves from the underground. Among the modifications of underground shoots can be called rhizomes, tubers and bulbs.

Rhizome - underground oblong escape with shortened interstices. They usually thickened, sometimes fleshy, are located in the ground horizontally or obliquely. Rhizome has at one end the upper kidney, it grows this end; The opposite end it gradually dies. In the nodes of escape are small, scaly leaves, and in their sinuses - side kidneys. From lateral and top kidneys grow overhead shoots. On the bottom side of the rhizomes, urine appling roots are formed.
Long, thin, branched rhizomes, non-folctating nutrients, are called underground creeping shoots. They serve for vegetative renewal.
The tuber is a strong thickened, short, swollen underground escape, accumulating spare nutrients, in its surfaces in the recesses are kidneys, single or collected several pieces in the sinuses of scaly quickly falling leaves from these kidneys in spring grow green above-ground shoots. Some plants simultaneously have two tubers, one old, another new, last year.
The bulb consists of a very shortened, cone-shaped stem, forming, the so-called, donce, as well as the surrounding unknown scaly or fleshy leaves, in which spare substances accumulate. The leaves are tightly adjacent to each other and form a large onion, covered by external, dry, protective scales. From the bulb in the spring grows green, friction, colorless escape. New bulbs are formed in the fleshy sinuses of old scales and serve for vegetative renewal. Such underground shoots are found in plants of monocoons, as well as with a short period of vegetation (so-called spring ephemeroids).
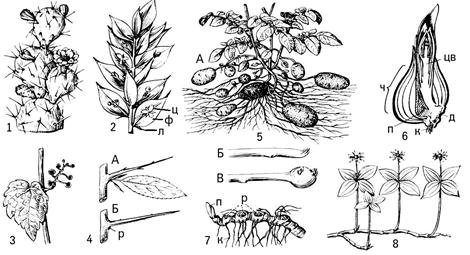
Escape Metamorphosis: 1 - Cactus Sucmation - Stem Sukkulet; 2 - Iligita: L - Chesow-shaped leaf, f - stuffing philocladium, c - flower; 3 - Vintage with suction cups; 4 - Birthday barns: A - Young barley with rudiments of leaves, sitting in a tiny leaf sinus, b - adult barb, p - scar of the crumbling sheet; 5 - potatoes with underground tubers - a, b and in - the formation of a tuber at the end of the staff, the leafy scars are visible; 6 - Lukovitsa Tulip in the longitudinal section: D - Donets, to - roots, h - bulbous scales, Col - Growing flowers, P - a subsidiary; 7 - rhizome bought: K - roots, P - kidney, r - scars of dead colorless shoots; 8 - Voroniye eyes, a system of rhizomes and overhead flower shoots.
Stems of shoots, performing certain functions, can be modified. There are modifications of overhead and underground parts of shoots.
Plants differ in the size of intersals. In a number of plants, interstices are developing rapidly, such plants are obtained with long stems. However, there are not few plants that are almost not growing, as a result, the leaves from different nodes are close to each other, and it turns out a stem in the form of a socket - this outlet plants (for example, plantain).
Plants differ in the method of finding a stem above the soil, the direction of its growth. If the growth of the stem is directed straight up, it develops streshuring stem. Such a stem from most plants, including all trees. Stems are fluttering on the ground. Shoulder stalks With developed apparel roots are called creeping (ivy, clover creeping). A lot of side shoots are formed on the steering shoots, they have small interstices. So they occupy large square on the ground.
If the creeping stems have long and thin interstices, they are called usami (for example, strawberries). On the mustache in the nodes, shortened sockets are developing with a lot of leaves. Mustache serve as a plant for vegetative reproduction and resettlement.
Liana - These are plants with curly stems. Lian a lot in tropical forests, these forests are very thick and plants easily find themselves support. In our latitudes, Lianami are cucumber, grapes, peas, beans. Lian develops radiation modifications, side shoots or leaves in the form of various hooks and mustaches. They are cling to the support. However, many Liana simply wrap support with their long stem.
In a number of plants, some shoots are modified in spines (pear, plum).
Rhizome, tuber and bulbs - This is the modification of underground shoots.
Rhizome is similar to the root, but it is escape, since he has knots, leaves and stubby kidneys. The leaves are usually similar to scales or may not be, but scars remain from them. In the nodes of rhizomes can grow appropriate roots. The rhizomes are, for example, in Prai and Lily of Lily.
In the rhizome, the plant lays spare nutrients. With the help of rhizomes, vegetative reproduction of plants can be carried out.
An example of the formation of tubers is potatoes (part of the plant, which people eat in food). The tuber is a thickened part of the stem of the rounded shape. It has spare nutrients (mainly starch). The potato tuber develops from the top kidney of a thin fragile stem - acer.
The value of tubers for the plants themselves is vegetative reproduction. For example, on the potato club there are kidneys - eyes.
The bulb is also thickened escape. It can be partially overhead. At the bulb, the stem is greatly bleached, it is called the Don. Numerous leaves grow from the Donets. Some of them (external) dry, and most of them are fleshy. In the juicy leaves of the bulbs are predominantly sugar. In the sinuses of the leaves develop kidneys from which subsidiaries may develop. Such side kidneys are called teeth (for example, there are many garlic), they are used by a plant for vegetative reproduction. The bulbs are not only at Luka and garlic, but also a number of other plants (lilies, tulips, etc.).