Melting point of different metals. Under what conditions copper melts
With a problem, how to melt copper at home, many owners face. Some want to cast out copper products, others have accumulated copper scrap, which takes a lot of space, and sorry to throw it. Those who believe that this is a complex process and melted copper at home will not work, you can calm down. Ancient people knew how to do this in a few centuries BC, without having any special devices for this.
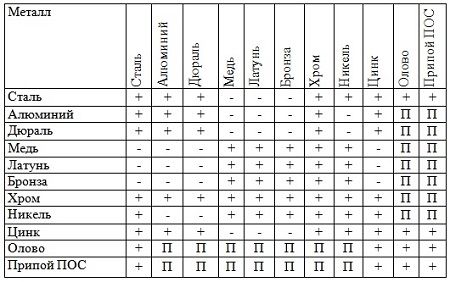
Among the metals that have been widespread in industry, this is the average. Tin, lead, magnesium, zinc, aluminum have significantly smaller and gold it is equal to 960 ° C and 1063 ° C, respectively. In the iron, the melting point is equal to 1539 ° C. Therefore, copper, silver and gold can be melted in iron dishes. Adding tin, lead and zinc makes it possible to significantly reduce the melting point of copper, but at the same time it is not clean - bronze and brass.
Before the start of melting, it is necessary to prepare:
- steel tongs
- hook for collecting an oxide film from the surface of the melt,
- fill shape.
The hook can be made of steel wire. The form can serve as any steel container, you can prepare a deepening in the ground, as our ancestors did. For art casting, a special form will be required.
Melting in a muffle
- Household muffle furnaces can be purchased in specialized stores. Modern furnaces are equipped with temperature controllers and a viewing window, can be vertical or horizontal loading. The furnace of medium quality is able to maintain temperatures up to 2000 ° C, and professional - up to 3000 ° C. It is possible to melt not only copper, but also iron. But it should be taken into account that at a temperature of 2560 ° C, the copper melt begins to boil. After cooling, the ingot will have a porous surface, which contributes to rapid oxidation and destruction. Such an ingot has a non-primary look, it is deprived of the characteristic copper glitter.
- Regardless of the melting method, the copper scrap should be crushed. This will reduce the process time and will guarantee that the melt will be homogeneous.
- The crushed copper scrap is falling asleep into the crucible, the crucible is placed in a muffle furnace, preheated above 1083 ° C.
- After making sure that the copper was melted, the crucible tigel was removed from the furnace and the crochet remove an oxide film, which is always formed on the surface of the melt. After that, the melt should immediately pour into the form.
It is not worth purchasing an expensive muffle furnace for one mowel. Copper can be melted in other ways.
Melting with homemade fixtures
You can melt copper using a gas burner
Some car enthusiasts in garages have homemade mines, with which metal can be melted. If the mountain could not be found, you can do it with my own hands.
- On Earth, the supports, such as silicate bricks, are placed on them with a steel grid with small cells.
- A layer of charcoal is poured onto the grid and set fire to it. To get a high temperature, you need to increase the influx of air. The easiest way to do with a vacuum cleaner working « to blow out, "sending the jet of the air to the place of burning coal.
- It remains to put a crucible to burning corners and wait when copper melts. The melt is in contact with atmospheric oxygen, so an oxide film is actively formed, which is constantly being removed. You can spray the surface of the melt with small coals or ashes from them. A slag is formed, which is then easily separated.
Copper alloys bronze and brass can be melted using a gas burner of autogenous welding or soldering lamp with a nozzle for turning the flame. The flame must heat the crucible evenly below.
Copper blanks
Today, copper is one of the most sought-after metals. High demand is explained by the distinctive characteristics inherent in this metal. Copper conducts electrotes better than any other metals, except for silver, due to this, it is used in the production of cables and electrical conductors. The melting point of copper is not high, the metal plastic and easily processing, due to this quality it has become possible its use in construction as a water pipe. This metal has high resistance to external annoying factors, therefore durable and can be used several times after mirroring. This copper quality is highly appreciated by environmentalists, since during re-processing the metal is spent a much smaller amount of energy than in the mining and processing of ore, it is also preserved earthly subsoil. The mining of copper ore does not pass without a trace, on the site of the spent mines there are toxic lakes, the most famous worldwide such a lake - Berkley-Pete in Montana in the United States.
Required temperature for melting copper
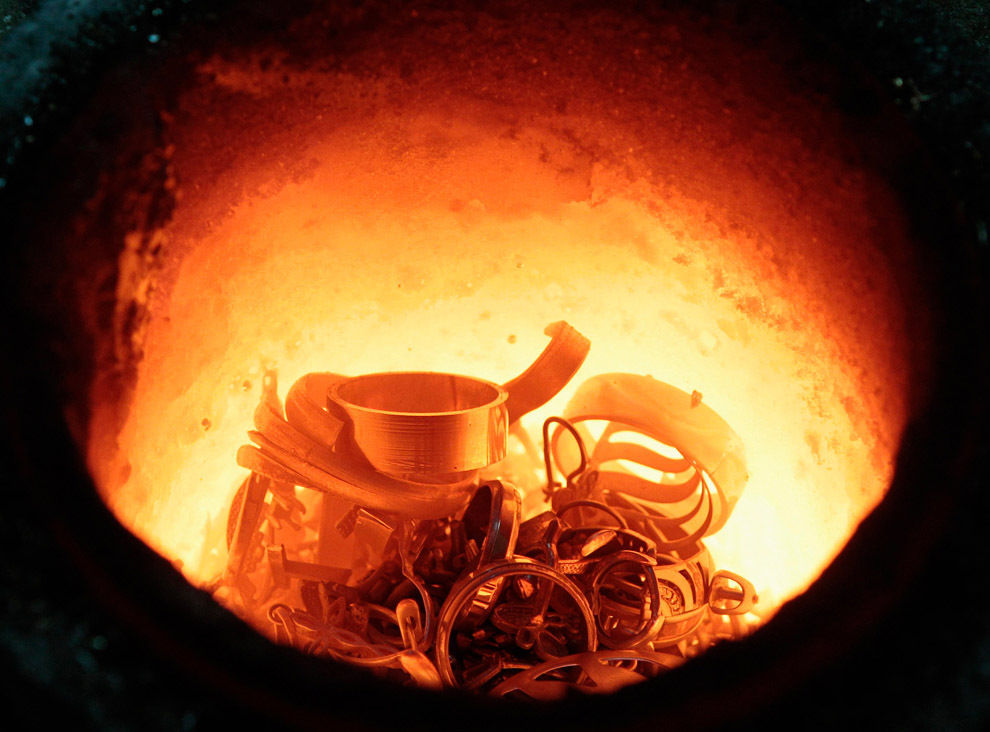

Copper is not a low-melting metal
People found the use of copper in ancient times, then it was mined in the form of nuggets. Due to the low temperature necessary for the implementation of the melting process, it began to be widely used for the manufacture of workers and hunting, nuggets can be melted at the fire. Nowadays, the technology of producing metal is not much different from the ovens invented in ancient times, only the furnaces are improved, the firing rate and the volume of processing are increased. Here arises the appropriate question - what is the melting point of copper? The answer to it can be found in any textbook on physics and chemistry - copper begins to melt at the heating temperature to 1083 o C.
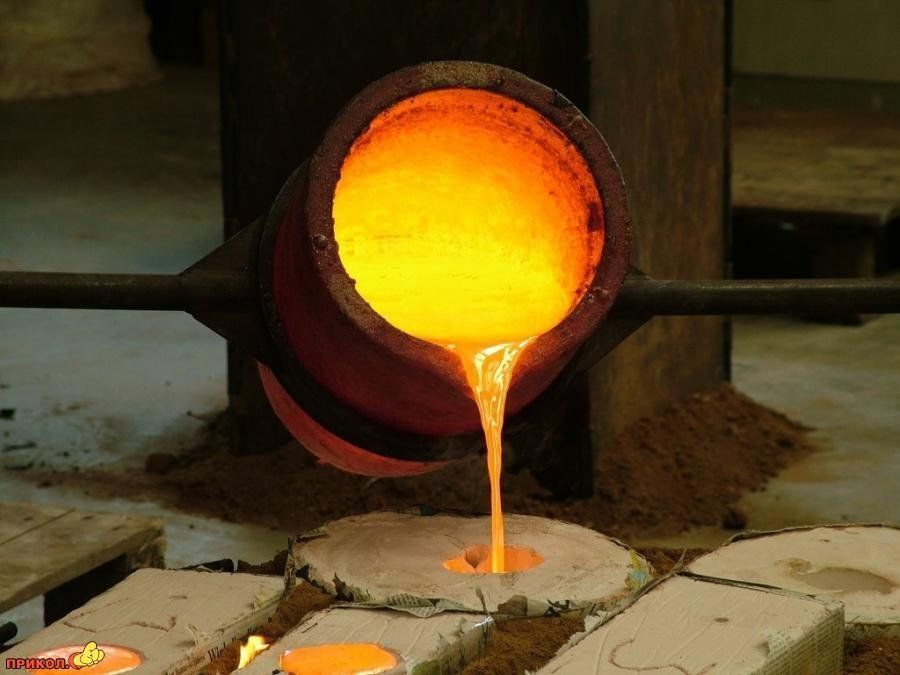

Copper boiling reduces its strength
In the process of thermal exposure to the metal, its crystal lattice is destroyed, this is achieved at a certain temperature, which for some time remains constant. At this moment, the metal melt occurs. When the process of the destruction of the crystals is fully completed, the metal temperature begins to rise again, and it goes into a liquid shape and begins to boil. The melting point of copper is significantly lower than that at which the metal boils. The boiling process begins with the appearance of bubbles, by analogy with water. At this stage, any metal, including copper, begins to lose its characteristics, is mainly reflected on the strength and elasticity. The boiling point of the copper is 2560 o C. During the cooling of the metal, a similar picture occurs, as when heated - first, the temperature drops to a certain degree, at this moment there is a hardening that lasts for a while, then the cooling of the conventional state continues.
How the metal changes under thermal exposure
Any heating of copper entails a change in its characteristics, the most significant is the magnitude of its resistivity. Copper is an electric current conductor, and the metal has resistance to the movement of charge carriers. The ratio of the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe conductor to the movement rendered and is called specific resistance.

So, this value for pure copper is 0.0172 Ohm mm 2 / m at 20 o C. This indicator may change after heat treatment, as well as due to the addition of various impurities and additives. Here there is an inverse dependence of copper resistance on temperature - the higher there was a metal processing temperature, the lower its resistance electric Toku.. To ensure the best electrolytic characteristics of the copper wire, it is treated at 500 o C.
During heat treatment, you can not only give metal the necessary shape and size, but also create different alloys. The most common copper alloys is bronze and brass. Bronze is obtained by mixing copper with tin, and brass with zinc. Adding aluminum and steel increases the strength of the material, and the addition of nickel increases the anti-corrosion properties. But it is worth noting that any admixture reduces the main property - electrical conductivity, therefore, it is used for the manufacture of an electric cable, a clean composition of the metal is used.
Annealing medal
Under the annealing of copper, it is necessary to understand the process of its heating in order to further process and attach the necessary forms of the product. During annealing, the metal becomes more plastic and soft, perceived by various transformations. When annealing copper, the temperature reaches 550 ° C, it acquires a dark red shade. After heating, it is advisable to quickly produce forging and change the product for cooling.

If the material is slow, natural cooling, then the formation of a latch is possible, so the instantaneous cooling is used more often by placing the workpiece in cold water. If you exceed the permissible amount of heating, the metal can become more fragile and brittle.
During annealing, the recrystallization of copper is carried out, during which new grains or metal crystals are formed, which are not distorted with the grid and are separated from the previous grains with angular boundaries. New grains in size can be very different from their predecessors, with their formation is released a large amount of energy, the density increases and appears. Recrystallization is carried out only after the deformation of the product, and only after reaching it a certain level. For copper, the critical level of deformation is 5%, if it does not reach the process of forming new grains will not begin. The recrystallization temperature of the copper is 270 ° C. It should be noted that at this temperature the growth process of crystals is only beginning, but it is quite slow, so it is enough to heat up to 500 ° C to achieve the desired result of copper, then there is enough time for cooling to complete the recrystallization process.
Video: Melting copper in the microwave
Content:
Each metal has the ability to melt. All of them differ in their own melting point, which depends on different factors. First of all, this indicator affects the structure of the metal and the presence of any impurities in it. The melting point of the copper is 1084 degrees.
Metal melting process
During the heating of metals, their crystal lattice begins to gradually collapse. IN initial stageAs heated, temperature increases. Having achieved a certain value, it continues to remain at the same level, despite the continuing heating. At such a moment, the melting process begins. It continues until the metal is completely melted. After that, further increase in temperature continues. Thus, everything is melting, without exception, metals.
During cooling there is a reverse phenomenon. The temperature begins to decline until the metal starts to harden. It will be kept on the same level to the final fold, and then again starts to drop. All occurring processes can be displayed graphically, in the form of a phase diagram. It accurately shows the state of the substance when exposed to a certain temperature.
If the molten metal will be heated and then, then when it reaches a certain limit, it will begin to boil. However, unlike fluid, the liquid metal begins to select non-bubbles of gas, and carbon, which is formed during oxidative processes.
Properties of media
Man used copper for his goals since ancient times. Melting copper at relatively low temperatures, made it possible to carry out a variety of operations with this metal. Thus, bronze was obtained, which is an alloy of copper with a tin. In its strength, it significantly exceeded clean copper, which made it possible to produce better weapons and tools.
Currently, copper is also not used in its pure form. In the composition of copper, in large quantities There are different components. Their content reaches 1%. Nickel, iron, arsenic and antimony is used as the main additives. Nevertheless, despite additives, from the technical side, copper is considered a clean metal with high thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. Therefore, it is an ideal material for cable-conductor products.
Copper alloy with other metals
The relatively low melting point of copper is 1084 ° C. This makes it possible to obtain metal alloys based on it with completely different properties.
Among them is well known brass, which is an alloy of copper and zinc, in a percentage ratio of approximately 1: 1. The resulting substance has a lower melting point of 800 to 950 degrees. The specific value of this indicator depends on the ratio of metals contained in the alloy: with a decrease in the amount of zinc, the melting of brass occurs at a lower temperature. This material is used in the foundry, as well as leaf and rolling products. In addition to zinc, other components affect the melting process are added to various brand brass.
Another famous alloy is bronze, in which copper and tin is present. In some cases, iron, aluminum or manganese additives can be used instead of tin. Alloy with tin melts at a range from 900 to 950 degrees. For bronze without tin, this indicator ranges from 950 to 1080 degrees. This material is used to produce various driving parts, as well as in the manufacture of decorative decorations.
Due to the fact that the melting point of copper is quite low, this metal has become one of the first to use ancient people to use for the manufacture of various tools, dishes, jewelry and weapons. Nuggets of copper or copper ore could be melted at a fire, which, in fact, did our distant ancestors.
Despite the active use of mankind from ancient times, copper is not the most common natural metal. In this respect, it is significantly inferior to the rest of the elements and takes only the 23rd place in their row.
How I melt copper our ancestors
Due to the low temperature of 1083 degrees Celsius, our distant ancestors not only successfully obtained pure metal from ore, but also made various alloys based on it. To obtain such alloys, copper heated and brought to a liquid molten state. Then the tin was simply added to such a melt or it was performed on the surface of the molten copper, for which a tin-containing ore (cassiteritis) was used. According to this technology, bronze was obtained - a alloy with high strength, which was used for the manufacture of weapons.
What processes occur when melting copper
Which is characteristic, the melting point of copper and alloys obtained on its basis differ. When having a smaller melting point, bronze with a melting point of 930-1140 degrees Celsius. And copper alloy with zinc (brass) melts at 900-10500 Celsius.
In all metals, the same processes occur during the melting process. Upon receipt of a sufficient amount of heat when heated, the crystal metal lattice begins to collapse. At that moment, when it passes into the molten state, its temperature does not rise, although the process of transferring heat to it with heating does not stop. The metal temperature begins to rise again only when it all goes into the molten state.

When cooling, the opposite process occurs: first the temperature decreases sharply, then for a while stops at a constant mark. After the entire metal goes into the hard phase, the temperature again begins to decline until its full cooling.
Both melting and reverse crystallization of copper are associated with the parameter of specific heat. This parameter characterizes the specific amount of heat that is required in order to translate the metal from the solid state into the liquid. When metal crystallization, such a parameter characterizes the amount of heat that it gives when cooled.
To learn more about the melting of copper helps the phase diagram showing the dependence of the metal condition on temperature. Such charts that can be made for any metals helps to study their properties, determine the temperatures under which they radically change their properties and the current state.
In addition to the melting point, the copper has a boiling point at which the molten metal begins to highlight bubbles filled with gas. In fact, no boiling of copper occurs, just this process is very much reminded. It is possible to bring it to such a state if you heat up to a temperature of 2560 degrees.
As it is clear from the foregoing, it is the low melting point of copper that can be called one of the main reasons that today we can use this metal with many unique characteristics.
If you at least once worried about the melting point of bronze, then this article is for you. Some historical data give the right to believe that the primitive people had copper in everyday life, but she was in nuggets, which could sometimes be impressive sizes.
What is copper?
The name "Copper" (on Latin "Cuprum") comes from the name of the island of Cyprus, on which this metal was mined the ancient Greeks. Due to the fact that copper has a not too high melting point, copper ore or nugget themselves in antiquity melted on a fire. And copper was used in weapons, as well as for the manufacture of different items. According to the presence and distribution in the earth's thicker, copper is on 23 locations about other elements, however, people began to apply it in ancient times. As a rule, in nature, copper is found in the compounds of sulfide ores, the most popular of which is considered copper cchedan and copper shine.
Methods of obtaining media
Technologies for the preparation of copper exist different. But each individual technology has not one stage. Copper is obtained from ore. As mentioned above, the melting point of copper gave the opportunity to cope with the ancient people with its processing. The very remarkable thing is that in antiquity people managed to develop a way of obtaining and further applying both clean copper and alloys.
The melting process is a change in the state of the metal from solid to liquid. It was for this that the bonfire was used, and due to the low melting point, this procedure could be done without any particular difficulties. To obtain alloys in molten copper, tin was added. It could be obtained by restoring from a special tin-containing ore (cassiteritis). Such an alloy was called bronze, which is much stronger copper. Bronze was also used in antiquity for the manufacture of weapons.
And it was also possible to get from the copper ore by melting a cleaner metal. Everyone knows that each metal has its melting point, which in turn depends on how much impurities are present in ore. For example, copper in which the melting point is 1083 ° C, when mixed with tin forms new Material - bronze. And the melting point of bronze is 930-1140 ° C, and different temperatures because it depends on how much it contains tin. Well, if you are interested in learn more, for example, what a bronze color is or what a bronze composition is, then this information can also be found on the Internet.
Brass
For example, brass is a zinc and copper alloy with a melting point of 900-1050 ° C. When the metal heats up and melts, then crystal lattices Begin to collapse. When the melting process, the temperature of the metal gradually increases, and then it becomes constant from a certain mark, but the heating remains the same. Here at the moment when the temperature stops at a certain value, the melting process begins. And at the time of melting metal, the temperature remains on the same meaning, but when the metal is completely melted, the temperature will increase again.
This process occurs relative to any metal. Well, in the process of cooling there is a reverse process, namely: first the temperature drops until the metal starts to harden, and further remains constant. When the metal fully solidifies, the temperature again begins to decline. So all metals behave, depicting this process graphically, it will have the form of a chart with phases, which will clearly see the state of the substance at a specifically temperature mark.
Many scientists enjoy such phase diagrams as the main tool for studying the processes occurring with metals when melting. For example, if already molten metal continue to heat, then when a certain temperature is reached, the mass will start boiled. For example, copper boils at a temperature of 2560 ° C. Regarding metals, such a process was also called boiling, because by analogy of boiling liquid, gas bubbles appear on its surface.
Video: Melting copper in graphite crucible