Grain of grain crop
Bread cereals It is customary to divide into two groups:
. real bread(cereals) - wheat, rye, barley, oats;
. prosja bread(cereals) - corn, rice, millet, sorghum. These groups differ primarily by the structure of the fetus, which is called the grain. In real cereals, a grain of an oblong or oval form, from the side of the back, clearly distinguish the embryo in the form of a dent. On the opposite germin, the late - a beard formed by the growth of cells of the shells. From the side of the abdomen along the whole grain passes a groove.
In prosecidate cereals, a grain of various shapes, for example, at rice - oblong, at millet is rounded. The grooves and the beard are absent.
The grain is covered with a flower film (with the exception of corn, which is called a false creek). If the flower film is easily separated, the cereals are called holoper (wheat, rye), if it is impossible to separate it - with a balloon (barley, oats, rice, millet).
There are two forms of cereals - winter and spring. The spring plants are sown in spring, during the summer months they pass a full cycle of development and the crop gives the autumn. Winter plants sow autumn, until winter, they germinate, and in the spring continue their life cycle and ripen somewhat earlier than springtime. Winter grades give usually more high yieldBut they grow them only in areas with soft winter and abundant snow cover. Real cereals are both spring and winter, and the projections are torn.
Family of cereals is characterized by the following main features: the root is basic, the leaves of lancelovoid (long, sometimes rolled plates), stems in the form of thin straw with hollow interstices, flowers are collected in inflorescences. They distinguish cereals with blurred inflorescence (Oats, millet, rice) and cooled in the form of a complex chaser (rye, wheat, barley). In corn, inflorescence in the shape of the patch.
The structure of grain grain. The grain of any creek consists of three main parts - the embryo, endosperma and shells. They have a different structure and chemical composition.
The most outdoor shell- The fruit developing from the walls of the wound, consists of three cell layers. These cells are large, thick-walled, weathered, hollow. Next for the fruit shell - the seed, also consists of three layers - a transparent waterproof layer, tightly popped with a second brightly colored pigment layer, and a hyaline completely transparent swelling layer.
The bulk of grain is filled endosperm,or torrential core. Endosperm consists of an outdoor aleron layer formed by thick-walled large cells filled with protein vents with splashes, fat droplets. Actually, endosper is represented by thin-walled large cells, often incorrect formfilled with starch and squirrels. Proteins form a solid matrix into which starch granules of different sizes are enclosed. As the cell is removed from the center, the size of the starch is reduced accordingly, and the amount of protein increases.
From the side of the back to the endosperma adjacent germ -concept of the future plants. It consists of kingdoms, a stuffed root and a shield. The embryo contains many sugars, nitrogenous substances, fat, vitamins and enzymes. Through the shield nutrients Enter into the embryo.
The grain of various cereals consists of the same anatomical parts and has a similar chemical composition.
Chemical composition grains.Gallest specific gravity in grain occupy carbohydrateswhich are presented mainly by starch (in wheat - 60-70%). Starch consists of amylose (20-25%) and amylopectin (.75-80%). Sugar is contained in small quantities. In the grain, the proportion of monosaccharides, dextrins, maltose, which adversely affects the quality of bread increases.
Cell walls consist of non-hosted polysaccharides - ballast substances that are not absorbed by the body, but have a positive effect on the processes of digestion, and also contribute to the removal of heavy metals and radionuclides from the body. Nonchramal polysaccharides include cellulose (fiber), hemi cellulose (half-flip), pectins. Part of the hemicellulose, called Penozhan, is dissolved in water, while forming viscous colloidal solutions - mucus (gummy). The greatest number of muzzles in rye (2.5-7.0%), oats (8.0-12.0%), barley (up to 15%).
Belkovwheat is 10-20%. The main part of proteins - prolamines (spiritors; in wheat, they are called glyadin, in the corn - zine) and bugness (alkaline-soluble). When mixing wheat test, glyadin and bugness swell and, bonding, form a continuous phase of the test, when gluing the gluten forms: In addition, the proteins include albumin (water-soluble proteins) and globulines (saline), which contain all indispensable amino acids. Cultures containing more of these proteins (rye and oats - 30-35% of the total number of proteins) are valuable in amino acid composition. Proteins of millet and corn are defective.
Content lipidin the cereals fluctuate on average from 2 to 3%, with the exception of corn and oats. Simple lipids are in the embryo and are spares that are used during germination. Complex lipids are part of the membranes of cell shells and take part in cellular, processes. In general, lipids are unsaturated, linoleic and oleic acids predominate. On the one hand, lipids serve as a source of valuable essential fatty acids, and on the other, they can quickly oxide.
In the cereals contain water and fat-soluble vitamins:carotenoids (carotene), vitamin E (tocopherol), vitamins of group B (thiamine, riboflavin, pantothenic acid, pyroxine), niacin, etc.
Share mineral elements- 1.5-3.0%. Macroelements have a lot of phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, but they are in the associated state in the form of polyathic acid salts and poorly absorbed; In the film cultures, many silicon. The grain is the source of many microelements - zinc, manganese, molybdenum, cobalt, etc., often toxic to which are set extremely permissible norms According to security requirements.
The quality of the products obtained influence enzymesand p-amylases, hydrolyzing starch, phytase, splitting fitting, proteinase - protein. In a healthy grain, the activity of enzymes is small. Increased activity of enzymes is characteristic of defective grain.
Coloring grain due to presence pigments- chlorophyll and carotenoids.
Wheat. It is basic food Culture. Wheat is divided into soft and hard. Soft wheat is designed to obtain bakery flour, and solid - pasta flour, cereals. Soft and solid wheat differ from each other. Corn soft wheat oval-rounded shape, with a well-visible groove, white color Or with a red tint. The grain of solid wheat is a narrow, ribbed, dense, amber-yellow, a beard is almost imperceptible. Gluten obtained from flour from solid wheat, elastic, strong.
Wheat is divided into six types of botanical features and character of culture (winter or spring); Types are divided into subtypes depending on the glassy and grain color. Type 1 - soft spring red.
Subtype 1 - dark red, vitreous, glassyness of at least 75%. Subtype 2 - red, glassyness at least 60%. Subtype 3 - light red, glassyness of at least 40%. Subtype 4 - yellow, glassyness less than 40%. Type 2 - Summer hard.
Subtype 1 - dark amber, glassyness of at least 70%. Subtype 2 - light amber, glassyness is not rationed. Type 3 - soft spring white.
Subtype 1 - white, glassyness is at least 60%. Subtype 2 - white, glassy glass is less than 60%. Type 4 - Soft Oshamis Mountain, is divided into four subtypes similar to wheat type 1.
Type 5 - Soft Wester Blue Corroser, not divided into subtypes. Type 6 - winter firm, it is not divided into subtypes. The division of types and subtypes does not give a complete idea of \u200b\u200bwheat quality, so the standard provides for the division of soft wheat into six classes, and solid - five. To the first three classes (the highest, first, second) soft wheat include wheat, which can be used not only independently for bakery, but also as an enriferry of weak wheat. Such wheat is called strong. The third-class wheat refers to the valuable, as it is used independently for the bread maker and does not require improvement. The fourth grade refers wheat, which should be improved strong and only after that can be used for bread accumulation. The fifth grade wheat is used as a fodder.
Rye. Ranked second in the production of bakery flour.
Grain of rye is narrow and long, therefore the share of the shells, alarium layer and the embryo more, and the endosperma is less. Compared to wheat in the grain of rye less proteins (by 1.7-2.0%), but they are more complete. In addition, rye proteins are able to firmly swell and form viscous colloidal solutions. Under normal conditions, gluten do not form, the launder prevents the mucus.
Grain rye divide, in quality to four classes. Rye of the first three classes (group A) is intended for recycling in flour; Fourth grade (group b) - for feed purposes. The basis of the division of rye into classes is the indicator of the "number of fall", which for food rye fluctuates from 200 to 80 s, and for rye, intended for feed purposes, is less than 80 s.
Family Zlaki. - One of the largest family of flowering plants, has about 10,000 species. For the most part, it is grass, but the stems of some tropical bamboo bamboo are decorated, reach 40 m of height and 20 cm in diameter.
Cereals play a huge role in the plant cover of the planet, these are the main bread and cereal cultures, and wheat, rice and corn - the main food plants mankind. The value of rye, barley, oats, millet and sorghum is also great. In tropical countries, a sugar cane is widely cultivated, the juicy core of which contains up to 20% sugar. This culture gives more than half of the global sugar production. In a number of countries, young shoots of many cereals are widely eating, especially bamboo. Green mass of these plants - valuable pet food. The main feed plants of cereals: Mattik, Timofeevka, hedgehog team, oatmeal. The cereals are also used for the lawn device, the arrow of the airfields and the sports grounds, for fastening the sands, embankments. A number of cereals gives construction Materials and raw materials for paper production (reed, bamboo).
Among the cereals there are malicious weeds: creeping powder, oatsi, bonfire rye. Almost all the cereals are pollinated by the wind, but there are also self-polls (wheat).
Corn
November 5, 1492 years, a few days after the opening of the new light, Columbus recorded: "I saw a cereal called Mais." And one of his companions described Mais More: "There were some strange plants in the fields. more meter. It seemed that they were from pure gold, and their leaves were from silver. " The ancient inhabitants of America grown by maize, or corn, more than 7 thousand years. She served them main food. She was worshiped as a sacred plant. Ancient Maya knew several varieties of corn: "Corn - an old woman", having matured half a year, "corn - a girl", having slept twice as fast, and a variety called "Peush's Song", which gave the fruits only two months after germination of seeds. Once in the old light, corn quickly "won" it (many times faster than potatoes). Corn grain contains up to 70% starch, 10-12% protein, 8% fat. The plant is heat-loving, so in middle lane Russia does not affect Russia, and corn here is grown only on a green mass for livestock (it is obtained up to 50 and even 100t with hectares). In every female inflorescences (cob) up to 1 thousand. Zenovok. More often there are varieties with yellow fruits, but there are varieties with red, blue and even almost black centers.
Wheat
Wheat man cultures more than 10 thousand years. But in different epochs, people grown different types Wheat (total wheat includes them about 20). Recall, for example, "a fairy tale about Pop and an employee of his Bald" A. S. Pushkin. Hiring a job, Balda says:
I will serve you nice
Diligently and very well
Per year for three closures to you on the forehead,
There is me let's boil the wool.
These lines remember many, but what is the shell, few people know. This is one of the most ancient cultural wheat. She was the main "bread" of the inhabitants of ancient Egypt and Mesopatamia. It was cooked delicious and nutritional porridge. The shepherd tolerates drought well, but low-yielding, the seeds should be released from the films. Therefore, in the twentieth century. The shell almost forgotten and practically they do not grow anywhere.
The ancient Egyptians were the first to add yeast to the dough. The ancient Greek historian Herodotus was surprised about this: "All people are afraid that food does not hesitate, and the Egyptians knead the dough so that it is subjected to rotting" (we would say to fermentation). At the same time, more magnificent, noworthy bread gives strong wheat varieties, in whose grains whose protein is more than 15%. Weak varieties are less than 11%. (And starch in wheat grain up to 75%.)
Sugarcane
Credit juice of sugar cane - Sakaru - in India they drank another 5 thousand years ago. In IV century BC. One of the commander of Alexander Macedonian wrote: "There is a reed in India, which without bees gives honey." And at the beginning of our era, travelers in India have already tried the real sugar - "stone honey", "white and similar to salt, but very sweet." From the crusades, European knights were disappeared and sugar, and in 1163 one of them was presented by the King of France Louis VII a sugar head, which he kept as an expensive thing. Christopher Columbus, it turns out, not only brought many new plant species to Europe, but also the new light "presented" sugar cane. Here this plant found the second homeland. From the XVI century Sugar cane began to grow in Cuba and Haiti, using the cheap labor of African slaves. Now two thirds of sugar in the world is made from the cane. It is a powerful grace up to 6 m. Height. In the juice of its stems up to 26% sucrose. Cut the stem with one blow with heavy tone (in Spanish "Machete") so that not sweet juice. Grinding stems (Bagaso) are fuel for sugar factories. Make them and paper.
Fig
Rice is called the "second bread of mankind," the root of the East. Many scientists believe even that Rice is the most ancient cultural plant. Around rice grains, which gives life and requires tirelessly, focused after the entire spiritual world of residents of many Asia countries. Dramed rice steel in India about 15 thousand years ago. His ancestor was a wild multi-year rice growing in the mountains. Initially, rice and bred on the slopes of the hills, but then noted that in flooded shorts, the harvest is many times richer. For a long time, all the processing of the soil was reduced to the fact that buffaloes were driven by the flooded field, which messed the soots of the soil and water. Then manually planted rice seedlings. And now in rice production prevails manual labor. The inhabitants of Vietnam say that in order to grow a handful of rice, you need to shed a fear of sweat, - and there is no exaggeration here. In the world, the average rice crop from hectare is 23 centners. In rice grains, about 75% starch and 8% proteins. Rice straw is used for weaving hats, mats, production of super-quality papers.
Rye
History of rye as cultural plant Quite unusual. Her origin was established by Academician Nikolai Ivanovich Vavilov. Wildling rye has long clogged wheat crops and barley. In front of Asia, it was called "Jajor", which means "Torzaya". But in frosty or dry years, wheat died, and then the farmer had taken away the crop of unpretentious weed. And with the time, rye began to sow specially, especially in the middle lane of Russia. So a former weed became the main bread of Russian peasants.
Sorghum
The sorghum is called the "vegetable camel" for the ability to transfer the lack of water for a long time. Therefore, in the other areas of Africa (in some places already 5 thousand years), sorghum cakes are the main bread of the local population. In China, sorghum is called "Galyan", in Egypt - "Durier". Externally, the plant sorghum resembles millet, but much larger (up to 5 m. Height). By the way, the inhabitants of Russia almost every day, without being suspected, use the products produced from sorghum. We are talking about ordinary brooms.
Corn
Grain is the raw material for the flour and cereal industry.
Distinguish grain for food and for fodder purposes. Food grain on the intended purpose It is customary to divide on flourish, cereal, technical (brewing, starch, oil, alcohol, alcohol, etc.) - the grain of the same culture can be used for different purposes. For example, corn is raw materials for the production of flour, cereals, starch, canned, vegetable oil, but also a fodder culture.
The use of grain crops depends on their chemical composition. By chemical composition, grain crops are customary to divide into three groups:
Rich in starch - bread cereals. Starch content 70-80%, proteins - 10-15%. To them. include wheat, rye, barley, oats, rice, millet, corn (false grace), family of buckwheat;
Rich in squirrel - legumes. The content of carbohydrates is 50-55%, proteins - 25-40%;
Rich in fats - oilseeds. The content of fats is 25-35%, proteins - 20-40%.
The cultivated grain crops on botanical features (fruit, inflorescence, stem, root) refer to three families: cereal, buckwheat, legumes.
Family Zlatkov
Bread cereals are customary to divide into two groups:
real bread (cereals) - wheat, rye, barley, oats;
prosja bread (cereals) - corn, rice, millet, sorghum. These groups differ primarily by the structure of the fetus, which is called the grain. In real cereals, a grain of an oblong or oval form, from the side of the back, clearly distinguish the embryo in the form of a dent. On the opposite germin, the late - a beard formed by the growth of cells of the shells. From the side of the abdomen along the whole grain passes a groove.
In prosecidate cereals, a grain of various shapes, for example, at rice - oblong, at millet is rounded. The grooves and the beard are absent.
The grain is covered with a flower film (with the exception of corn, which is called a false creek). If the flower film is easily separated, the cereals are called holoper (wheat, rye), if it is impossible to separate it - with a balloon (barley, oats, rice, millet).
There are two forms of cereals - winter and spring. The spring plants are sown in spring, during the summer months they pass a full cycle of development and the crop gives the autumn. Winter plants are sowing in the fall, before the winter of winter they germinate, and in the spring they continue their life cycle and ripen somewhat earlier than the snealing. Winter grades give, as a rule, a higher harvest, but they grow them only in areas with a soft winter and abundant snow cover. Real cereals are both spring and winter, and the projections are torn.
Family of cereals is characterized by the following main features: the root is basic, the leaves of lancelovoid (long, sometimes rolled plates), stems in the form of thin straw with hollow interstices, flowers are collected in inflorescences. They distinguish cereals with blurred inflorescence (Oats, millet, rice) and cooled in the form of a complex chaser (rye, wheat, barley). In corn, inflorescence in the shape of the patch.
The structure of grain grain. The grain of any creek consists of three main parts - the embryo, endosperma and shells. They have a different structure and chemical composition.
The most outdoor shell - The fruit developing from the walls of the wound, consists of three cell layers. These cells are large, thick-walled, weathered, hollow. Next for the fruit shell - the seed, also consists of three layers - a transparent waterproof layer, tightly popped with a second brightly colored pigment layer, and a hyaline completely transparent swelling layer.
The bulk of grain is filled endosperm, or torrential core. Endosperm consists of an outdoor aleron layer formed by thick-walled large cells filled with protein vents with splashes, fat droplets. Actually endosper is represented by thin-walled large cells, often irregular shape filled with starch and proteins. Proteins form a solid matrix into which starch granules of different sizes are enclosed. As the cell is removed from the center, the size of the starch is reduced accordingly, and the amount of protein increases.
From the side of the back to the endosperma adjacent germ - concept of the future plants. It consists of kingdoms, a stuffed root and a shield. The embryo contains many sugars, nitrogenous substances, fat, vitamins and enzymes. Through the shield, nutrients come into the embryo.
The grain of various cereals consists of the same anatomical parts and has a similar chemical composition.
Chemical composition of grain.The greatest share in the grain occupy carbohydrates which are presented mainly by starch (in wheat - 60-70%). Starch consists of amylose (20-25%) and amylopectin (.75-80%). Sugar is contained in small quantities. In the grain, the proportion of monosaccharides, dextrins, maltose, which adversely affects the quality of bread increases.
Cell walls consist of non-hosted polysaccharides - ballast substances that are not absorbed by the body, but have a positive effect on the processes of digestion, and also contribute to the removal of heavy metals and radionuclides from the body. Nonchramal polysaccharides include cellulose (fiber), hemi cellulose (half-flip), pectins. Part of the hemicellulose, called Penozhan, is dissolved in water, while forming viscous colloidal solutions - mucus (gummy). The greatest number of muzzles in rye (2.5-7.0%), oats (8.0-12.0%), barley (up to 15%).
Belkov wheat is 10-20%. The main part of proteins - prolamines (spiritors; in wheat, they are called glyadin, in the corn - zine) and bugness (alkaline-soluble). When mixing wheat test, glyadin and bugness swell and, bonding, form a continuous phase of the test, when gluing the gluten forms: In addition, the proteins include albumin (water-soluble proteins) and globulines (saline), which contain all indispensable amino acids. Cultures containing more of these proteins (rye and oats - 30-35% of the total number of proteins) are valuable in amino acid composition. Proteins of millet and corn are defective.
Content lipid in the cereals fluctuate on average from 2 to 3%, with the exception of corn and oats. Simple lipids are in the embryo and are spares that are used during germination. Complex lipids are part of the membranes of cell shells and take part in cellular, processes. In general, lipids are unsaturated, linoleic and oleic acids predominate. On the one hand, lipids serve as a source of valuable essential fatty acids, and on the other, they can quickly oxide.
In the cereals contain water and fat-soluble vitamins: carotenoids (carotene), vitamin E (tocopherol), vitamins of group B (thiamine, riboflavin, pantothenic acid, pyroxine), niacin, etc.
Share mineral elements - 1.5-3.0%. Macroelements have a lot of phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, but they are in the associated state in the form of polyathic acid salts and poorly absorbed; In the film cultures, many silicon. The grain is the source of many trace elements - zinc, manganese, molybdenum, cobalt, etc., often toxic, to which the maximum permissible norms are established according to safety requirements.
The quality of the products obtained influence enzymes and p-amylases, hydrolyzing starch, phytase, splitting fitting, proteinase - protein. In a healthy grain, the activity of enzymes is small. Increased activity of enzymes is characteristic of defective grain.
Coloring grain due to presence pigments - chlorophyll and carotenoids.
Wheat. It is the main food culture. Wheat is divided into soft and hard. Soft wheat is designed to obtain bakery flour, and solid - pasta flour, cereals. Soft and solid wheat differ from each other. The grain of soft wheat oval-rounded shape, with a well-visible groove, white or red tint. The grain of solid wheat is a narrow, ribbed, dense, amber-yellow, a beard is almost imperceptible. Gluten, obtained from solid wheat flour, elastic, strong.
Wheat is divided into six types of botanical features and character of culture (winter or spring); Types are divided into subtypes depending on the glassy and grain color. Type 1 - soft spring red.
Subtype 1 - dark red, vitreous, glass
at least 75%. Subtype 2 - red, glassyness at least 60%. Subtype 3 - light red, glassyness of at least 40%. Subtype 4 - yellow, glassyness less than 40%. Type 2 - Summer hard.
Subtype 1 - dark amber, glassyness of at least 70%. Subtype 2 - light amber, glassyness is not rationed. Type 3 - soft spring white.
Subtype 1 - white, glassyness is at least 60%. Subtype 2 - white, glassy glass is less than 60%. Type 4 - Soft Oshamis Mountain, is divided into four subtypes similar to wheat type 1.
Type 5 - Soft Wester Blue Corroser, not divided into subtypes. Type 6 - winter firm, it is not divided into subtypes. The division of types and subtypes does not give a complete idea of \u200b\u200bwheat quality, so the standard provides for the division of soft wheat into six classes, and solid - five. To the first three classes (the highest, first, second) soft wheat include wheat, which can be used not only independently for bakery, but also as an enriferry of weak wheat. Such wheat is called strong. The third-class wheat refers to the valuable, as it is used independently for the bread maker and does not require improvement. The fourth grade refers wheat, which should be improved strong and only after that can be used for bread accumulation. The fifth grade wheat is used as a fodder.
Rye. Ranked second in the production of bakery flour.
Grain of rye is narrow and long, therefore the share of the shells, alarium layer and the embryo more, and the endosperma is less. Compared to wheat in the grain of rye less proteins (by 1.7-2.0%), but they are more complete. In addition, rye proteins are able to firmly swell and form viscous colloidal solutions. Under normal conditions, gluten do not form, the launder prevents the mucus.
Grain rye divide, in quality to four classes. Rye of the first three classes (group A) is intended for recycling in flour; Fourth grade (group b) - for feed purposes. The basis of the division of rye into classes is the indicator of the "number of fall", which for food rye fluctuates from 200 to 80 s, and for rye, intended for feed purposes, is less than 80 s.
Bread cereals are customary to divide into two groups:
real bread(cereals) - wheat, rye, barley, oats;
prosja bread(cereals) - corn, rice, millet, sorghum. These groups differ primarily by the structure of the fetus, which is called the grain. In real cereals, a grain of an oblong or oval form, from the side of the back, clearly distinguish the embryo in the form of a dent. On the opposite germin, the late - a beard formed by the growth of cells of the shells. From the side of the abdomen along the whole grain passes a groove.
In prosecidate cereals, a grain of various shapes, for example, at rice - oblong, at millet is rounded. The grooves and the beard are absent.
The grain is covered with a flower film (with the exception of corn, which is called a false creek). If the flower film is easily separated, the cereals are called holoper (wheat, rye), if it is impossible to separate it - with a balloon (barley, oats, rice, millet).
There are two forms of cereals - winter and spring. The spring plants are sown in spring, during the summer months they pass a full cycle of development and the crop gives the autumn. Winter plants are sowing in the fall, before the winter of winter they germinate, and in the spring they continue their life cycle and ripen somewhat earlier than the snealing. Winter grades give, as a rule, a higher harvest, but they grow them only in areas with a soft winter and abundant snow cover. Real cereals are both spring and winter, and the projections are torn.
Family of cereals is characterized by the following main features: the root is basic, the leaves of lancelovoid (long, sometimes rolled plates), stems in the form of thin straw with hollow interstices, flowers are collected in inflorescences. They distinguish cereals with blurred inflorescence (Oats, millet, rice) and cooled in the form of a complex chaser (rye, wheat, barley). In corn, inflorescence in the shape of the patch.
The structure of grain grain. The grain of any creek consists of three main parts - the embryo, endosperma and shells. They have a different structure and chemical composition.
The most outdoor shell- The fruit developing from the walls of the wound, consists of three cell layers. These cells are large, thick-walled, weathered, hollow. Next for the fruit shell - the seed, also consists of three layers - a transparent waterproof layer, tightly popped with a second brightly colored pigment layer, and a hyaline completely transparent swelling layer.
The bulk of grain is filled endosperm,or torrential core. Endosperm consists of an outdoor aleron layer formed by thick-walled large cells filled with protein vents with splashes, fat droplets. Actually endosper is represented by thin-walled large cells, often irregular shape filled with starch and proteins. Proteins form a solid matrix into which starch granules of different sizes are enclosed. As the cell is removed from the center, the size of the starch is reduced accordingly, and the amount of protein increases.
From the side of the back to the endosperma adjacent germ -concept of the future plants. It consists of kingdoms, a stuffed root and a shield. The embryo contains many sugars, nitrogenous substances, fat, vitamins and enzymes. Through the shield, nutrients come into the embryo.
The grain of various cereals consists of the same anatomical parts and has a similar chemical composition.
Chemical composition of grain.The greatest share in the grain occupy carbohydrateswhich are presented mainly by starch (in wheat - 60-70%). Starch consists of amylose (20-25%) and amylopectin (.75-80%). Sugar is contained in small quantities. In the grain, the proportion of monosaccharides, dextrins, maltose, which adversely affects the quality of bread increases.
Cell walls consist of non-hosted polysaccharides - ballast substances that are not absorbed by the body, but have a positive effect on the processes of digestion, and also contribute to the removal of heavy metals and radionuclides from the body. Nonchramal polysaccharides include cellulose (fiber), hemi cellulose (half-flip), pectins. Part of the hemicellulose, called Penozhan, is dissolved in water, while forming viscous colloidal solutions - mucus (gummy). The greatest number of muzzles in rye (2.5-7.0%), oats (8.0-12.0%), barley (up to 15%).
Belkovwheat is 10-20%. The main part of proteins - prolamines (spiritors; in wheat, they are called glyadin, in the corn - zine) and bugness (alkaline-soluble). When mixing wheat test, glyadin and bugness swell and, bonding, form a continuous phase of the test, when gluing the gluten forms: In addition, the proteins include albumin (water-soluble proteins) and globulines (saline), which contain all indispensable amino acids. Cultures containing more of these proteins (rye and oats - 30-35% of the total number of proteins) are valuable in amino acid composition. Proteins of millet and corn are defective.
Content lipidin the cereals fluctuate on average from 2 to 3%, with the exception of corn and oats. Simple lipids are in the embryo and are spares that are used during germination. Complex lipids are part of the membranes of cell shells and take part in cellular, processes. In general, lipids are unsaturated, linoleic and oleic acids predominate. On the one hand, lipids serve as a source of valuable essential fatty acids, and on the other, they can quickly oxide.
In the cereals contain water and fat-soluble vitamins:carotenoids (carotene), vitamin E (tocopherol), vitamins of group B (thiamine, riboflavin, pantothenic acid, pyroxine), niacin, etc.
Share mineral elements- 1.5-3.0%. Macroelements have a lot of phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, but they are in the associated state in the form of polyathic acid salts and poorly absorbed; In the film cultures, many silicon. The grain is the source of many trace elements - zinc, manganese, molybdenum, cobalt, etc., often toxic, to which the maximum permissible norms are established according to safety requirements.
The quality of the products obtained influence enzymesand p-amylases, hydrolyzing starch, phytase, splitting fitting, proteinase - protein. In a healthy grain, the activity of enzymes is small. Increased activity of enzymes is characteristic of defective grain.
Coloring grain due to presence pigments- chlorophyll and carotenoids.
Wheat is divided into six types of botanical features and character of culture (winter or spring); Types are divided into subtypes depending on the glassy and grain color. Type 1 - soft spring red.
Subtype 1 - dark red, vitreous, glassyness of at least 75%. Subtype 2 - red, glassyness at least 60%. Subtype 3 - light red, glassyness of at least 40%. Subtype 4 - yellow, glassyness less than 40%. Type 2 - Summer hard.
Subtype 1 - dark amber, glassyness of at least 70%. Subtype 2 - light amber, glassyness is not rationed. Type 3 - soft spring white.
Subtype 1 - white, glassyness is at least 60%. Subtype 2 - white, glassy glass is less than 60%. Type 4 - Soft Oshamis Mountain, is divided into four subtypes similar to wheat type 1.
Type 5 - Soft Wester Blue Corroser, not divided into subtypes. Type 6 - winter firm, it is not divided into subtypes. The division of types and subtypes does not give a complete idea of \u200b\u200bwheat quality, so the standard provides for the division of soft wheat into six classes, and solid - five. To the first three classes (the highest, first, second) soft wheat include wheat, which can be used not only independently for bakery, but also as an enriferry of weak wheat. Such wheat is called strong. The third-class wheat refers to the valuable, as it is used independently for the bread maker and does not require improvement. The fourth grade refers wheat, which should be improved strong and only after that can be used for bread accumulation. The fifth grade wheat is used as a fodder.
Rye. Ranked second in the production of bakery flour.
Grain of rye is narrow and long, therefore the share of the shells, alarium layer and the embryo more, and the endosperma is less. Compared to wheat in the grain of rye less proteins (by 1.7-2.0%), but they are more complete. In addition, rye proteins are able to firmly swell and form viscous colloidal solutions. Under normal conditions, gluten do not form, the launder prevents the mucus.
Grain rye divide, in quality to four classes. Rye of the first three classes (group A) is intended for recycling in flour; Fourth grade (group b) - for feed purposes. The basis of the division of rye into classes is the indicator of the "number of fall", which for food rye fluctuates from 200 to 80 s, and for rye, intended for feed purposes, is less than 80 s.
Family Zlaki. - One of the largest family of flowering plants, has about 10,000 species. For the most part, it is grass, but the stems of some tropical bamboo bamboo are decorated, reach 40 m of height and 20 cm in diameter.
The cereals play a huge role in the plant cover of the planet, these are the main bread and cereal cultures, and wheat, rice and corn - the main food plants of humanity. The value of rye, barley, oats, millet and sorghum is also great. In tropical countries, a sugar cane is widely cultivated, the juicy core of which contains up to 20% sugar. This culture gives more than half of the global sugar production. In a number of countries, young shoots of many cereals are widely eating, especially bamboo. Green mass of these plants - valuable pet food. The main feed plants of cereals: Mattik, Timofeevka, hedgehog team, oatmeal. The cereals are also used for the lawn device, the arrow of the airfields and the sports grounds, for fastening the sands, embankments. A series of cereals gives construction materials and raw materials for the production of paper (reed, bamboo).
Among the cereals there are malicious weeds: creeping powder, oatsi, bonfire rye. Almost all the cereals are pollinated by the wind, but there are also self-polls (wheat).
Corn
November 5, 1492 years, a few days after the opening of the new light, Columbus recorded: "I saw a cereal called Mais." And one of his satellites described Mais More: "There were any strange plants with a height of more than a meter in the fields. It seemed that they were from pure gold, and their leaves were from silver. " The ancient inhabitants of America grown by maize, or corn, more than 7 thousand years. She served them main food. She was worshiped as a sacred plant. Ancient Maya knew several varieties of corn: "Corn - an old woman", having matured half a year, "corn - a girl", having slept twice as fast, and a variety called "Peush's Song", which gave the fruits only two months after germination of seeds. Once in the old light, corn quickly "won" it (many times faster than potatoes). Corn grain contains up to 70% starch, 10-12% protein, 8% fat. The plant is heat-loving, so in the middle lane of Russia the fruits do not ripen it, and the corn here is grown only on the green mass for livestock (it is obtained up to 50 and even 100t with hectares). In every female inflorescences (cob) up to 1 thousand. Zenovok. More often there are varieties with yellow fruits, but there are varieties with red, blue and even almost black centers.
Wheat
Wheat man cultures more than 10 thousand years. But in different epochs, people grown different types of wheat (total wheat includes them around 20). Recall, for example, "a fairy tale about Pop and an employee of his Bald" A. S. Pushkin. Hiring a job, Balda says:
I will serve you nice
Diligently and very well
Per year for three closures to you on the forehead,
There is me let's boil the wool.
These lines remember many, but what is the shell, few people know. This is one of the most ancient cultural wheat. She was the main "bread" of the inhabitants of ancient Egypt and Mesopatamia. It was cooked delicious and nutritional porridge. The shepherd tolerates drought well, but low-yielding, the seeds should be released from the films. Therefore, in the twentieth century. The shell almost forgotten and practically they do not grow anywhere.
The ancient Egyptians were the first to add yeast to the dough. The ancient Greek historian Herodotus was surprised about this: "All people are afraid that food does not hesitate, and the Egyptians knead the dough so that it is subjected to rotting" (we would say to fermentation). At the same time, more magnificent, noworthy bread gives strong wheat varieties, in whose grains whose protein is more than 15%. Weak varieties are less than 11%. (And starch in wheat grain up to 75%.)
Sugarcane
Credit juice of sugar cane - Sakaru - in India they drank another 5 thousand years ago. In IV century BC. One of the commander of Alexander Macedonian wrote: "There is a reed in India, which without bees gives Honey." And at the beginning of our era, travelers in India have already tried the real sugar - "stone honey", "white and similar to salt, but very sweet." From the crusades, European knights were disappeared and sugar, and in 1163 one of them was presented by the King of France Louis VII a sugar head, which he kept as an expensive thing. Christopher Columbus, it turns out, not only brought many new plant species to Europe, but also the new light "presented" sugar cane. Here this plant found the second homeland. From the XVI century Sugar cane began to grow in Cuba and Haiti, using the cheap labor of African slaves. Now two thirds of sugar in the world is made from the cane. It is a powerful grace up to 6 m. Height. In the juice of its stems up to 26% sucrose. Switching the stem with one blow with heavy tone (in Spanish "Machete") so that it does not give a sweet juice. Grinding stems (Bagaso) are fuel for sugar factories. Make them and paper.
Below are the mains views gracious crops, Main types of grain. Mainly rice, corn, wheat, rye, oats, barley, sorghum, movies, flax seeds, shelves, buckwheat, shells and millet.
Grass cultures are one of the main groups of products needed for the body, and therefore one of the most important in the human diet. They belong to plants from the grain family, which are grown by grain and feed.
Grain has a structure with several elements. One of them is the embryo that is located in the core of the seed and allows you to develop a new plant. Another example is an endosperm, with a pulmonary or starch structure surrounding the embryo. The outer layer that lies on the grain is still a layer, much more hard, which ensures the protection of the head.
These products are also high water and carbohydrates.
Classification of grain crops
There are various types of cereals, but they can be divided first into three classes depending on their processing:
- Refined: These are the types of porridge for which bran and embryos were taken, which make it up. Because of this process, its texture becomes more subtle and their shelf life is much more. The problem is that this process removes a large amount of nutrients, especially fiber.
- Complex: This type of grain, which preserves its shell, that is, who do not remove bran, nor the embryos during grinding. For this reason, nutritional properties are preserved, such as fibers, potassium, selenium and magnesium.
- Enriched: We are talking about grain, in which artificial nutrients were added. However, they are no better than complex, because although some nutrients are added, lost fibers cannot be restored.
Types of cereals

This is one of the most famous grasses in the world and one of the most consumed. It grows on soils with water, which should be well polisted or located in the river delta.
It is very versatile food that has several varieties. Depending on the form, the long-grain short, medium or large can be classified. Color or aroma can be aromatic or pigmented. And in accordance with their industrial processing, there may be steady or heat-treated. It can also be whole or refined.
Rice is more grain starch. In addition, it contains carbohydrates and a small amount of thiamine, riboflavin and niacin. The overwhelming majority of rice species arose in Asia and is used in several ways: as a side dish, in stew, in salads and even for the production of oil and wine.

Corn is the most grown in the volume of cereals in the world. Its stem is usually very high, and the grains can be of different colors: from dark purple to (the most common) yellow. Most of the production of this food is done in America.
These are very universal grains that allow you to create various food products. Very nutritious, since rich in vitamin A and B, magnesium, phosphorus, antioxidants and carbohydrates. It is also useful for the body to help adjust the intestinal microflora and disease prevention as diabetes and heart problems. It can also be consumed by patients with celiac disease, as it contains gluten.

This is one of the most cultivated grain in the world, especially because it is used for a wide variety of products. Refined flour and coarse flour, for bran or beer, etc .. exists various varieties This grain, depending on its hardness, color, and even the season, in which it is grown.
Wheat is one of the most calorie deer, as it provides 339 calories per 100 grams. Contains carbohydrates and fats such as saturated, unsaturated and mononaturated. But this includes proteins, vitamins and minerals. Good for diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, dementia and female infertility.

Arriving in Iran, rye is part of the wheat family. The spike is long and thin. It is widely used for the production of alcoholic beverages, such as vodka, whiskey or brandy, as well as for the production of flour.
This croup can be prepared in the form of flakes or grinding in flour. This is food that has antioxidants, fiber and phenolic acids and is associated with the functioning of the digestive system. It is used for seedlings of vegetables, rice, stewed dishes and for different species of bread.
Oats

This is one of the most popular products. It is rich in the content of fiber, complex carbohydrates, trace elements, amino acids, vitamins (B1, B2 and vitamin E, etc.), as well as mineral substances (calcium, iron, magnesium and zinc).
This is an excellent ally to combat such diseases, as diabetes, provides energy and helps stabilize blood sugar levels. It also helps to control the high level of cholesterol and works as a natural diuretic.
Oatmeal Zlak, which is ideal for cold and moderate climatic conditions. Its color may be black, gray, beige or yellow, depending on whether refined or solid grain. Can be found on the entire market, in the form of flakes or muesli.
![]()
This is a grain, like wheat, which is also used to produce bread. Barley can be prepared in the form of flakes or grinding in flour. It differs from other sweet and nut flax products. Its culture is very universal, as it is suitable for any climate and can be of different colors: brown, light brown or purple.
The most popular use of this creek is the main ingredient in the preparation of beer and other alcoholic beverages. Also serves to prepare various dishes. It contains more protein than wheat gluten. On the other hand, it is one of the richest cereal fibers, antioxidants, vitamins and minerals.
![]()
This is a cereal that is intended not only for a person, but also for animal consumption. It originated in America, Asia and Europe, and also due to the fact that it is sustainable for drought and heat, can be grown in arid regions. Sorghum is widely used in the production of alcoholic beverages because it does not have gluten.
Soups are usually prepared from sorghum or used as additives. Sorghum has a wide variety, but differentiate colors can be classified as white and red sorghum beans.
On the other hand, it has high quality sugar, slow suction and low fat content. Proteins contained in it, not very good quality, but in combination with milk or vegetables, proteins of high biological value can be obtained for the body.

The swan is not so bread plantbut consumed as such. Compared to the majority of grain, this food contains more protein, fiber and fat, especially unsaturated. In addition, it is known for its contents of omega-3 and omega-6 acids, contains less carbohydrates.
As nutritious trace elements, the winch contains calcium, potassium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus and zinc and B-complex of vitamins and vitamin E. It has a low glycemic index and helps to control blood cholesterol. Usually eaten as rice, in salads, add to cutlets, pies, etc.

Appearance This plant is similar to wheat. It contains a large amount of bran, but is lost when processing grain. The shell has an elastic structure that makes it ideal for cooking and bread. This composition of cereals whose water is about 10%.
Like other grain crops, the shelter is rich in vitamins A, B, C and E, and also contains mineral salts, such as calcium, potassium, iron, magnesium and phosphorus. In addition, it contains polyunsaturated fatty acids, protein and insoluble fibers.
Thanks to its properties, there is a lining function that plays, helps prevent constipation, diabetes and other diseases, such as hypercholesterolemia and colon cancer.
Flax-seed

Flax seeds, like a winch, not quite grace, but used as such. They are seeds rich in fiber, weak estrogen, omega 3 and omega-6 fatty acids, vitamins and minerals. In addition, they contain digestive enzymes that not only facilitate digestion, but also conducive to intestinal transit.
These seeds are highly recommended in diets to lose weight and reduce cholesterol and prevent constipation problems. In use grind seeds, include in homemade bread, pies and buns. They can also be mixed in fruit juices, yogurts, salads, sauces, soups, etc.
Buckwheat

It is recommended as a healthy replacement of ordinary wheat, as it does not contain gluten and richer by proteins, minerals and antioxidants than other grain crops. Often it is used in the form of grain, or flakes, flour.
Due to its important content of fiber, helps to control blood sugar levels. It also helps to improve heart health, good for circulation and reduces the risk of developing colon cancer.

This wheat variety was widely used in antiquity. His origin in Iran, Egypt and even in China, where it was used for the manufacture of beer and alcoholic beverages.
Gradually, its use has spread to Europe and is used in the manufacture of bread for the highest classes.
Spells is one of the best sources of plant protein and when used in an amount and with a corresponding combination, ultimately can replace red meat. This solid grain contains proteins with a high tissue content and low fat content. In addition, it does not contain cholesterol and provides vitamins and minerals.

This is one of the oldest grains. This is a sheltering food, which also remine the body. It is usually regularly consumed in the east and grain able to withstand sudden temperature differences. It grows rapidly, requires some water and has high resistance to pests.
The millet is easily absorbed and suitable for people with celiac disease, because it does not contain gluten. It is rich in fiber, magnesium, phosphorus, fatty acids, iron and group vitamins in
Thanks to all these properties, ideal for those who suffer from problems with digestion, as constipation, heartburn, ulcer, gas, diarrhea, etc. Consumption is also recommended in cases of diabetes, iron deficiency anemia, stress stage, depletion, pregnancy and lactation period.
The best types of cereals
Today, most cereals that can be bought in the market is a refined view. However, since almost all fiber and other nutrients are removed in their processing process, the most recommended are solid.
The cereals, in general, give energy, complex (good) carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and fiber; All necessary elements for balanced nutrition.
Grain of grain crops.
The main grainiferous cultures are corn, barley, oats, wheat, rye, millet, sorghum. About two thirds of grain mass falls on starch, which is digested by 95%. The high concentration of light-alternate carbohydrates provides high energy nutrition of grain grain - from 0.91 to 1.28 MJ of exchange energy (CRS) in 1 kg. In grain grain crops, there are on average about 120 g of crude protein in 1 kg, including about 75% digestible (Table 79).
79. Chemical composition, digestibility and nutrition of grain feed (by A.I. Devyatkin)
Continuation of table. 79.
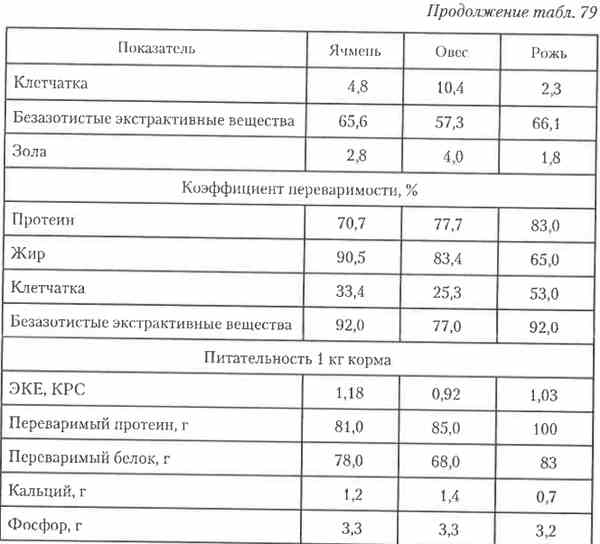
Protein grain grain consists on average 85-90% of proteins and has a relatively low biological value. In all the feeds of this type of raw materials, the limitating amino acid is lysine.
Of grass grain Corn is the poorest protein, as well as lysine and tryptophan (Table 80).
Grain of grain crops contains from 2 to 5% of raw fat. The smallest fat content in the grain of wheat and rye, and the greatest - in oats.
On average, the grains of cereals contain about 6% crude fiber, but in separate species Grain This indicator varies greatly (from 2.2% in corn up to 10% in OVE).
All cereal cereals contain a rather large number of group vitamins in and especially much - vitamin E (135 mg / kg). At the same time, in most grains of cereals, very little carotene, and only in the grains of yellow corn, the level of carotene reaches 5 mg in 1 kg.

Of all the types of grain of grain crops, barley, corn, oats and wheat have the greatest use in animal husbandry.
Barley is an excellent dietary feed for animals of all kinds and age groups. The barley in pig breeding is especially appreciated, since when feeding it in combination with other feeds, meat and high-quality fat are obtained. When feeding milk cows with a barley or flour, milk and good quality oil receive. Barley protein is characterized by moderate solubility (45-50%) and satisfactory amino acid composition. The barley contains about 6% of the fiber, so when using it for young, part of the grain should be released from the film or feed in a mixture with wheat and corn. In the feed bark, it is desirable to include up to 30-40%.
Corn as an energy source exceeds all grain feed (12.2-12.8 MJ of exchange energy in 1 kg), but differs from them the smallest content of raw protein.
Corn grains contain 9-10% protein, 4% fat, about 70% - starch and 2-3% of fiber. Comparatively low solubility of protein (25-30%) makes corn valuable component of feed for ruminant animals.
Oats is a valuable dietary product, which is used mainly for the preparation of animal feed feed, breeding animals, dairy cows and a bird (25-30% of the mass feed).
In the grain of oats, there is a 10-p% of crude protein, up to 5% fat, about 9% - fiber and over 50% starch. OPS protein is characterized by high solubility (55-60%). The dietary properties of oats are determined by fine-grained starch and polyunsaturated fatty acids that are well absorbed by animals.
A good oats film make up not more than 30% of the grain mass. When you enter into a feed for young people, Oats are released from films.
In the rations for the refillable pigs, turn on oats in large quantities is not recommended, since the fat becomes stitching.
Wheat, compared with the grain of other cereals, is characterized by a higher protein content (up to 15%) and has satisfactory taste.
Wheat protein is characterized by a sufficiently high solubility (about 50%) and on the amino acid composition close to the probe barley and oats.
In wheat, there is a fairly high content of gluten. It must be taken into account, since when the wheat feeding is in large quantities, it turns into the stomach into the adhesive mass and leads to a violation of the processes of digestion.
Wheat is advisable to use in the composition of animal feed in the mixture with other types of grain for all animal species in an amount of from 30 to 50% by weight.