Common vitality of plants of your area. Life forms of plants
8.2. Life forms Plants
The concept of O. "Life form" as a totality of adaptive signsfor the first time, he introduced one of the founders of plants ecology in 1884, Danish botanist E. Warming. By his definition, this is a form in which the vegetative body of the plant (individual) is in harmony with an external environment throughout his life. The definition of this concept, more brief and in common, we find a variety of modern scientists. By A.P. Shennikova (1964), "Plant species, similar in shape and adaptation to the medium, are combined in one vital form." V.V. Alekhin (1944) believes that "the life form is the result of a long-term fixture of plants to local existence conditions, expressed in its appearance."
A wide application in environmental and phytocenotic studies is a classification of life forms developed by the Danish Botany K. Rowuncier (1934). It is based on the idea that similar types of plant fixtures to the medium are primarily similar ways to transfer the most difficult conditions. Indeed, favorable conditions are generally favorable for all plants (except in cases of a sharp shift of environmental optima in special conditions) and do not require special devices. Adaptive changes are mainly connected with overcoming the conditions underlying the optimal. In areas with seasonal climate periodicity, such difficult conditions for plants occur mainly in autumn-winter season, and in arid areas - also during the period of summer droughts. Hence the main similarity of plant adaptations to the environment should be in the similarity of the methods of transferring an unfavorable period of the year. K. Rowuncier to classify the life forms of plants chose only one character, but having a large adaptive value: the position of the kidneys or the tops of the shoots during the unfavorable time of the year in relation to the surface of the soil and snow cover. This feature at first glance is private, has a deep biological meaning (protection of meristems intended to continue growth ensures the continuous existence of individuals in conditions of a sharp environment variable) and widespread environmental content due to the fact that it is not one of any Factor, and to the entire complex of environmental factors. The sign chosen by K. Rowuncier, thus, turned out to be correlatively connected with a number of others, including with purely physiognomic, and the classification became universal.
All plants K. Rowuncier divided into five types of life forms (Fig.8.2).
- Punerofit(PH) - renewal kidneys, open or closed, are high above the soil surface (above 30 cm). According to the consistency of the stem, at the height of the plant, on the rhythm of the development of foliage, the renal protection is divided into 15 subtypes.
- Hamfiti(CH) - renewal kidney at the soil surface or not higher than 20-30 cm. Divided into four subtypes.
- Hemicriptophy(NK) - renewal kidney at the surface of the soil or in its superficial layer, often covered with a litter. Includes three subtypes and smaller divisions.
- Cryptophytes(K) - renewal kidney is hidden in the soil (geophytes) or under water (heat and hydrophitis). Divided into seven subtypes.
- Terophytes(TH) - renewed after the unfavorable time of the year only by seeds.
Fig. 8.2. Life forms of plants (according to K. Rawniku, 1934):
1 - plywood (poplar); 2 - Hamfits (blueberries); 3 - hemicriptoofy (buttercup, dandelion, cereals); 4 - Geophytes (anemone, tulip); 5 - Terophytes (bean seed)
Winter kidneys are highlighted in black
Subtype division based on the use morphological signs, such as the nature and location of the shoots, the security of the kidneys, etc.
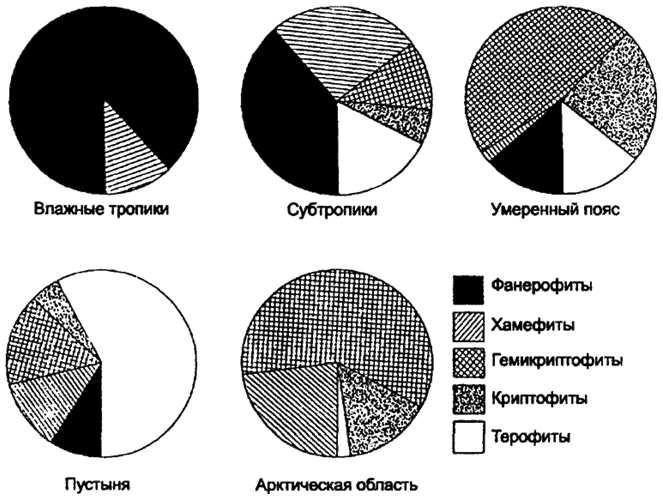
K. Rowuncier believed that the vital forms add up historically as a result of the plant adaptation to the climatic conditions of the medium. He called the percentage distribution of species on life forms in plant communities on the territory studied by the biological spectrum. Biological spectra were drawn up for different zones and countries that could serve as climate indicators (Fig. 8.3).
The continental climate of the moderate belt was called the hemicritic climate, and the hot and wet climate of the tropics - the climate of the plywood.
At the same time, the types of vital forms of plants, according to K. Rounnika, are too extensive and inhomogeneous. Thus, the Hamfitis include plants with different attitude to climate. There are many of them, both in the tundra and deserts.
For the vegetation of moderate areas, various systems of life forms were proposed in relation to the specific tasks of vegetation areas in relation to individual plant groups and types of vegetation. G.N. Vysotsky in 1915, a system of life forces for the steppe communities of the South of Russia was developed. Subsequently, it was supplemented and developed by L.I. Kazakevich (1922) and to date, it finds use when analyzing plant communities compiled
herbatous perennials. Methods of vegetative reproduction and resettlement of plants were taken as the basis of the allocation of life forms of the authors, so much attention is paid to the structure of their underground bodies.
On an ecological and morphological principle, a classification of life forms IG was built. Serebryakova (1962, 1964), developed mainly for shrub and wood forms. It defines the vital shape as a kind of general appearance or a habit of plant group, including their overhead and underground authorities ( underground shoots and root systems). Habitus occurs in ontogenesis as a result of the growth and development of the plant under certain conditions of the medium and expresses adaptability to the most complete use of the entire complex of collaboration conditions, spatial resettlement and consolidation of the territory. IG Serebryakov emphasized that the life form is a kind of external form of organisms, due to biology of development and the internal structure of their bodies, arises in certain soil-climatic conditions as an adaptation to life under these conditions, i.e. they are forms
adapted under the prolonged influence of environmental factors. Due to the variety of complexes of conditions on Earth, there is also a large number of life forms of organisms. In plants, such forms are distinguished as woody, half aless, terrestrial herbaceous and aqueous herbaceous. Each of them, in turn, is represented by many smaller groups of life forms (Table 8.1).
Table 8.1.
The ratio of departments and types of life forms of coated brine (according to I.G. Serebryakov, 1962)
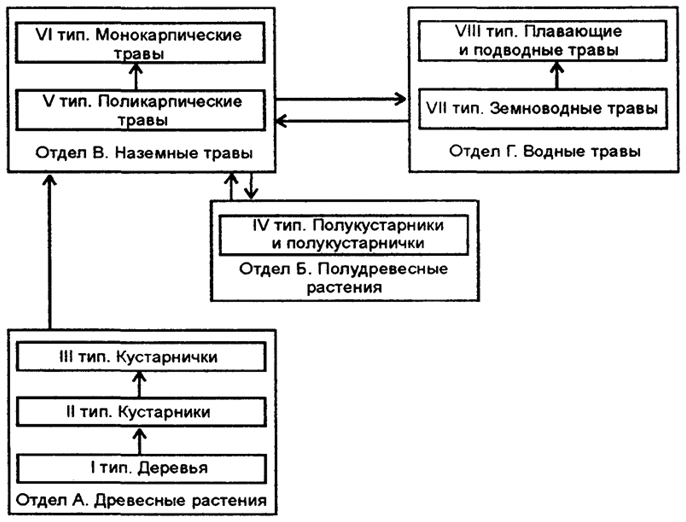
To vital form treesrelate perennial plants With one shredded trunk (birch, aspen, pine, spruce, etc.), which remained throughout the life of the plant. They can be leaf fall and evergreen. Among them are allocated forms terrestrial krono-forming,where there are trees: with reprehensive trunks, bush(Little) and single-barrels with low trunks(Fig. 8.4).
In all, they have a new one with sleeping renal, new one or several replacement (secondary) stems can grow from sleeping kidneys. This vital form of plants is widespread very widely and is an indicator. optimal conditions habitat. Among terrestrial crown-forming trees there are vital forms

with lying trunks - stalans.They are formed in areas, little favorable wood plants where long winter, cool summer, where cold winds often blow.
The volume of wood plants includes a large group of life forms - shrubs.A characteristic feature is the presence of many or several equal in the size of the trunks. The main trunk, existing in the early life, in the future practically does not stand out in length among the side. The height of the trunks of shrubs is usually from 0.5-0.8 to 5-6 m.
Shrub- Third type of vital forms of wood plants. These include a lingonberry, blueberry, a richness, etc. For all, they are characterized by low rising stalks (from 5-7 to 50-60 cm). The main stem exists no more than three to seven years. To replace it develops rooting side underground woody stalks, as a rule, from sleeping kidneys.
Among the life forms should be selected semi wood plantsto which belong polukstarniki(Steppe wormwood, Prucunion, Astragal Pants and others). A characteristic feature for semi-stares is a regular dying of the upper parts of overhead escapes. The remaining, unpleasant parts of the stems are decorated and persist in this form for several years. On these weathered above-ground parts of the stem, there are renewal kidneys, of which numerous new herbaceous stems develop the next year. These are semi-stares and differ from real herbaceous plants.
Large and diverse group of life forms - ground grassyplants. They are divided by I.G. Serebryakov in two parts: grassy polycarpicsfruiting many times in their lives and herbaceous monocarps,fruit-free only once. In turn, herbal polycarpicsare divided into a number of life forms: terminalplants (Perennial Matliki Herbs, etc.), long-terribleplants (Lucerne, Kermek, Sage, etc.), shortoyryplants (Son-Grass, Jacob's Honor, etc.), cherrynevy(Buttercup, Bolotnaya Kaluchny, etc.), shortocornias(bouche, anemone, etc.), purunional grassypolycarpics (shyunocustal, rylocker, long-lung plants), table-formingplants (Martick Two-Leaf, Strawberry, Strawberry, etc.), creeping grassypolycarpics (Veronica Drug moneywort and etc.), clothyGziepolycarpics (Labor Doubles, Potatoes, Rolls, etc.), bulbouspolycarpics (goose bows, onions, tulips, snowdrop Snowy, etc.).
Herbatous monocarpicswidely distributed in arid areas of the moderate zone of the northern hemisphere. Among those
Among all types of life forms are often encountered pillow-shapedforms. This is mostly perennial herbaceous, less often wood plants, sometimes evergreen. They are characterized by a small increase in the main axis and the strong branching of lateral shoots, which, located radially or floors, create a compact form of "pillows" (Akantolymon Alatava, Dryadotziver, stamps, etc.)
Most of the sushi are populated by those or other plants. And although they all belong to the same kingdom of living organisms, their form and physiology is individual. For the first time, the term "vital form of the plant" was introduced in 1884 by the Danish botany E. Warming. He believed that a certain vital form characterizes the state of the plant in which it ideally coexists with the environment. Subsequently, many plant classification systems were created at a similar criterion.
Life forms K. Rowuncier
The famous scientist K. Rowucker at one time has developed its own classification of plants, which is guided by the only criterion. Here, an important sign of adaptation to the influence of the external environment is taken into account, namely the position of renewal kidney in relation to the soil. According to this system, the following forms are distinguished:
- Punerofit- The tops of the shoots of such plants are located in the air even in the most unfavorable seasons. As a rule, the distance from the renoval renewal to the soil surface is more than 30 centimeters. Such plants are well tolerated the effect of the external environment.
- Hamfiti- The top of such escape is also located above the soil surface, but the distance between them does not exceed 20 - 30 centimeters.
- Hemicriptophy- Life form of plants, which is characterized by a low resumption kidney. As a rule, in unfavorable periods of the year, the tip of escape is on the surface of the soil, under the litter.
- Cryptophytes- the kidney of the resumption of such plants is stored either in the soil itself or under water;
- Terophytes- Another group of which is preserved exclusively in the form of seeds.
The scientist believed that the vital forms of plants are the result of centuries-old adaptations to survival under certain climatic conditions. However, such a system is not accurate. On the other hand, to today it is popular, constantly undergoing modifications.
Life forms of plants: Classification I. Serebryakova
It is this classification developed in 1962 - 1964 IG Serebryakov, to date, is considered the most complete and accurate. With its creation, the scientist took into account the features and conditions of growing, as well as the structure of vegetative and generative bodies. The four main departments were allocated, each of which includes its own types:
(Division a). Here it is customary to distinguish three types:
- Trees - the plants of this form are characterized by the presence of a powerful, weeding trunk. This is a perennial representatives of the flora.
- Shrubs are another large group of plants, which is characterized by the presence of simultaneously several trunks that germinate from sleeping kidneys.
- Sustainers are plants that are very similar to shrubs, but have some weighty differences, including smaller sizes and duration of life.
Half-tree plants (department b).This group is divided into two types:
- Politicists are quite similar to shrubs and shrubs, but has its own distinctive features. For example, their skeletal axes live no more than 5 - 8 years, and after dying, sleeping kidney has not formed.
- Semi-shop.
Ground herbs (department c) - The name clearly talks about what representatives vegetable world Communicated in this group. Severe two types:
- Polycarpic herbs are grassy bloom of which can be observed every year, sometimes even several times a year.
- Monocarpic herbs - these plants can live from one to several years. A distinctive feature is blooming only once for the period of plant development, after which the body dies.
Water herbs (department d) - These include organisms, the vital activity of which one way or another is associated with the water medium. It is customary to allocate two types:
- Amphibian floating herbs are the vegetative body of such a plant, as a rule, is on the surface of the water, on the border of the earth and water.
- Underwater herbs - Life forms of plants having exclusively
In fact, the vital forms of plants and animals are very diverse. And today the ideal system of their classification.
Life forms of plants
Life form (biomorph) - This is the appearance of plants (Habitus), reflecting their fitness to environmental conditions. In the process of individual development (ontogenesis), the appearance of the plant is changing. These changes affect how external factors ( environment), so the internal, laid in the genetic code. The teaching of life forms is a major section of morphology.
For the first time, the term "life form" introduced the Danish Botanist Johanes Eugenius Warming (1884) - the founder of the environmental geography of plants. He understood under this term "the form in which the vegetative body of the plant is in harmony with an external environment throughout life, from seed to death."
In appearance (habitus) and lifespan, the following life forms are distinguished:
trees.- perennial plants with decisive overhead parts, with a well-pronounced one barrel, not lower than 2 m high;
shrub- perennial plants with decisive overhead units, in contrast to trees have several trunks, as the branching begins on the base of the stem;
shrub- similar to shrubs, but not higher than 50 cm;
polukstarniki- differ from shrubs by the fact that only the lower parts of the shoots are shredded, and the upper annually die;
liana- plants with curly, clinging, climbing stems;
succulents- perennial plants with juicy shoots containing water supply;
grass- the above-ground part is dying annually; W. perennial herbs Under the ground, rhizomes, bulbs, tubers are preserved, the underground part of the annuals is died.
In 1903, the Danish scientist K. Rowuncier, summarizing the knowledge, created a system of life forms of covered bridges, widespread so far. It is based on the following principles. Morphological - the position of renewal kidneys in relation to the surface of the soil and the methods of their protection during the unfavorable time of the year. Physiological - plants reaction for rest season. In abbreviated form, the classification of life forms on the rounder is as follows:
punerofit- plants with renewal kidney, which are above 25 cm above the surface of the soil;
hamfiti- plants with low renewal kidneys (not higher than 25 cm above the soil surface);
hemicriptophy- plants with renewal kidney, located at the level of the soil surface, protected by the dead cover or the upper layer of the soil itself;
cryptophytes- plants whose kidney renewed is underground or under water;
terophytes- Annual, carrying adverse season in the form of seeds.
The system of K. Rowuncier is universal, it covers all the vital forms found in different ecological geographical areas of the globe. This system not only classifies the vital forms of coated bridges, but demonstrates their evolution - from trees to herbs. The composition of life forms can be an indicator (indicator) of the country's climatic conditions. K. Rowucker developed and applied the method of statistical analysis when studying the patterns of distribution and distribution of vitality.

In 1962, Russian Botanist I.G. Serebryakov offered a classification based on the structure and duration of the life of the above-ground skeletal axes of plants, in which the largest units (departments and types) are highlighted in the structure and duration of the life of overhead skeletal axes (trees with a barrel living dozens and hundreds of years, shrubs - with axes, Living 20-30 years, shrubs - 5-10 years, herbs with annual escapes). IG Serebryakov calls the life form a peculiar habit of certain groups of plants arising in ontogenesis as a result of growth and development under certain conditions of the medium and historically developed in these soil-climatic and centuries as an expression of adaptability to these conditions.
They are formed in the process of long-term fixture of the plant to local conditions of existence and are expressed in its appearance.
The vegetation cover of each ecologically separable area has a special appearance, which in turn depends on the appearance of the components of its plants. Characteristic appearance have meadow, forest, deserted, mountain vegetation. Groups of species growing on rock oids, alpine meadows, the borders of the snowflies also differ from each other. Initially, the researchers were allocated about two dozen life forms forming the appearance of plant landscapes, and now Botanists have them more than 60.
In addition to the appearance, the vital form of plants is characterized by physiological properties: leaf response, development rhythm, life expectancy. However, the main attribute is considered the appearance of the plant as a manifestation of growth features.
Appearance of plants
In generalized classification life forms of plants According to the peculiarities of the growth and life expectancy of vegetative organs, it looks like this:
Trees- Perennial plants with wood-in-law parts and a pronounced one barrel not lower than 2 m high. They are divided into evergreen and deciduous, broad-willed, finely, light and dark and dark.
A set of species peculiar to the forest zone of moderate climate is small, but are extensive areas occupied by one breed. Part of the species, depending on the conditions, can grow and in a bush form: Linden mellitis, kleples Ginnala and Tatar, cherry, rowan, apple tree Siberian, cherry, scamping, white acacia, Sumums Oleneher-legged, Willow. The bush forms of trees are valuable material in green construction.
Shrub
- Perennial plants with wood-in-law parts. The branching of the above-ground shoots begins from the earth itself, therefore several equivalent trunks are formed.
In green construction great importance There is a lifetime of individual shoots, the location of sleeping kidney and renewal kidneys (in the upper, middle or lower parts of the shoots), since it depends on the ability to dense branching during the haircut and education of offspring.
Polukstarniki
- Perennial plants that only shovels only the lower parts of the shoots, the upper parts die away.
In the harsh climate of Russia, many thermal-loving types of shrubs are roses, buddhom, Magonia Padoliste grown as half-workers. The height of the wintering shoots does not exceed the height of the snow cover.
Sustainers are low, not higher than 50 cm high, shrubs. Used for low borders, background spots, in rockers.
Liana - Plants with subtle weak shoots, climbing on a vertical support with the help of mustaches, apparent roots, barns or churrics. There are liana annual and perennial with decisive or herbaceous shoots.
In the middle lane, evergreen coniferous, suitable for intricate topical haircuts: Sugit, Tis, honeysuckle, but they are successfully replaced by Liana. Reception of phytoplasty - whipping figured supports - gives excellent results.
Otset The plant has strongly shortened vegetative above-ground shoots. All leaves are located at the surface of the Earth and form a rounded bush - a socket. Primula, Badan, Median Sugar Thanks to the originality of the appearance and compact form are often used in curbrad, in the forefront of flower beds, compositions.
Plant- "Pillow" Forms many short twigs pressed against each other. This original form is peculiar to mountain plants - smins, minuing, groom. Used mainly in rockers.
Succulents - Perennial plants with juicy shoots containing water supply. Meet flora middle strip (Cleans, MEDO). Apply in all types of compositions.
Herbatous plants divided into groups
Annolete - During the season, they grow out of seeds and after fruiting die. Sneakers annual development cycle take place in one year. Winter germinate from seeds in autumn, winter in the form of a socket, and from spring next year Flower, fruit and die. In the garden compositions, perennials cultivated as annuals - anti-crunch, verbena, ticklaith are widely used. Their assortment is expanding, as well as the palette of the paints and forms of numerous varieties. Indispensable for complex color schemes, where bright color stains are required for a variety of shades. Real annuals are often resumed by self-sowing, sometimes littering gardens. - Efemers - the inhabitants of the desert, annuals with a shortened development cycle, usually lasts only a few weeks. In the gardens, the gardens are cultivated by the duration of the flowering of perennials - ephemeeroids.
Two-bedrooms- Live two years. In the first year, the seed develops a shortened escape with a rosette of leaves and a rod root, and the second color-point shooting is formed. After fruiting, twilights die away. Some plants can be annual, then two-year-old - violets, poppies, or two-year-old, then perennial - barley grivoy, cornflowers. - Perennial - with annual die overhead shoots, with perennial underground bodies. We are divided into numerous groups of life forms. Efemeroids - plants with underground bulbs, clubnelluca, tubers, rhizomes. In the spring they appear overhead flower-free shoots, dieting to the beginning - middle of the summer after flowering, ripening and dispersion of seeds.
Widely represented in the forest zone of the middle strip of Russia. Thanks to the compactness Kurtin and short deadlines growing up in close proximity to others decorative plants - trees, shrubs, grassy perennials, annual. Dynxulusized plants have long underground branching rhizomes with kidneys. Grounding, such plants form curtains, thickets. In compositions, some particularly fast-growing species have to land in containers without the bottom, covered in the ground, or limit geocanies. Split kinds of this group segments of kidney rhizomes. Short-cornese plants are distinguished by a short rhizome and powerful deep root system, it is inherent in geranium, volzhanka.
Materials to the topic:
 |
If they decided to build ... read ... |  |
The main durable foundation ... Read ... | We build a bath ... read ... | |
 |
What to build walls ... read |  |
We are building a fence according to the rules .. taking ... |  |
In order not to go the roof ... read ... |
Types of this group are especially valued for the long-haired compact form of bushes. They are used in the parade compositions where a long-term decorative effect is required, and the division is propagated. Sneakers of the corneous plants form deeply going down the vertical weak root. They do not tolerate the transplant in adulthood, so they are more often divorced by seeds (poppy, gypsophila, sharp). Cutton plants form a brush of thickened roots. Many plants of this group are in wet rich soils and have a lateral period of active increment of foliage and bunning (primrose), the growth of young suction roots (peonies). Dersurbation plants, growing, form a ferrisin - a nocidal system of escaped escapes. Iiris Siberian, cereals - Good neighbors for plants of other groups, as they save moisture in turns and thus form a favorable microclimate. Zimnese high species retain the leaves with green under the snow until spring. This group of species is distributed in the forests of a moderate belt. The leaves are saved only under the snow cover (it is stable in the forest), and the change of old leaves on new occurs gradually, without losing decorativeness. Hoofs, clarity, luggage, violets, Badan are appreciated as components of early spring compositions.