Windows 7 virtual memory for games. Paging file
The swap file or swap file (from the original swap-file) is a hidden virtual memory file.
It is used by the system in case of insufficient physical RAM (aka RAM).
For example, a running application runs out of memory installed by RAM. Then the swap file is used.
The application can write its data to it, as well as read them if necessary.
The virtual storage is located on the hard disk of the computer.
With insufficient physical RAM, the swap is forced to be used constantly.
At the same time, the process of exchanging data with takes a long time, because of this, performance is significantly lost.
If you are running low on RAM and the system is constantly using the paging file as additional storage, buy extra.
If there is no more place (slot) for its installation, purchase one strip, but with an increased volume.
The device will work more efficiently.
Optimal paging file size
There are different sizes and ratios of physical and virtual memory.
For acceptable performance the minimum size of the paging file must be equal to the size of the RAM.
The maximum allowable value is twice that.
For example, your computer has 2 GB of physical memory, which means that the RAM should be 2 GB or 4 GB, respectively.
It is best to set the same values and make it static.
In this case, the system file is less fragmented.
Why was it done? It's simple.
This reduces the overall load on the system and therefore increases productivity.
Is it possible to improve performance if the swap remains dynamic? Of course.
To do this, you just need to start cleaning the file after the operating system is shut down. Below we will show you how to do this.
Swap file cleanup
To clear the paging file, you need to write the command in the command line secpol.msc.
To do this, open Start→ in the command line, enter secpol.msc→ press Enter.
After all the manipulations, the local security policy should open in front of us.

Click on it with the left mouse button. Additional items will open, as in the screenshot:
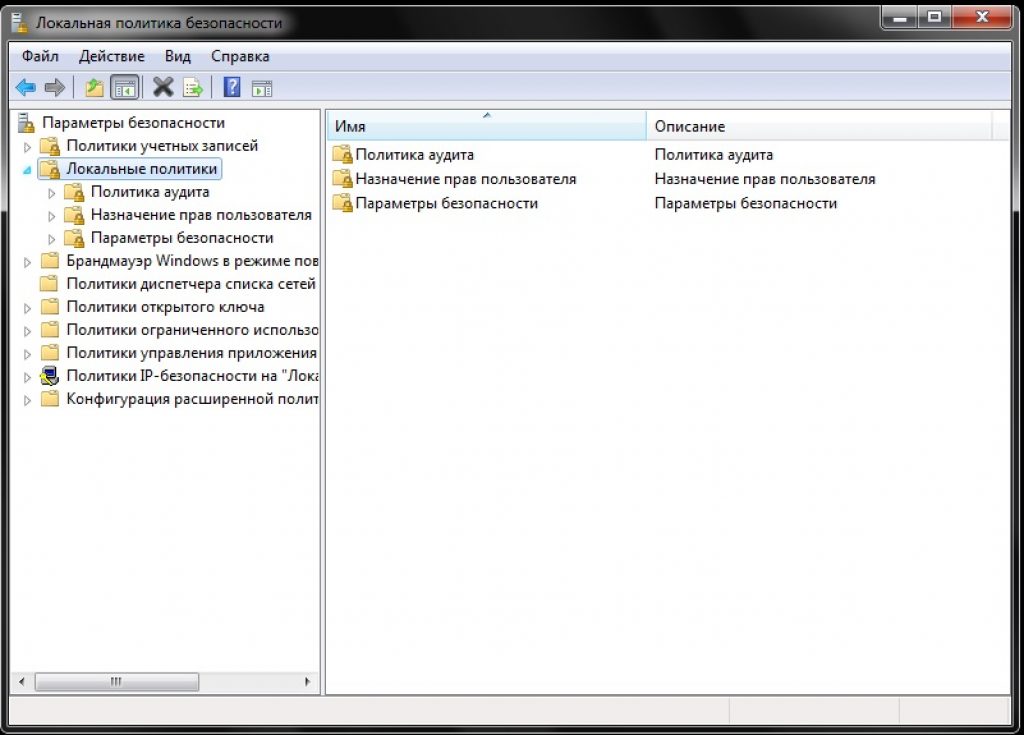
From the menu that appears, select "Security Options" and press the same with the left button.
If everything is done correctly, then you will see a list of tasks.
Looking for a line Shutting Down: Clearing the Virtual Memory Paging File.
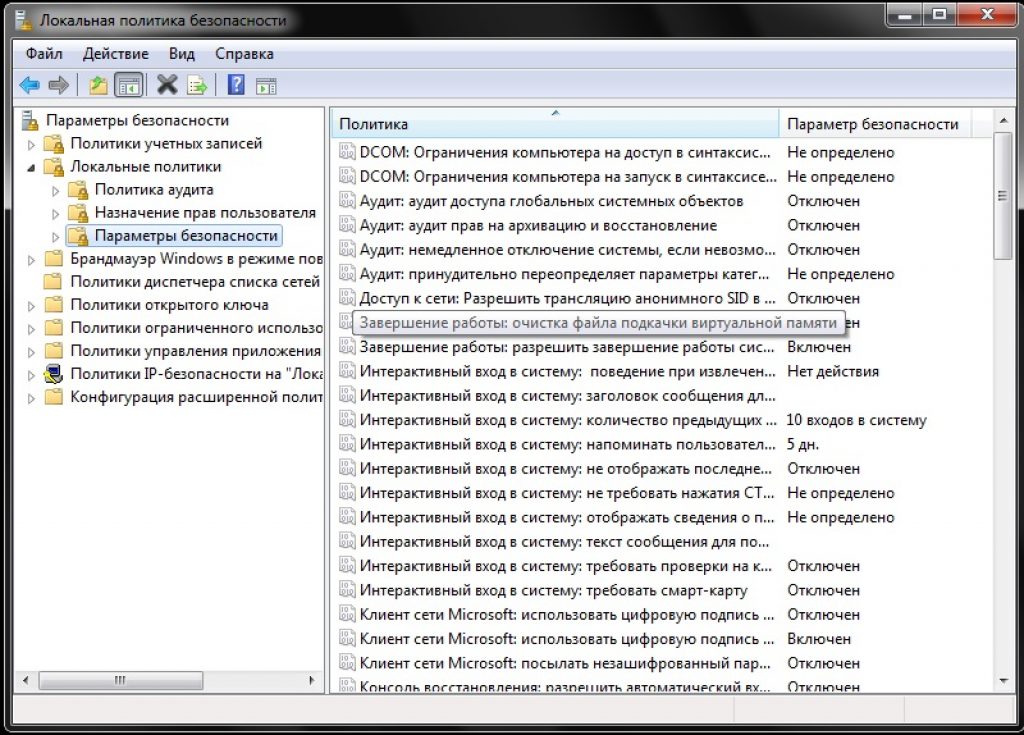
Open it with a double click.
Changing the status "Disabled" on "Switched on" and click Apply.

From this moment, the changes you made take effect.
After these steps, the swap will be on each shutdown of the computer.
It took only five minutes of time, and the performance has already improved.
Choosing a file location
The shutdown function is also available for any user.
This is a justified action if you do not want to lose performance, and the size of physical RAM is enough for you.
Swapping takes a lot of time, and for some users it is much easier to insert additional strips of RAM.
Additional ramps expanding RAM are guaranteed to speed up your work and will increase productivity at times.At the moment, you can find the necessary components at fairly low prices, which will not hit your wallet at all.This is especially true for relatively weak computers.
Disable the paging file as follows:
In the virtual memory section (how to go to it is indicated above), put a checkmark in front of the inscription "Without swap file" .
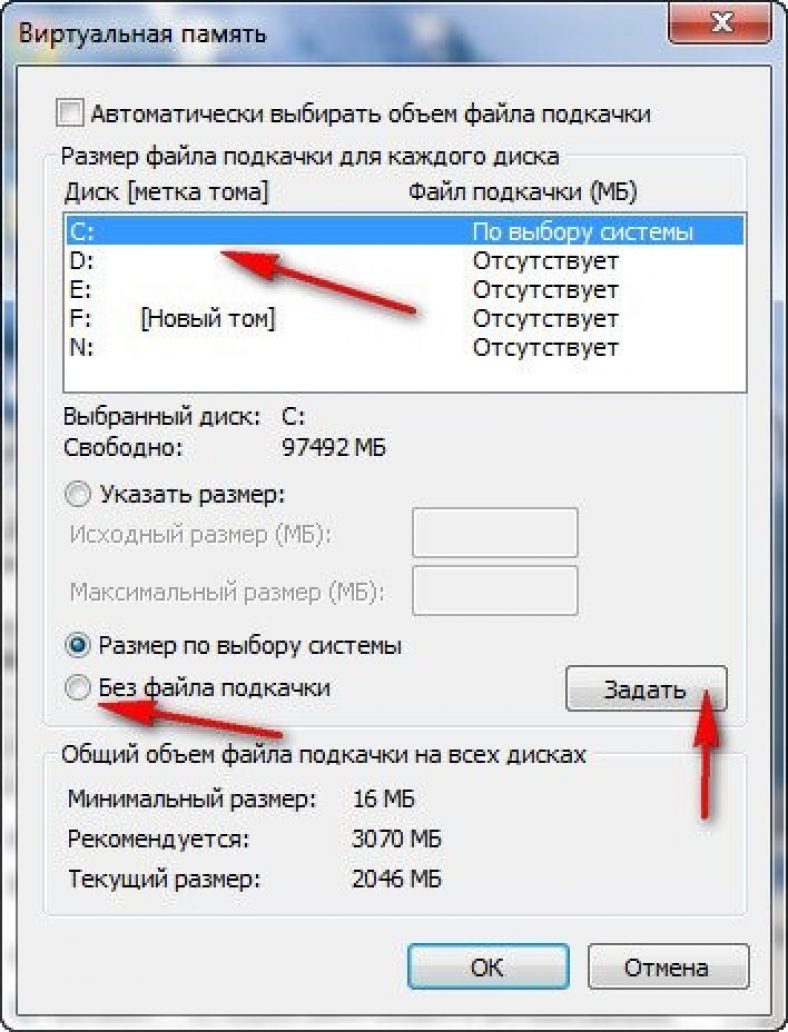
You can enable the hidden virtual memory we need in the same section.
To do this, uncheck the box "Without swap file" and put it opposite "Size at the choice of the system" .
Optionally, you can set your own values by activating the field "Specify size" .
What values will be optimal for you is described above.
Windows - Swap file
Optimizing the paging file on one hard drive
Microsoft made the swap file dynamic by default, and we have found that the best performance is obtained with a static file.
If you have two or more hard drives, then transfer the paging file to any other than the system one.
But what if there is only one hard drive? This method is suitable for just such cases.
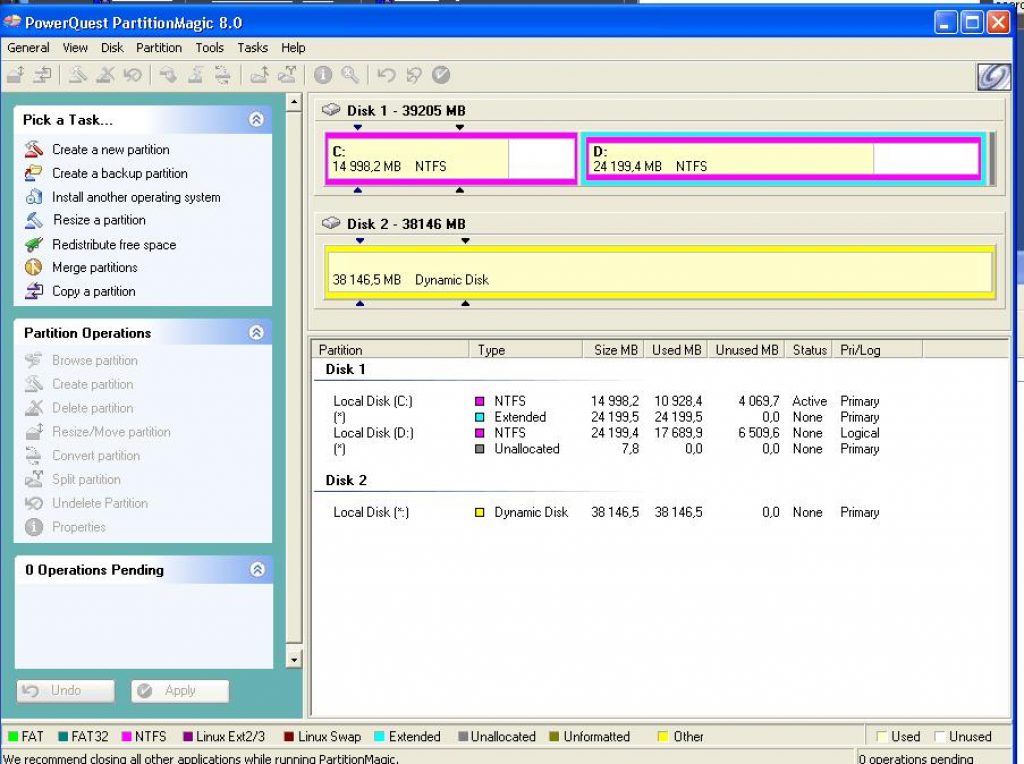
First, you need to "split" the hard disk by creating an additional 2-3GB partition on it.
To do this, you can use special programs such as PartitionMagic (PowerQuest Corporation), which allow you to partition the disk without losing data.
You can, of course, use the built-in Windows program for - Fdisk, but it has many disadvantages.
Including a rather complex interface, so it will not be easy for beginners.
Our advice is to use the fast and relatively handy PartitionMagic (PowerQuest Corporation).
We just follow the specified algorithm. Download and install the program.
We open it.
In the upper right corner, click the left one and select the desired disk (in this case, there is only one).
By requesting "windows paging file" in any search engine, you can get a thousand or two copied from each other, or slightly different answers on choosing the optimal sizes for pagefile.sys.
The most common advice looks something like this: for machines with low RAM, you need to set the paging file size k * RAM, where RAM is the amount of physical memory, k is some factor, of which there are many very different. And 1.5, and 2, and even 3 met. If there are 4GB or more of memory sticks, then “feel free to disable virtual memory in principle”.
An article on whether to believe these tips, and if so, how much.
What is a paging file?
pagefile.sys, it is also a paging file - a file that is a virtual memory that allows a large number of processes to run simultaneously, which all at once could not fit in physical memory.By default, after installing Windows, the paging file grows automatically when the current space is full.
If you disable the paging file
If you try to disable the paging file in windows 7, the system will display a warning window, which will inform you of unpleasant consequences:It follows from this that you should not completely abandon the use of virtual memory, otherwise, in the event of a crash, it will not even be possible to analyze the cause of the failure. The minimum size of 1MB indicated in the screenshot is taken from the calculation of the memory dump configuration in the "load and restore" settings: 
If you select a full dump for writing debug information, then the size increases by several orders of magnitude. It was 400MB for me.
In addition to the inability to write a dump, after disabling the paging file, an annoying message about insufficient memory may appear. Its appearance will be accompanied by terrible brakes of resource-intensive applications.
If you move the paging file to another partition
A bunch of articles on optimizing your OS recommends transferring the paging file to a separately created and formatted in FAT32 hard disk partition. This improves performance and reduces the fragmentation of this file.With such manipulations, do not forget that the swap file must be present in the system partition for the correct recording of debug information. You have to choose between speed and the ability to collect data about the troubles that have arisen.
Swap file size
Let's return to our oranges to the question of the optimal size. After digging through many articles, information publications, and even Microsoft's recommendations, I still have not found a clear and unambiguous answer to this question. And I would not have found it, as it became clear to me after reading the translation of Mark Russinovich's article Breaking Windows Limits: Virtual Memory ... In conclusion, I will give links to the translation and the original, and now I will try to explain where to get the file size from.To get started, you need the Process Explorer utility, it is a free analogue of the default Task Manager "a, but it has many advantages. You can download it here.
After starting Process Explorer "a, select the most memory-intensive applications that you use in everyday life, and start them all at the same time. In the Process Explorer" window, press CTRL + I or select View / System Information from the menu, from the variety of presented in the data window, select the Commit Charge area 
Peak is the peak value of allocated memory for all applications, summed up of physical and virtual memory.
Next, we arm ourselves with a calculator and subtract the size of RAM from this value. If a negative value is obtained, we take the 400MB required by the system (there may be a different value) required to create a dump. If a positive value is obtained, we set the minimum and maximum values of the paging file to this. You can play it safe and set the maximum "in reserve" higher, but then the fragmentation of the file will increase if its size increases. Therefore, it is better to fix it in one place.
In cases where the computer does not have enough RAM, the Windows 7 paging file is used. You will find out where this file is located by reading the article. In addition, by following the advice of experienced users, you can determine the optimal size of the swap file required for correct operation of the OS.
In some cases, this file is generally not recommended to use, as this will affect the computer's performance. Therefore, the paging file is sometimes disabled. But first things first.
What is a paging file for?
There are situations when there is not enough RAM (physical memory). For example, you want to install a game that requires 4 GB of "RAM", but you only have 3 GB on your computer. In this case, the OS uses virtual memory, that is, the paging file (hereinafter FP).
It should be noted that today the cost of RAM is not very high, so it is better to purchase and install several strips of physical memory, since the virtual one is located on the hard disk and takes longer to read.

As a result, your computer will "slow down". In addition, due to such loads, the HDD or SDD will shrink.
However, if you configure the FP correctly, then it will not increase, "eating up" free space on the hard drive, besides, the fragmentation of the hard disk will significantly decrease.
By the way, the paging file in Windows XP7 can be transferred from the C (system) drive to another drive, although some users advise against doing this.
Where is the swap file located?
It is located in one of the sections of the hard drive and is called pagefile.sys. This is why, if you want to see it, you will need to activate the visibility and files.

Click "Start" and open PU. Go to the "Folder Options" section, and then to the "View" tab. Scroll down the slider and set the checkbox opposite the "Show hidden files" function. Now click "Apply".
Now you can find the Windows 7 paging file. You already know where it is (the system disk partition). But it will not work directly with him. However, there is another way.
Deactivating the paging file
If you have a sufficient amount of "RAM" installed on your computer, then most likely you will want to deactivate the paging file in Windows 7. To do this, you need to right-click on the "My Computer" icon and select "Properties". There is another way - the "Start" menu, then enter the PU and open the "System" section.
On the left there is a menu where you will need "Additional system parameters". Here you are interested in the "Advanced" tab, the "Performance" subsection. Click on "Options" and select "Advanced" again. Click "Change" and in the window that opens, uncheck the box next to the option to automatically select the paging file. Check the "No swap file" option and confirm the settings by clicking "OK". Restart your OS.

So, you have learned where in Windows 7 the paging file is located and how to deactivate it.
Setting up a swap file
For the laptop or computer to work correctly, you need to properly configure the swap file. First of all, you need to know how much space to allocate for the Windows 7 paging file. You remember where it is located, so you can change its value yourself. Open the "Virtual Memory" section again and click "Specify Size".

Note: the maximum volume of the VP should be approximately 2 times the volume of the "RAM". It is better to set the original size the same as the maximum. Alternatively, specify the value that is indicated opposite the "Recommended" item.
Another important point is transferring the swap file from the disk on which you have the OS installed to another hard drive, which will increase the performance.
Now that you know what the paging file is for, the optimization should be straightforward.
- It was already mentioned above that it is better when virtual memory does not take up space on the system hard drive, since it is already loaded. A separate hard drive is ideal.
- If possible, install additional RAM strips so as not to use virtual memory. As a result, the operating speed of the OS will increase. For the "seven" 6 GB of physical memory is quite enough, which will not greatly shake your financial position.
- Set your own size for the swap file, as the system is constantly increasing it. This is the reason for the fragmentation of the hard drive. It is recommended that you set the same value for the maximum and initial amount of virtual memory.
By the way, the minimum FP size should not be less than 1 GB to prevent HDD fragmentation.
Conclusion
So, now you understand why you need a Windows 7 swap file, where it is located and how to configure it correctly. Of course, it would be better not to use a swap file at all, especially since now physical memory is not that expensive. However, if you have an old computer, which does not have additional slots for RAM brackets, then the use of a swap file in most cases is a necessity, since modern games and programs use a lot of "RAM".

As for optimization, then you can independently make all the settings, while following the recommendations of experienced people. It's not that difficult, so you won't have any difficulties. When communicating with experienced users, ask questions, and you will definitely get answers to them.
To increase the amount of available RAM, the computer uses virtual memory by writing a specific amount of RAM data (for example, 1834 MB) to the hard disk, in the paging file. Further, the system can access this data as needed.
RAM(English Random Access Memory, random access memory; computer jarg. Memory, RAM) - a volatile part of the computer memory system, which temporarily stores data and commands necessary for the processor to perform operations.
Windows 7 writes paging files to hard drives in the pagefile.sys format.
The initial paging file is automatically created for the drive on which the operating system is installed. By default, there are no paging files on other drives, but you can create them manually. However, in most cases this will not be necessary because placing paging files on multiple disks does not necessarily improve performance.
In Windows 7, automatic virtual memory management works much better than in previous versions. Typically, Windows 7 allocates an amount of virtual memory equal to the amount of RAM on your computer. This prevents fragmentation of the paging files, which would degrade performance.
Data fragmentation - a process in which a file, when written to a disk, is divided into blocks of different lengths, which are written to different areas of the hard disk. The opposite process is defragmentation.
Some parameters can be manually adjusted. You will most likely want to limit the amount of virtual memory. To do this, you can set the initial and maximum size of the paging file, which will also help to avoid fragmentation.
In most cases, the optimal paging file size will be twice the size of the system's RAM. For example, for a computer with 1024 MB of RAM, it is better to have at least 2048 MB of paging files on all disks.
However, if your computer has more than 4 GB of RAM, you can set the paging file size so that it is one and a half times larger than the RAM. For example, for a computer with 6144 MB of RAM, it is better that the Total paging files on all disks be at least 9216 MB.
For optimal performance, the minimum paging file size should be equal to the amount of RAM, and the maximum size should be equal to the amount of RAM multiplied by a number between 1.5 and 2. The advantage of limiting the size of the paging file is that the system initially allocates a certain amount of this memory and does not should increase it as the user launches programs.
To configure virtual memory settings, follow these steps:
1. Click on the Start menu button and select Control Panel.

Start Menu - Control Panel

3. Open the System window. At the bottom left side, click the Performance Counters and Tools link.

System Window - Performance Counters and Tools


5. On the Advanced tab, click the Change ... button, and the Virtual Memory dialog box appears with the following information.

Change button ...
- Disk [volume label] and paging file (MB). Shows the current virtual memory configuration. The dialog box lists all volumes with associated paging files (if any). For paging files, the original and maximum sizes are given.
- The paging file size for each disk. Shows information about the selected disk (in particular, the amount of free space) and allows you to change the size of the paging file on it.
- The total size of the paging file on all drives. Shows the recommended amount of virtual memory and the amount of virtual memory currently allocated.

6. By default, Windows itself determines the size of the paging files. If you want to set this parameter manually, clear the Automatically select paging file size check box.

7. From the Disk list, select the volume to configure.

8. Select Specify Size, then enter the original and maximum dimensions.


10. Repeat steps 6-8 to configure all volumes.
11. Click the OK button. If the system prompts you to overwrite the existing pagefile.sys file, click the Yes button.
12. If you have changed the settings of the paging file that is currently in use, you will see a message that you need to restart your computer for the changes to take effect. Click the OK button.

13. Click the OK button twice to close all dialog boxes. The system will prompt you to restart Windows. Click the Restart Now button.
To have the computer set everything up automatically, follow these steps:
2. Open the System window. At the bottom left side, click the Performance Counters and Tools link.
4. On the Advanced tab, click the Change ... button and the Virtual Memory dialog box appears.
5. Select the Automatically select paging file size check box.

6. Click the OK button twice to close all dialog boxes.
Virtual memory partially improves system performance because virtual memory frees up main memory to store only actively used applications.
Active areas of memory are stored in RAM, while less active areas are moved to virtual memory and stored on one of the hard disk partitions. Accessing virtual memory always causes latency, and visually it looks like the system thinks for a few seconds.
If your RAM does not exceed 2 GB, and you regularly notice such phenomena, then perhaps there is not enough RAM for all applications and services running on your computer.
How do you know if your PC is running at the limit of RAM?
To do this, display a gadget on the Desktop that displays the load of RAM and processor. To do this, do the following:
1. Place the mouse pointer on the Desktop in an empty space and click on the right mouse button. Select Gadgets from the context menu.

Context Menu - Gadgets
2. In the window that appears, select the CPU Indicator gadget.

3. Close this window.
The desktop will display a CPU load indicator and the amount of RAM used.

Page file (pagefile.sys) is a hidden file on the hard disk of a computer that is used by the Windows operating system on the principle of random access memory. The paging file and RAM together make up virtual memory. By default, the Windows operating system stores the paging file in the boot partition (the partition where the operating system and support files are installed). Usually the size of the paging file is set at 1.5 times the total amount of RAM.
The paging file is necessary in order to offload the RAM during periods of high load. If you run several applications at the same time that heavily load RAM, then some of these applications will be inactive (they will be minimized or simply will not be used at the moment) and, as a result, their data will be unloaded to a less fast area, i.e. in paging file, and the data of the currently active applications will be located directly in RAM. When an inactive application is accessed, the data from the paging file will be moved directly into RAM to speed up its operation. In case of an acute shortage of RAM in the system, the paging file is used directly, that is, the data of active applications is also dumped into it. If the total size of virtual memory is too small, some applications may become unstable, and the operating system may display a message that there is not enough virtual memory. In such situations, the size of the paging file must be increased.
If your computer has more than one hard drive, to improve system performance, the paging file should be moved to a different partition on a different hard disk. In this case, the operating system will process multiple I / O requests faster.
If your computer has one hard drive, it is also recommended to move the paging file to a different partition on the hard drive. When the paging file is located on the boot partition, the Windows operating system directs read from disk and write to disk requests to both the system folder and the paging file. By moving the paging file to a different partition, the contention between read and write requests decreases.
If your computer has both HDD and SSD drives, then it is recommended to place the paging file on one of the partitions of the HDD-drive. This will reduce the number of read / write requests, which in turn can have a beneficial effect on the fault tolerance of the SSD.
To avoid fragmentation of the paging file, it is recommended to create a separate partition on the hard disk, in which only the paging file will be located. Using a separate partition for the paging file has the following advantage: in this case, the file is not split into chunks. A paging file located in a partition containing other data can be split into fragments as it grows to increase the size of virtual memory. A defragmented paging file allows faster access to virtual memory.
On computers with 8 GB or more of RAM, the use of the paging file can be disabled - this can significantly increase the performance of the computer.