Hygienic handling algorithm of medical staff. Antiseptic handling of medical staff
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted by http://www.allbest.ru/
Posted by http://www.allbest.ru/
GOU SPO "Tula Regional Medical College"
Department of Postgraduate Education
TEST
Medical Hand Processing Rules, Hygienic Hand Treatment
Professional retraining cycle in the specialty "Nursing case"
Performed: Plugs Sergey Vladimirovich
Introduction
1. Historical information
2. Microflora Skin Hands
3. Resident Microflora
4. Transient microflora
Bibliography
Introduction
Hands are one of the main factors of the transfer of pathogens of the WBI. Through the hands of staff, transient pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic microflora, microbes-opportunists are transmitted. Possible contamination of the operating room and representatives of the residency microflora
1. Historical information
For the first time treatment with a solution of carbolic acid (phenol) for the prevention of the wound infection was applied by the English surgeon by Joseph Lister in 1867. D. Listera method (1827 - 1912) became a triumph of the XIX century medicine.
Robert Koh (1843 - 1910) - German microbiologist, one of the founders of modern bacteriology and epidemiology
In their publications, Koh developed the principles of "obtaining evidence that one or another microorganism causes certain diseases." These principles still underlie medical microbiology.
Hand hygiene is a priority measure that has proved high efficiency in preventing the WBI and the spread of antimicrobial resistance of pathogenic microorganisms. However, even today, the problem of treating the hands of medical personnel cannot be considered solved to the end. WHO studies have shown that insufficient compliance with hand hygiene rules with medical workers is observed both in developed and developing countries.
According to modern ideas, the transfer of pathogens of VBI occurs in various ways, but the most common transmission factor is the contaminated hands of medical workers. At the same time, infection through the hands of personnel occurs in the presence of a number of the following conditions:
1) the presence of microorganisms on the peat cover of the patient or the subjects of its closest environment;
2) contamination of the hands of medical workers by pathogens with direct contact with the patient's skin or its surrounding items;
3) the ability of microorganisms to survive on the hands of medical personnel at least a few minutes;
4) incorrect implementation of the procedure for processing hands or ignore this procedure after contact with the patient or items of its nearest environment;
5) direct contact of the contaminated hands of a medical worker with another patient or subject, which will come into direct contact with this patient.
2. Microflora Skin Hands
I. Resident (normal) microflora are microorganisms that are constantly living and breeding on the skin.
II. The microflora transient is a non-policing microflora acquired by medical personnel in the process of working as a result of contact with infected environmental objects.
1. The pathogenic microflora is a microflora that causes a clinically pronounced disease in healthy people.
2. A conditioned pathogenic microflora is a microflora that causes the disease only in the presence of a specific predisposing factor.
3. Microbes - opportunists are a microflora, which causes a generalized disease only in patients with a pronounced decrease in immunity.
3. Resident Microflora
The resident microflorastimulates the formation of an antibody and prevents the skin settlement with gram-negative microorganisms. The skin layer lives in the horny follicles, coarse, sweat glands, in the field of nail rollers, under the nails, between the fingers.
It is predominantly represented by Cockkops: epidermal and other types of staphylococci, dipteroids, propionibacteriums.
It is impossible to completely remove with the usual washing of hands and processing with antiseptics.
4. Transient microflora
Presented mainly by microorganisms that are in the external environment of the institution, dangerous in epidemiological terms:
pathogenic microorganisms (Salmonella, Shigella, Rotavirus, Hepatitis A viruses, etc.);
conditional pathogenic microorganisms:
Gram-positive (staphylococci gold and epidermal);
Gram-negative (intestinal wand, chlebseyella, pseudomonada);
Mushrooms (Candids, Aspirgilla).
It is saved on hands no more than 24 hours and can be removed by conventional washing of hands and processing with antiseptics.
The most polluted areas of the skin of the hands are:
Subnamed space;
Ocolone rollers;
Pillows of fingers.
The most difficult plots are considered:
Subnamed space;
Interfallated intervals;
Large finger.
Hand disinfection is one of the most effective measures to prevent VBI and to protect patients and medical personnel from infection. The basis of the prevention of VBI - hygienic culture and preparedness in the epidemiological plan at all stages of work.
5. Hand processing rules for medical personnel
To achieve effective washing and disinfection of hands, the following conditions must be observed:
1. Clean, short trimmed nails, no varnish on nails, no artificial nails; Well-groomed (without cracks and sowing) hands, curved (European) manicure;
2. The absence on the hands of rings, rings and other jewelry; Before treating the hands of surgeons, it is also necessary to remove hours, bracelets, etc.;
3. The use of liquid soap using the dispenser;
4. Application for drying the hands of pure fabric individual towels or paper napkins of one-time, when processing the hands of surgeons - only sterile tissue.
6. Hygienic hand treatment
Hygienic handling of the hands of the skin antiseptic should be carried out in the following cases:
Before direct contact with the patient;
Before putting on sterile gloves and after removing gloves when setting the central intravascular catheter;
Before and after the setting of central intravascular, peripheral vascular and urinary catheters or other invasive devices, if these manipulations do not require surgical intervention;
After contact with the intact patient's skin (for example, when measuring the pulse or blood pressure, the patient shifting, etc.);
After contact with secrets or excretions of the body, mucous membranes, bandages;
When performing various patient care manipulations after contact with contaminated microorganisms of the body;
After contact with medical equipment and other objects in close proximity to the patient.
Hygienic handling of hands is carried out in two ways:
Hygienic washing with soap and water to remove contamination and reduce the number of microorganisms;
Treatment of hand skin antiseptic to reduce the number of microorganisms to a safe level.
A liquid soap is used for washing hands using a dispenser (dispenser). Wipe the hands with an individual towel (napkin), preferably disposable.
Hygienic handling of hands with alcohol-containing or other, allowed to use the antiseptic (without their pre-washed) is carried out by rubbing it into the skin of the hands in the amount, recommended by the application for use, paying special attention to the processing of finger tips, leather around the nails, between fingers. An indispensable condition for effective disinfection of hands is maintaining them in a wet state during the recommended processing time.
When using the dispenser, the new portion of the antiseptic (or soap) is poured into the dispenser after its disinfection, washing water and drying. Preference should be given to elbow dispensers and dispensers on photocells.
Skin antiseptics for hand processing should be easily accessible at all stages of the medical diagnostic process. In units with high intensity of patient care and high load on personnel (intensive care and intensive care departments, etc.) Skin antiseptic dispensers must be placed in place-friendly places (at the entrance to the ward, in the bed of the patient and etc.). It should also provide for the possibility of providing medical workers with individual capacities (vials) of small volumes (up to 200 ml) with a skin antiseptic.
7. Hand processing techniques with alcohol-containing skin antiseptic
Rub an antiseptic for hygienic hand treatment! Wash your hands only in the case of the presence of visible contaminants!
8. Hand washing machinery soap and water
Duration of processing - 2-3 minutes, special attention is paid to nails and subnodes.
The movements of each stage are repeated five times, constantly following the hand to remain wet during the entire hand. If necessary, use a new portion of the disinfectant solution. Currently, an alcoholic solution of 0.5% chlorhexidine of Bigluconata in 70% ethyl alcohol, octatenters, octeniman, octenisept, well-axis, AHD 2000 special, decopate plus, 60% isopropanol, 70% ethyl alcohol with mitigating skin additives and DR .
Recently, studies have appeared that prove that wristwrites, fountain pen and mobile phones of medical professionals are also a seedler of microbes
Thus, human hygiene is an integral part of the system of measures for the prevention of nosocomial infection in a medical organization.
infection Hand Antiseptic
Bibliography
Athenogenov G.E., Athenogenova A.G. Modern approaches to medical personnel hygiene // Clinical microbiology and antimicrobial chemotherapy. 2004. T. 6. No. 1.
Opimakh I.V. The history of antiseptics is the struggle of ideas, ambition, ambitions ... // Medical technologies. Evaluation and selection.
WHO management Hand hygiene in Healthcare: Summary, 2013.
Sanpin 2.1.3.2630-10 "Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations carrying out medical activities."
Posted on Allbest.ru.
...Similar documents
Hand skin microflora: resident and transistor. Types of hand treatment: household, hygienic and surgical. Types of microorganisms on the skin. Preparation of hands to hygienic procedures. The sequence of washing procedure. Requirements for skin antiseptic.
presentation, added 01/14/2015
The means used for the hygiene of the hands of medical personnel: disinfectants, antiseptics, sterilians, chemotherapeutic agents, antibiotics, cleansing agents and preservatives. Possible negative consequences Hand processing and their prevention.
course work, added 03/31/2013
Sanitary and hygienic treatment of products representing epidemiological hazards. Thermal, radiation and chemical sterilization. Processing of medical equipment with the help of water vapor, dry hot air, infrared radiation.
presentation, added 10/20/2016
Principles of asepsis. Sources and paths of infection of the operating wound. Activities to reduce the bacterial semination of air. Methods and stages of sterilization. Processing of the surgeon's hands. Ways to control sterility. Rules for processing the operating field.
presentation, added 11/09/2014
Proper and timely processing of hands as a guarantee of the security of medical personnel and patients. Hand processing levels: household, hygienic, surgical. Basic requirements for antiseptics for hands. European hand processing standard EN-1500.
presentation, added 06/24/2014
Requirements for hygienic and surgical antiseptics for handling the hands of medical workers, and its technique. The overall characteristics of myeloma disease, a description of its symptoms and clinical manifestations. Diagnosis, treatment and forecast.
abstract, added 02/27/2014
Characteristics of the work of the city clinical hospital. Hygienic assessment of the location and operation of the reception office. Sanitary improvement of the therapeutic department. Organization of patients. The working conditions of the medical worker.
examination, added 02.03.2009
Rules of wearing medical hats, bathrob, shoes. Requirements for personal linen, clothes. Hygienic principles of medical staff outside the hospital walls. Hygiene premises for medical staff. Requirements for the medical staff when visiting the operating, dressing
abstract, added 07.08.2009
Name of posts relating to medium and younger medical personnel. Hygienic requirements for the working conditions of medical staff. Responsibilities of midwife, paramedics, nurses, dental equipment, laboratory, instructor on therapeutic physical education.
presentation, added 11.02.2014
The concept of disinfection, its types, methods, means and equipment. Basic orders for sanitary-anti-epidemic regime. Types of control of the suitability of disinfectants. Levels and handling rules. Running and removal of sterile gloves.
Places for the sampling of the hands of medical personnel must be equipped according to Sanpin 2.1.3.2630-10. In case of violation of the requirements of the specified SanPIN, the CEAP provides a number of penalties. For example, for a person who violated these requirements, a fine of 1,000 rubles to 2,000 rubles, and for a medical unit - from 10,000 rubles to 20,000 rubles or temporary termination of activities. Below we will look at how to organize the processing process of employees.
Processing of the hands of medical personnel in Sanpina
For high-quality processing of medical personnel in Sainpin, it is necessary that each room is equipped with a washbasin connected to water supply. Mandatory condition - the presence of hot water and cranes with a mixer.
In the premises for which a special procedure for activity is provided, it is required to establish a sinks equipped with an elbow-driven mixer.
"The correct and timely processing of the hands of medical staff, without a doubt, is the security deposit of both the employees of medical institutions and patients. There is such a thing as infections related to the provision of medical care (ISMP). And the reduction in the risk of their appearance can be considered one of the priorities. Directions in the work of the clinic of any profile. According to the World Health Organization, from 100 hospitalized patients at least 7 are infected with IPM.
AnSMP is often associated with the treatment of the hands of the medical staff of the clinic, because the source of pathogenic microorganisms for the patient are exactly what. Now washing hands with medical personnel or their treatment with skin antiseptics is extremely actual infection control measures. Moreover, it is necessary to understand that the pathogenic microorganisms often appear not only on the surface of infected wounds, but also in areas of absolutely healthy skin.
In the Russian Federation, the rules for processing the hands of medical staff have been identified by Sanpin 2.1.3.2630-10 "Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations carrying out medical activities." Hand treatment is made depending on the nature of the medical manipulation performed. Among the mandatory requirements - short-cut worker's nails without chemical (varnished) coating, no decorations.
Two types of disinfection of medical workers are distinguished: hygienic handling of hands and treatment of surgeons. Naturally, in the second case, the processing is of a deeper character. As for hygienic processing, it is always required - to any contact with the patient. She, in particular, provides for washing with soap, as well as processing their skin antiseptic. For hand washing, liquid soaps are used, dosing with a dispenser, but without too hot water. At the same time, alcohol-based skin antiseptics are considered more efficient compared to water-based antiseptics. The surgeon's hands are processed by both methods before operations, and the washing in water should continue at least two minutes.
The third way to protect the hands of medical staff, as well as the warnings of the IPMP are medical gloves - this is perhaps one of the most "protected" ways to interact with patients. "
In the zones equipped for handling the hands of medical personnel, in addition to washbasins, special devices must be provided for use when washing the hands of liquid soap and antiseptics. It is necessary to ensure that they constantly have means for washing and handling hands. In addition, there are also means of care products nearby. Near the washbasin it is necessary to install a bucket that opens with the help of a foot drive. There must be paper towels.
Dispensers for applying liquid soap and antiseptics should be installed not only near washbasins, but also in other areas available for employees. For example, paragraph 12.4.6 ch. I SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 Indicates that the dispensers can be installed at the entrance to the chambers, in the corridors and gateways of offices, in the beds of resuscitation and severely ill patients, on the working and manipulation tables.
Perhaps you will be interested:
Washing Hands of Medical Personnel in Sanmpina: how to choose a dispenser
To handle the hands of medical personnel according to SanPiN, the clinics have a dispenser - this is a special device for issuing something in a certain amount. These devices should be selected on the basis of needs. For example, the dispenser can be both a mechanical pressure and wall-driven-driven (with interchangeable pumps) and even sensory, working without contact. In addition, system dispensers are also considered to be automatically dosing liquid soaps or antiseptic.
Expert says
Dmitry Gornastolev, Chief Physician Network Medical Centers "Medskan"
"The global standard of patient safety is JCI standards, and specifically-information of the International Patient Safety Objectives (IPSG).
In the Russian Federation, the processing of the hands of medical personnel regulated Sanpin 2.1.3.2630-10. The nature of the medical manipulation performed requires a certain level of reducing the microbial contamination of the skin. It is hygienic or surgical treatment of hands of medical staff.
Hygienic handling of hands - medical staff should during the working day and when performing medical manipulations handle hands.
Surgical handling - is carried out in cases where the patient is made by manipulation, accompanied by damage to the skin (invasive manipulations) or surgical treatment methods, incl. Performing a biopsy under the control of computed tomography. This hand processing is different from the hygienic time that the process technologies must also be expected. Surgical processing is more thorough and requires a higher degree of disinfection of the skin to further reduce the patient's contamination.
Tools for processing are usually used alone. And alcohol-based tools show greater efficiency.
Hygienic handling of hands allows in case of an urgent situation just handle hands with an antiseptic and put on sterile gloves. Surgical processing of hands in routine practice does not allow this. Such processing is allowed only in military field conditions (and extremely difficult situations when each second in the account).
Surgical handling of hands begins with the use of soap and has its own characteristics:
- hand treatment begins with fingertips and ends forearm;
- it should be spent at least 5 minutes;
- the back surface of the brushes, interdigital gaps, nail bed, palm, wrist and forearm must be processed;
- after handling hands (from the tips to the forearm), hands are still clean, but only a brush part, the forearm is no longer processed again;
- next comes double processing with an antiseptic (in the same sequence as when washing soap);
- after exposure, the antiseptics on the skin is worn sterile gloves and medical manipulations are produced.
Proper hand processing with medical personnel significantly reduces the frequency of infectious complications, reduces the consumption of antibiotics and reduces the costs of stationary medical care. "
Before purchasing a dispenser for repeated use, you must examine the manufacturer's data to make sure that the manufacturer shows the dispenser cleaning methods. In the event that the dispenser is provided for filling with an alcohol-containing antiseptic, then the presence of permission is necessary for its use with flammable materials.
The advantage has a dispenser working without contact and having a set of disposable cartridges. The device must have accurate incommable labeling with a liquid level, as well as a zone for the location of the shortcut with the name of the applied antiseptic. The instruction to the dispenser should contain data that it can be used with liquids of various manufacturers and that machine cleaning and disinfection of the dispenser can be performed.
Before replenishing the dispenser, it is necessary to clean and disinfect its container. If the dispenser is partially filled, then you should not add a new dose of liquid soap or antiseptic.
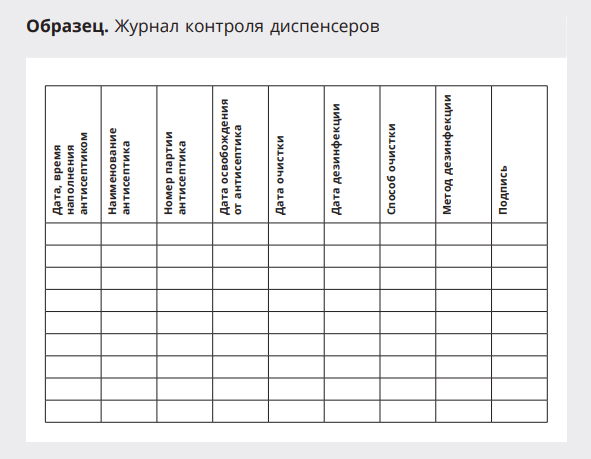
In order to control the dispense service procedures, it is necessary to maintain a sample below.
Standard "Hand processing at the social level"
purpose: removal of dirt and transient flora with contaminating skin of the hands of medical personnel as a result of contact with patients or environmental objects; Ensuring infectious safety patient and personnel.
Indications: Before distributing food, feeding the patient; After visiting the toilet; Before and after care for the patient, if the hands are not contaminated with the patient's biological fluids.
Prepare: Liquid soap in one-time dispensers; Clock with a second arrow, paper towels.
Algorithm Action:
1. Remove the rings, rings, hours and other decorations with fingers, check the integrity of the skin of the hands.
2. Wrap the robe sleeves on 2/3 of the forearm.
3. Open the water tap with a paper napkin and adjust the water temperature (35 ° -40 ° C), thereby preventing the hand contact with microorganisms located on the tap.
4.
Wash your hands with soap under running water up to 2/3 of the forearm for 30 seconds, paying attention to the phalanges, interfallated spaces of hands, then wash the rear and palm of each brush and rotational movements of the base of large fingers of the hands (this time is enough to decontaminate hands at the social level If the surface of the skin of the hands is embedded carefully and dirty areas of the skin of the hands are left).
5. Rinse your hands under running water to remove soap foam (keep your hands with your fingers up so that the water glass into the sink from the elbows, without touching the sink. The phalanges of the fingers should remain the cleanest).
6. Close the elbow cock with the elbow movement.
7. Dry the hands with a paper towel, in the absence of an elbow crane, close the edges with a paper towel.
Standard "Hand processing on hygienic level»
Purpose:
Indications: before and after the implementation of invasive procedures; before putting on and after removing gloves, after contact with biological fluids of the body and after possible microbial contamination; Before leaving a patient with a weakened immunity.
Prepare: Liquid soap in dispensers; 70% ethyl alcohol, watches with a second arrow, warm water, paper towel, safe recycling container (CBU).
Algorithm Action:
1. Remove the rings, rings, clocks and other decorations from your fingers.
2. Check the integrity of the skin's skin.
3. Wrap the robe sleeves on 2/3 of the forearm.
4. Open the water tap with a paper napkin and adjust the water temperature (35 ° -40 ° C), thereby preventing the contact of the hands with microorganisms. Located on the crane.
5. Under a moderate jet of warm water vigorously handhed hands
2 / 3Replace and wash your hands in the following sequence:
- palm about palm;
Each movement is repeated at least 5 times for 10 seconds.
6. Rinse hands under the running warm water Up to the complete removal of soap, keeping hands so that the wrists and brushes were above the level of elbows (in this position water flows from a clean zone to the dirty).
7. Close the crane right or left elbow hand.
8. Dry the hands with a paper towel.
In the absence of an elbow crane, close the crane with a paper towel.
Note:
- in the absence of the necessary conditions for hygienic handwash, you can handle them using an antiseptic;
- Apply on dry hands 3-5
ml of antiseptic agent and rub it on the skin of the hands before drying. Wipe your hands after processing! It is also important to observe the exposure time - the hands must be wet from the antiseptic of at least 15 seconds;
- The principle of processing surfaces "from pure to dirty" is observed. Washing hands can not be touched before foreign objects.
1.3. Standard "Hygienic Handling Antiseptic"
Purpose: Removal or destruction of transient microflora, ensuring patient and personnel infectious safety.
Indications: Before injection, catheterization. Operation
Contraindications: Presence on hand and body of guns, cracks and injuries of skin, skin diseases.
Prepare; Skin antiseptic for hand treatment of medical personnel
Algorithm Action:
1. Spend decontamination of hands on the hygienic level (see Standard).
2. Dry the hands with a paper towel.
3. Apply 3-5 ml of the antiseptic to the palm and rub it into the skin for 30 seconds in the following sequence:
- Palm about palm
- right palm on the back of the left hand and vice versa;
- palm to the palm, fingers of one hand in the interfallated intervals of the other;
- the rear side of the fingertips of the right hand on the palm of the left hand and vice versa;
- rotational friction of large fingers;
- collected together with the tips of the left hand about the right palm with circular movements and vice versa.
4. Ensure complete drying of the antiseptics on the skin of the hands.
Note: Before using the new antiseptic, you need to explore methodical instructions to him.
1.4. Standard "Wearing sterile gloves"
Purpose:ensuring infectious safety patient and personnel.
- gloves reduce the risk of professional infection when contacting patients or their secretions;
- gloves reduce the risk of contamination of the hands of personnel with transient pathogens and subsequent patients,
- Gloves reduce the risk of infection of patients with microbes, which are part of the residential flora of medical workers.
Indications: When carrying out invasive procedures, with contact with any biological fluid, with impaired integrity of the skin, both a patient and a medical worker, with endoscopic studies and manipulations; In clinical and diagnostic, bacteriological laboratories when working with material from patients, when conducting injections, when caring for the patient.
Prepare: Sterile Packaging Gloves, Safe Recycling Container (CBU).
Algorithm Action:
1. Spend decontamination of hands on the hygienic level, handle your hands with an antiseptic.
2. Take gloves in sterile packaging, expand.
3. Take the glove for the right hand for the lapse with your left hand so that the fingers do not touch the inner surface of the glove challenge.
4. Commmise the fingers of the right hand and enter them into the glove.
5. Front the fingers of the right hand and pull the glove on them without disturbing its challenge.
6. Start the left glove on the last glove, the 3rd and 4th fingers of the right hand, already dressed in the glove so that the 1st finger of the right hand was directed toward the 1st finger on the left glove.
7. Keep the left glove 2nd, 3rd and 4th fingers of the right hand vertically.
8. Compact the fingers of the left hand and enter them into the glove.
9. Open your fingers and pull the glove on them without disturbing its challenge.
10. Pour the lapse of the left glove by pulling it on the sleeve, then on the right with the help of the 2nd and 3rd fingers, taking the fluid turned on the edge.
Note: If one glove was damaged, it is necessary to change both immediately, because it is impossible to remove one glove, without polluting the other.
1.5. Standard "Removing gloves"
Algorithm Action:
1. To the fingers of the right hand in the glove, make a lapse on the left glove, touching it only outdoor.
2. To the fingers of the left hand in the glove make a lapse on the right glove, touching it only from the outside.
3. Remove the glove with the left hand, turning it inside out.
4. Keep removed from the left hand the glove for the outstand in the right hand.
5.
Left hand Take the glove on the right hand for the lapse from the inside.
6. Remove the glove with the right hand, turning it inside out.
7. Both gloves (left in the right) Place in the CBU.
Composition of detergent solution
3. Immerse all the medical products in a disassembled form in the detergent solution for 15 minutes, after completing the cavity solution, the channels, close the lid.
4. Proceed by the ears (gauze tampon) in the detergent solution every item for 0.5 minutes (pass the detergent solution through the channels).
5.
Place medical products in the tray.
6. Rinse under running water for 10 minutes each product, passing water through the channels, cavities of products.
7. Perform quality control of preservation with azopyram. The control is subjected to 1% of the simultaneously processed products of one name per day, but not less than 3-5 units.
8. Prepare a working solution of azopyram reagent (the use of the working reagent -2 hour after cooking).
9. Apply a worker reagent with a pipette "for reagent" to medical products (on the body, channels and cavities, places of contact with biological fluids).
10. Keep medical products over cotton or napkin, watching the color of the flowing reagent.
11. Rate the result of azopiram sample.
Standard "Care for ears"
purpose: Compliance with personal hygiene patient, prevention of diseases, preventing hearing reduction due to sulfur accumulation, injection of medicinal substance.
Indications: Heavy condition of the patient, the presence of sulfur in the auditory passage.
Contraindications:inflammatory processes in the ear shell, external auditory passage.
Prepare:sterile: tray, pipette, tweezers, minzur, cotton turtle, napkins, gloves, 3% hydrogen peroxide solution, soap solution, disinfecting solutions, CBU.
Algorithm Action:
1. Explain to the patient the course of the procedure, get it consent.
3. Prepare a container with soap solutions.
4. Tilt the patient's head to the side opposite to the ear ones, substitute the tray.
5. Moisten the napkin in the warm soap solution and wipe the ears, dry the dry cloth (to remove dirt).
6. Pour into a sterile menu, pre-heated in a water bath (T 0 - 36 0 - 37 0 C) 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide.
7. Take a cottling tapurund in the right hand and moisten a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide, and delay the ear shell back and top to align the auditory passage and enter the turtle movements to the outer hearing passage to the depth of no more than 1 cm for 2 - 3 Minutes.
8. Enter dry Turundum with light rotational movements into the outer hearing passage to a depth of no more than 1 cm and leave for 2 to 3 minutes.
9. Remove Turundum by rotational movements from the outer auditory passage - it is possible to remove the discharge and sulfur from the auditory pass.
10. Process another hearing pass in the same sequence.
11. Remove the gloves.
12. Place the used gloves, tours, napkins in the CBU, tweezers, a menzurka in a container with disinfecting solutions.
13. Wash and drain your hands.
Note: When processing the ears, the wool can not be coated on solid items, perhaps a hearing aid injury.
Algorithm Action:
1. Explain to the patient the purpose of the procedure, get its consent.
2. Spend decontamination of hands on the hygienic level, put on gloves.
3. Sharpen under the patient the oilbox.
4. Pour warm water in the pelvis.
5. Adjust the top of the patient's body.
6. Moisten the napkin, part of a towel or a moster in warm water, slightly peel out the excess water.
7. Wipe the patient's skin in the following sequence: face, chin, ears, neck, hands, chest, folds under the lactic glands, armpit depressions.
8. Wipe the patient's body in the same sequence with a dry end of the towel and cover the sheet.
9. Treat the back, alive, thigh, legs in the same way.
10. Put the nails on your hands.
11. Change and bed linen (if necessary).
12. Remove the gloves.
13. Wash and drain your hands.
Algorithm Action:
1. Wash your head seriously ill in bed.
2. Remove the head exalted position, i.e. Put a special headrest or roll the mattress with a roller and turn it under the patient's head, beds on it glued.
3. Throw the patient's head at the neck level back.
4. Put a basin with warm water into a stool at the head end of the bed at the patient's neck level.
5.
Moisten the jet of the patient's head, wash the hair, carefully massage the scalp.
6. Wash your hair towards the head of the head back with soap or shampoo.
7. Rinse your hair and squeeze them with a towel dry.
8. Combing hair with a frequent comb daily, short hair should be combed from the roots to the ends, and the longs are divided into strands and slowly combed from ends to the roots, trying not to pull them out.
9. Purpose Clean Cotton Sloves on the head.
10. The headrest, remove all objects of care, straighten the mattress.
11. Place the used lesor care objects.
Note:
- Wash your head as seriously ill (in the absence of contraindications) follows 1 time per week. The optimal, device for this procedure is a special headrest, but the bed at the same time should be with a removable back, which greatly facilitates this time-consuming procedure;
- women every day combing hair with frequent ridge;
- Male briefly cut hair;
- a frequent comb, moistened in a 6% vinegar solution, is well combed to dandruff and dust.
Standard "Summary"
Purpose:ensuring physiological shipments in a patient.
Indication: Apply patients in strict bed and bedding during the empty of the intestines and the bladder. Prepare: Disinfected vessel, oilcloth, diaper, gloves, diaper, water, toilet paper, Capacity with deshercy, CBU.
Algorithm of action:
1. Explain to the patient the purpose and course of the procedure, get its consent,
2. Rinse the vessel with warm water, leaving in it some water.
3. Extinguish the patient with a screen from others, remove or lean the blanket to the wax, to put the patient under the pellet, the diaper from above.
4. Spend the decontamination of hands on the hygienic level, put on gloves.
5. Help the patient turn on the side, legs slightly bend in the knees and spread in the hips.
6. Left-handed the side under the crushes, helping the patient raise the pelvis.
7. The right hand is moving the vessel under the patient's buttocks so that his crotch is above the vessel opening, while the shower is rapidly.
8. Strong the patient of the assaulomygostnyy, leave it one.
9. At the end of the act of defecation, slightly turn the patient to the next hand, holding the ship with the right hand, remove it from under the patient.
10. Wipe the area of \u200b\u200bthe anal opening toilet paper. Place the paper into the ship. If necessary, fit the patient, drain the crotch.
11. The ship, the oilbox, diaper and shirma. Forwards replace the sheet.
12.
Help the patient make it convenient, cover the blanket .
13.
Cover vertexailoilenenco-toilet room.
14.
Pour the contents of the vessel in the toilet, rinse with rye .
15.
Immerse the vessel in the container with deeschor, lose gloves in
CBU.
16.
Wash and drain your hands.
Dedicated liquid
9. Secure the amount of drunk and injected fluid into the body in the accounting sheet.
Insertion
10. At 6 00 o'clock in the morning the next day, the patient gives a nurse accounting list.
The difference between the amount of drilled liquid and the daily amount of the night is the magnitude of the water balance of the body.
Nurse must:
- Make sure the patient will be able to record fluid.
- Make sure the patient did not take diuretics within 3 days before the study.
- Tell a patient as the amount of fluid should stand out with urine normally.
- Explain the patient an approximate percentage of water in food products to facilitate the accounting of the injected fluid (not only the polls of water in food, but also introduced parenteral solutions).
- Solid food can contain from 60 to 80% water.
- Accounting for the amount of dedicated fluid is not only urine, but also vomit masses, patient feces.
- The nurse calculates the number of insertion and bred night per day.
Determined by the percentage of fluid removal (80% normal amount of liquid removal).
Number of urine derived x 100
The percentage of removal \u003d
The number of injected fluid
Calculate the accounting of water balance according to the following formula:
The total number of selected urine per day is multiplied by 0.8 (80%) \u003d the amount of night, which should be highlighted normally.
Compare the amount of dedicated fluid with the amount of calculated liquid is normal.
- The water balance is considered negative if less fluid is released than calculated.
- The water balance is considered positive if more fluid is isolated than calculated.
- Make records on a sheet of water balance account and evaluate it.
Result rating:
80% - 5-10% - the expenditure rate (-10-15% - in the hot season; + 10-15%
- in the cold time;
- positive water balance (\u003e 90%) indicates the effectiveness of the treatment and convergence of edema (reaction to diuretics or unloading diets);
- Negative water balance (10%) indicates the increase in edema or the inefficiency of dosuretic dose.
I.IX. Puncture.
1.84. Standard "Preparation of a patient and medical instruments for pleural puncture (picking, thrauccenis)".
Purpose: Diagnostic: study of the nature of the pleural cavity; Medical: Introduction to the cavity of medicines.
Indications: Traumatic hemotorax, pneumothorax spontaneous valve pneumothorax, respiratory organs (brute pneumonia, pleurisy, pulmonary emphasis, tuberculosis, lung cancer, etc.).
Contraindications: Increased bleeding, skin disease (pyodermia, slimming, chest burns, acute heart failure.
Prepare: Sterile: cotton balls, gauze napkins, diapers, needles for in / to and p / k injections, needles for puncture 10 cm long and diameter 1 - 1.5 mm, syringes 5, 10, 20, 50 ml, tweezers, 0, 5% novocaine solution, 5% iodine alcohol solution, 70% alcohol, clamp; Cleol, adhesive plaster, 2 radiographs of the chest, sterile tank for pleural fluid, a container with a derazor, direction to the laboratory, a set to assist in anaphylactic shock, gloves, CBU.
Algorithm Action:
2. Let's put the patient, put on the belt, on the chair face to his back, ask him to rely on the back of the chair, and another (on the side of the localization of the pathological process) begged.
3. Ask the patient slightly tilt the torso to the side opposite to the one where the doctor will conduct puncture.
4. The pleural puncture is performed only by the doctor, the nurse assisters him.
5. Conduct the decontamination of hands on the hygienic level, treat them with a skin antiseptic, put on gloves.
6. Process the estimated place of the puncture of 5% alcohol solution of iodine, then 70% solution of alcohol and again with iodine.
7. Apply a syringe doctor with a 0.5% novocain solution for the infiltration anesthesia of intercostal muscles, pleura.
8. The puncture is made in VII - VII intercostal on the upper edge of the underlying edge, since a vascular-nerving beam passes along the bottom edge of the rib and the intercostal vessels can be damaged.
9. The doctor introduces the puncture needle into a pleural cavity and pumps the contents into the syringe.
10. Substitute the container for the extracted fluid.
11. Release the contents of the syringe into a sterile bank (tube) for a laboratory study.
12. Apply a syringe doctor with an antibiotic to introduce into the pleural cavity.
13. After removing the needle, the prolque place is treated with 5% iodine alcohol solution.
14. In place of the puncture, impose a sterile napkin, fix the leukoplasty or rolling.
15. Spend a tight binting of the chest sheet for slowing the exudation of the liquid into the pleural cavity and prevention of the collapse development.
16. Remove the gloves, wash your hands and drain.
17. Used disposable syringes, gloves, cotton balls, napkins Put in the CBU, a puncture needle into a container with a deeschor.
18. Watch out for the patient's well-being, the state of the bandage, calculate the pulse, measure the hell.
19. Scroll into the patient to the Chamber on the catal, lying on the stomach.
20. Warning the patient about the need to comply with bed regime for 2 hours after the manipulation.
21. Send the resulting biological material to study in the laboratory with a direction.
Note:
When extracting from the pleural cavity, more and more than 1 liter of liquid is large, the risk of the occurrence of the collapse;
Delivery of pleural fluid to the laboratory must be carried out without delay in the essence of the destruction of enzymes and cell elements;
If the needle gets into the pleural cavity, the feeling of "failure" appears in the free space.
1.85. Standard "Preparation of a patient and medical instruments to carry out abdominal puncture (laparocenesis)."
Purpose: Diagnostic: laboratory study of ascitic fluid.
Medical: Removing the accumulated liquid from the abdominal cavity during ascite.
Indications: Ascites, with malignant neoplasms of the abdominal cavity, chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis, chronic cardiovascular failure.
Contraindications: pronounced hypotension, adhesion process in the abdominal cavity, a pronounced meteorism.
Prepare: Sterile: cotton balls, gloves, trocar, scalpel, syringes 5, 10, 20 ml, napkins, bank with lid; 0.5% novocaine solution, 5% iodine solution, alcohol 70%, tank for extracted liquid, pelvis, tubes; Wide towel or sheet, leucoplasty, a set for an anaphylactic shock, a container with a deceor, direction to the study, dressing material, tweezers, CBU.
Algorithm Action:
1. Inform the patient about the upcoming study and get its consent.
2. In the morning on the day of research, make a patient a cleaning enema to the effect of "clean water".
3. Immediately before carrying out the manipulation, offer the patient to empty the bladder.
4. Ask the patient to sit on the chair, leaning on his back. Patient legs cover with loaf.
5. Extend the decontamination of hands on the hygienic level, process them with the skin antiseptic, put on the gloves.
6. Feed a 5% alcoholic iodine alcohol solution, then a 70% alcohol solution for skin treatment between navel and pubic.
7. Apply a syringe doctor with a 0.5% novocain solution for layer-by-layer infiltration anesthesia of soft tissues. The puncture with laparocentsis is made along the middle line of the front abdominal wall at an equal distance between the navel and the pubic, retreating 2-3 cm to the side.
8. The doctor with a scalpel opens the skin, the right hand with ruling movements push the trocar through the thickness of the abdominal wall, then removes the stiletto and the ascitic fluid begins under pressure on the water cannula.
9. Substitute the capacitance (pelvis or bucket) in front of the patient for fluid flowing from the abdominal cavity.
10. Type 20 - 50 ml of liquid for laboratory research (bacteriological and cytological) in a sterile jar.
11. Put under the bottom of the patient's abdominal sterile sheet or a wide towel, the ends of which should keep a nurse. Tighten the stomach with a sheet or a towel covering it above or below the point of puncture.
12. A wide towel or sheets periodically tighten the front abdominal wall of the patient as fluid removes.
13. After the procedure is completed, it is necessary to remove the cannula, the wound to take the skin seam and process with 5% iodine solution, impose a aseptic bandage.
14. Remove the gloves, wash your hands and drain.
15. Used tools. Put in deeschor, gloves, cotton balls, syringes. Put in the CBU.
16. Determine the patient the pulse, measure the hell.
17. Transport the patient to the Chamber on the catal.
18. Warning the patient to observe the bed regime within 2 hours after the manipulation (in order to avoid hemodynamic disorders).
19. Send the resulting biological material to study in the laboratory.
Note:
When conducting manipulation, strictly follow the Asepta rules;
With the rapid seizure of the liquid, a collapse and a fainting condition may develop, due to the fall in intra-abdominal and intrabrudal pressure and the redistribution of circulating blood.
1.86. Standard "Preparation of a patient and medical instrument for the conduct of spinal puncture (lumban)".
purpose: Diagnostic (for the study of the cerebrospinal fluid) and therapeutic (for the introduction of antibiotics, etc.).
Indications: meningitis.
Prepare: Sterile: syringes with needles (5 ml, 10 ml, 20 ml), puncture needle with mandzers, tweezers, napkins and cotton balls, tray, nutrient medium, test tubes, gloves; pressure gauge tube, 70% alcohol, 5% alcohol solution of iodine, 0.5% novocaine solution, leucoplasty, CBU.
Algorithm Action:
1. Inform the patient about the upcoming procedure and agree.
2. The puncture is carried out in conditions of strict compliance with Asepta rules.
3. Spend patient to the procedural office.
4. Squeeze the patient on the right side closer to the edge of the couch without a pillow, tilt your head forward to the chest, bend your legs as much as possible and tighten to the stomach (the back should be flexing with arc).
5. Slide the left hand under the side of the patient, holding the patient's legs with his right hand to fix the position piled back. During the puncture, another assistant fixes the patient's head.
6. The puncture is made between III and IV lumbar vertebrae.
8. Treat the skin on the site of the puncture of 5% iodine solution, then 70% solution of alcohol.
9. Type a solution of a 0.5% solution of novocaine in a syringe and submit a doctor to carry out infiltration anesthesia of soft tissues, and then a puncture needle with mandren on the tray.
10. Collect the spinal fluid in the amount of 10 ml into the test tube, write the direction and send to the clinical laboratory.
11. Collect 2-5 ml of spinal fluid into a tube with a nutrient medium for bacteriological research. Write the direction and send biological material to the bacteriological laboratory.
12. Apply the doctor a pressure gauge to determine the likvorn pressure.
13. After removing the puncture needle, processes the prolque position of 5% iodine alcohol solution.
14. Take a sterile napkin to the place of puncture, glue the leukoplasty.
15. Place the patient on the stomach and take on the boarding school.
16. Squeeze the patient on the bed without a pillow in the stomach position for 2 hours.
17. Observe the patient's condition during the day.
18. Remove the gloves.
19. Place the syringes, cotton balls, gloves in the CBU, used toolkit in the deeschor.
20. Wash and dry.
1.87. Standard "Preparation of a patient and medical instrument for sterile puncture".
purpose: Diagnostic: Bone marrow research to establish or confirm the diagnosis of blood diseases.
Indications: Diseases of the hematopoietic system.
Contraindications: Myocardial infarction, bouts of bronchial asthma, extensive burns, skin diseases, thrombocytopenia.
Prepare: Sterile: Tray, syringes 10 - 20 ml, puncture needle of cashier, slide glass 8 - 10 pieces, cotton and gauze balls, Corncang, tweezers, gloves, 70% alcohol, 5% alcohol iodine solution; Adamoplasty, sterile dressing material, CBU.
Algorithm Action:
1. Inform the patient about the upcoming study and get its consent.
2. Sternal puncture is carried out by a doctor in the procedural office.
3. Punctured yard at level III - IV intercostal.
4. The nurse assists a doctor when conducting manipulation.
5. Invite the patient to the procedural office.
6. Offer the patient to undress to the belt. Help him lie on the couch, on the back without a pillow.
7. Spend the decontamination of hands on the hygienic level, treat them with skin antiseptic, put on gloves.
8. Treat the front surface of the patient's chest, from the clavicle to the Zpigastric region with a sterile cotton ball, moistened with 5% iodine solution, and then 2 times 70% alcohol.
9. Spend a layered infiltration anesthesia of soft tissues with 2% novocaine solution up to 2 ml in the center of the sternum at the level III - IV interchange.
10. Apply to the Cassirsky punctural needle, setting the limiter shield to 13-15 mm tip of the needle, then sterile syringe.
11. The doctor pierces the outer plate of the sternum. The hand feels the failure of the needle, having reached Mandren, 20.0 ml of syringe join the needle and the 0.5 ml of bone marrow, which poule onto the slide glass to the needle.
12. Dry slide glass.
13. After removing the needle, the prolque place is treated with 5% iodine alcohol solution or 70% alcohol solution and impose a sterile bandage, fix the leukoplasty.
14. Remove the gloves.
15. Reset the spent gloves, syringes and cotton balls in the CBU.
16. Wash your hands with soap and dry.
17. Conduct the patient to the ward.
18. Send glass slots to the laboratory direction after the material drying.
Note: Cashier's needle is a short fat-walled needle with Mandren and a shield that protects against too deep penetration of the needle.
1.88. Standard "Preparation of a patient and medical instrument for conducting puncture of the joints."
purpose: diagnostic: determination of the character of the contents of the joint; Therapeutic: removal of reach, washing the body of the joints, the introduction into the joint of medicinal substances.
Indications: Diseases of the joints, intra-articular fractures, hemoarthrosis.
Contraindications: Purulent inflammation of the skin at the point of puncture.
Prepare: sterile: puncture needle 7 - 10 cm long, syringes 10, 20 ml, tweezers, gauze tampons; Aseptic dressing, napkins, gloves, tray, 5% iodine alcohol solution, 70% alcohol solution, 0.5% novocaine solution, test tubes, CBU.
Algorithm Action:
1. The puncture is carried out by a doctor in a procedural office in conditions of strict compliance with the Asepta rules.
2. Inform the patient about the upcoming study and receive its consent.
3. Spend decontamination of hands on the hygienic level, treat them with a skin antiseptic, put on the gloves.
4. Ask the patient to sit on the chair conveniently or take a convenient position.
5. Feed a 5% alcoholic iodine alcohol solution, then a solution of 70% alcohol for processing the intended place of puncture, a syringe with a 0.5% solution of novocaine for infiltration anesthesia.
6. The doctor with the left hand covers the joint at the point of puncture and presses the effusion to the place of puncture.
7. The needle is introduced into the joint and the syringe is gaining effusion.
8. Pour the first portion of the contents from the syringe into the test tube without touching the walls of the test tube for a laboratory study.
9. After puncture in the body cavity, antibiotics, steroid hormones are introduced.
10. After removing the needle, the prolque place is greased by a 5% iodine alcohol solution and impose a aseptic bandage.
11. Place the used syringes, napkins, gloves, gauze tampons in the CBU, puncture needle to destery.
12. Remove the gloves, wash and drain your hands.
I.XII. "Preparation of a patient to laboratory and instrumental research methods."
Standard "Preparing a patient for fibrogastroduodenoscopy"
Purpose:provide high-quality preparation for research; Visual inspection of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenal
Prepare:sterile gastroscope, towel; Direction for research.
FGDS holds a doctor, a nurse assistive.
Algorithm Action:
1. Explain to the patient the purpose and course of the upcoming study and get its consent.
2. Spend psychological training of the patient.
3. Inform the patient that the study is conducted in the morning on an empty stomach. Exclude meals, water, drugs; Do not smoke, not brush your teeth.
4. Ensure the patient in the evening with a light dinner no later than 18 hours, after dinner, the patient should not eat and drink.
5.
Make sure the patient before the study removed removable dentures.
6. Warning the patient that during endoscopy he should not speak and swallow saliva (saliva the patient spits in a towel or into a napkin).
7. Conduct the patient into an endoscopic office with a towel, the history of the disease, the direction to the appointed hour.
8. Scroll into the patient to the ward after the study and ask him for 1-1.5 hours not to eat until a complete recovery of the act of swallowing; Do not smoke.
Note:
-
Moving P / K is not carried out, because Changes the state of the under study;
- When taking material on a biopsy - food is fed to the patient only in a cold form.
Standard "Preparation of a patient for colonoscopy"
Colonoscopy -this is the instrumental method of studying highly located colon departments with a flexible endoscope probe.
Diagnostic value of the method:Colonoscopy allows you to justice
It is known that human skin performs a number of essential functions, one of which is protection against the impact of harmful environmental factors. The skin, especially the skin of the hands, is constantly populated by microorganisms. Intact (unharmed) human skin, even thoroughly washed, colonized by microorganisms, which can be different for individual areas of the skin and relatively constant for each person.
Man's skin microflora is divided into resident and transient.
Resident (constant)microflora is represented by bacteria that constantly live and multiply in the skin. These microorganisms colonize deeper layers of skin, including rigorous, sweat glands and hair follicles, and are mainly represented by staphylococci coagulates (more often than staphylococcus epidermidis) and dipteroids (CoryntBacterium SPP.) Basically the resident microflora does not cause pathological processes in patients with intact skin, However, it may cause the infectious process when entering sterile cavities of the human body. Resident microorganisms are almost impossible to remove, but their number can be significantly reduced. In the same time sterilization of hand It is not easy impossible, but also undesirable, because the resident microflora warns the skin settling with more dangerous microorganisms, and also synthesizes fatty acids that have an antimicrobial effect.
Transient (temporary) The microflora is represented by microorganisms, temporarily settled on the skin of the hands, they colonize surface layers of the skin and have the greatest epidemiological value. The transient microflora may consist of any microorganisms, including pathogenic, including causative agents of nosocomial (nosocomial) infections, such as Escherihia Coli, Klebsiella SPP, Pseudomonas SPP, Salmonella SPP., St. Aureus (including MRSA), Candidae albicans, rotaviruses, etc. When damaged skin cover, including during the use of inadequate methods of washing and disinfection of hands, the transient microflora penetrates deeper into the skin, displacing the resident flor from there.
The transfer of microorganisms through the hands depends on different conditions, including from the type of microorganisms, the possibility of their survival in the hands, the degrees of seeding of the skin with microorganisms etc. In this case, the species composition of microflora of the skin of the medical staff depends on the profile of the institution or department and the nature of professional work. According to the Central Research Institute of Epidemiology (Moscow, Corresponding Member. Ramna, Professor N. A. Semin, Professor A. P. Kovaleva), the number of nosocomial infections in Russia is 52-60 thousand annually. It has been proven that the cause of infections in hospitals in 50-80% of cases has hands of medical personnel, that is, hands are one of the key factors in the transfer of pathogenic microorganisms, both from medical personnel to patients and vice versa. According to the results of the analysis of the statistical indicators of the American Society for Control and Prevent Diseases (CDC), about 2 million patients annually receive nosocomial infections during treatment. The so-called nosocomial or hospital, hospital infections are the cause of not only the suffering and death of patients. They also cause significant economic damage and pay $ 5 billion annually for expenses for additional hospitalization and expensive antibiotic treatment. All outlined once again underlines the extreme importance of strict compliance with the principles of hand hygiene.
Medical staff hand processing methods
Hygiene hand - A common term used to identify procedures such as usual hand washing, hygienic disinfection of hands and surgical disinfection of hands.
Normal hand washing - It is washing hands with water and usual (non-antiseptic) soap.
Hygienic disinfection of hands It is carried out in order to reduce the number of pathogenic microorganisms on the skin of the hands, is applied in the following cases:
- before direct contact with the patient;
- before performing invasive procedures;
- before and after manipulation with wounds and catheters.
- before and after dressing gloves;
- after contact with the biological fluids of the body or after possible microbial insemination;
- before treatments to patients with weakened immunity;
- before the examination of the pure section after contact with the contaminated part of the body, etc.
It has been proven that the cause of infections in hospitals in 50-80% of cases has hands of medical personnel, that is, hands are one of the key factors in the transfer of pathogenic "microorganisms both from medical personnel to patients and vice versa.
It can be performed using special antiseptic recipes during surgical washing. There are two ways of hygienic disinfection of hands: hygienic washing of hands and processing (wiping) with antiseptic hands.
Hygienic hand washing - It is washing hands with water and soap or other detergent containing an antiseptic drug. As a result of hygienic washing, most of the transient microflora is removed, but even with routine washing, some skin sections (internal surfaces, fingertips) remain contaminated.
Treatment of hands antiseptic It is more often applied in practice and according to the results of laboratory research is more efficient. Hands are wiping with enough antiseptic agent without adding water to it before starting and during the procedure (most often it is a drug based on a combination of alcohols with a variety of antiseptic additives) so that the skin remains humid for the necessary exposure time from 30 to 60, depending on the manufacturer's recommendations. . The most carefully you need to handle your nails and fingertips.
Hygienic processing of hands (Using the antiseptics) after the implementation of medical manipulations should be carried out before washing, and not vice versa to avoid contamination of the surrounding surfaces by pouring polluted water. When care for patients with infections caused by sporing-forming bacteria (for example, Clostridium difficile), the use of only antiseptic agents without pre-hand washing will not provide reliable decontamination due to the fact that they do not have a sporocidal. activity. In such cases, as well as if the skin must be cleaned of visible contaminants (including organic origin), the previous hygienic hand washing is mandatory before treating the hands of the antiseptic.
An important condition for the effectiveness of hygienic hand treatment is observing the following rules:
- when carrying out hygienic disinfection of the hands by wiping the alcohol antiseptic, it is necessary to apply to the palm of one hand and rub over the entire surface of the brushes and fingers of both hands to their complete drying.
- when washing hands, you must first moisten with water, then apply the required amount of money and thoroughly wipe your hands for at least 15 s to process the entire surface of the brushes and fingers, then wash your hands with water and thoroughly dry them with a disposable towel that is used to close the crane ;
- it is advisable to use small slices of soap and apply supports in the form of grids for its rapid drying.
- it is not recommended to use reusable tissue towels.
Surgical disinfection of hands - It is handling hands before surgery, providing removal of transient and reduce the amount of residency microflora.
Surgical disinfection of hands It can be performed using special antiseptic recipes during surgical washing. This method has been applied for a long time, and the recipes used have long been known. These are such as treatment with chlorhexidine Bigluconate (hybitan), C-4 recipe (exception), etc. Specified antiseptic formulations are quite aggressive for the skin, especially considering the frequency of application by their medical personnel, which takes part in operational interventions. In addition, to mechanical damage to the skin, the appearance of microtrase leads and use during surgical washing of special brushes using the aforementioned antiseptic recipes.
Promising for today is to use for surgical disinfection of the hands of antiseptic agents made on the basis of a combination of alcohols with other antimicrobial additives. Such drugs are characterized by a rapid destructive effect on the microflora, high antimicrobial properties. For surgical disinfection of hands, the same drugs can be used as for hygienic disinfection, while the difference is to increase the amount of antiseptic for one processing (from 6 to 10 ml - the wrist and forearms are needed in additional processing) and the extension of time and exposure up to five minutes , depending on the manufacturer's recommendations. It is not necessary to use brushes during processing.
In order to reduce the number of microorganisms that breed on the skin under gloves, it is quite effective to use antiseptics with constituents that provide time prolonged antimicrobial effects. Reducing the number of residual skin bacteria in the members of the surgical brigade during the operation reduces the risk of bacteria to enter the site of the operating field in cases of punishing or breaking gloves during operational interventions.
To effectively carry out surgical disinfection of hands, it is necessary to strictly follow the following rules:
- before surgical disinfection, you need to remove rings, rings, clocks and bracelets;
- hands washing with water with soap, preferably liquid (the use of antiseptic soap is not necessary);
- thoroughly dry with sterile napkins (before starting treatment with an antiseptic, the skin must be absolutely dry, because the antiseptic rubbing into the moistened skin leads to its dilution, a decrease in efficient concentration and, as a result, to the impossibility of achieving the desired result.
- during treatment, the skin sections should remain a moistened antiseptic, while the drug is applied to the hands of 3-5 ml portions;
- fully dry the skin before dressing sterile gloves in order to prevent intense reproduction of microorganisms, which can occur in a wet layer.
With affordable antiseptics, alcohols are most safe, while ethyl alcohol is characterized by a less irritant action than propyl or isopropyl alcohol.
Side effect of antiseptics on the skin of the staff.
According to various studies, approximately 25% of the nursing staff feel the symptoms and signs of dermatitis with localization on the skin of the hands. Skin irritation associated with the use of antiseptic soap can be due to both the antimicrobial substance that is included in its composition and other components. Leather damage also leads to a change in the composition of its microflora, increasing the frequency of colonization of staphylococci and gram-negative microorganisms.
With affordable antiseptics, alcohols are most safe, with ethyl alcohol characteristic less irritating effect than N-propyl or isopropyl alcohol. Most often, contact dermatitis is observed when using iodoform. Other antiseptics that can cause contact dermatitis: chlorhexidine, chlorxylene, triclozane and alcohol-containing means. However, the factors causing the occurrence of contact dermatitis associated with frequent hand wash can be the following: use for washing very hot water, low relative humidity (especially in winter), insufficient use of protective creams, low quality paper towels and allergies to Latex.
It is worth noting that most often the cause of contact allergies when using hand hygiene tools is flavors and preservatives, and less frequently - emulsifiers. Liquid soap, lotions and creams may contain ingredients that can cause contact allergic reactions in health workers. Alcohi-containing means for hygienic disinfection rarely become the cause of allergic dermatitis, but it is necessary to take into account that, to enhance the antimicrobial properties, alcohol-containing drugs are combined with different substances, for example, with quaternary ammonium compounds (hour), lactic acid, chlorhexidine Bigluconatte, octalidine hydrochloride.
Recently, new antiseptics in the form of gels have been offered in the market of antiseptic tools.
Due to their recipe, such drugs are suitable for antiseptic processing particularly sensitive to skin irritation.
To prevent the occurrence of contact dermatitis, it is advisable to consider the possibility of reducing the risk of their occurrence, which may include:
- reducing the frequency of application of irritant (especially anionic detergents);
- replacement of funds having a strong irritating effect on those that are less irritated to the skin;
- training of health workers to the right use of antiseptics;
- ensuring health workers with skin care and protective creams.
Reducing the frequency of use of antiseptic treatments for hand hygiene is an unwanted strategy, given the low level of observance of the hygiene of the hands of health workers. The introduction into the practice of alcohol-containing antiseptics with softening additives allows to reduce the frequency of influence on the personnel of irritating substances (soap and detergents).
General approaches to the choice of antiseptic
The administration of the medical and prophylactic institution should take into account that, thanks to the acquisition of more efficient antiseptics, the practice of hand hygiene is improved, and therefore it is possible to prevent the emergence of nosocomial infections. The attention of all of several cases of nosocomial infections compensates for the additional costs of LPZ related to the acquisition of more effective tools For hygiene hands.
When choosing an antiseptic agent for hand hygiene, it is necessary to take into account the opinion of the staff of the compatibility of antiseptics with the skin, the frequency of irritation due to their use.
The cost of hand hygiene should not be the main factor in their choice, because low-cost disinfectants may not contain highly efficient skin care additives, warning the occurrence of allergies, irritations of skin cover.
Read:
|
Allocate 3 levels of decontamination (disinfection) of the hands:
1. Social.
2. Hygienic (disinfection).
3. Surgical.
Social level processing
Two washing not very polluted hands with water with water. Allows remote from the skin most transient microorganisms.
Social treatment of hands is carried out:
Before taking food
After visiting the toilet
Before and after patient care
With contamination of the hands
Before dressing gloves after removing gloves
Equipment: soap, liquid soap, napkins, sterile towel.
Using soap, it must be kept in a dry form (hanging or storing in a special soap) to prevent contamination with some microorganisms that grow in such an environment.
ALGORITHM
2. Out the palm, wash your hands by energetic mechanical friction of the strained palms for 10 seconds, washing the soap under running water, keep hands so that the wrists and hands are above the level of elbows.
Note: In this position, water flows from a clean zone to the dirty.
ATTENTION: Wet towel not apply !!!
Given the number of microorganisms transmitted through hands, it is important to understand that the washing of hands, the serious prevention of vibium, viral hepatitis.
Hygienic hand processing
A certain washing technique, including using antiseptic agents. This is a more efficient method for removing and destroying microorganisms.
Hygienic handling is carried out:
Before performing invasive procedures
Before leaving a patient with a weakened immunity
Before and after care for the wound, urinary catheter
Before dressing and after removing gloves
After contact with the biological fluids of the body
Before working with a sterile table
Equipment: soap, liquid soap, skin antiseptic, sterile napkins or disposable towels.
ALGORITHM
1. Remove all rings with hands, remove the clock, open a water tap using a disposable napkin, adjust the water temperature.
2. Naming the palm, wash your hands by energetic mechanical friction of embroidered palms within 10 seconds:
1) friction palms
2) Palm to palm: friction of interfallated gaps
3) washing the back of the fingers opposite palm
4) alternate friction of big palm fingers
5) Conduct variable friction palms with fingers of another hand wash the soap under running water.
3. Close the water tap using a paper napkin, dry your hands with a disposable towel.
4. Apply 3-5 ml of antiseptics.
Treatment of hands and mucous membranes when contact with biological fluids.
1. When contaminating the skin of the hands, blood, and the like. It is necessary to wash your hands with soap and water; Thoroughly dry hands with a disposable towel; Twice handle with antiseptic.
2. Hands in gloves to treat a napkin moistened with disinfectant, then wash with running water, remove gloves, wash your hands and treat the skin antiseptic.
3. If the biological fluid is hit on the mucous oxide, the mouth and the throat rinse with 70% alcohol or 0.05% solution of potassium mangartage.
4. In case of biological fluids in the eye, rinse with a solution of potassium mangartage in water in a ratio of 1: 10,000.
5. During injections and cuts, wash your hands without removing gloves, running water with soap, remove the gloves, squeeze blood out of the wound, wash your hands with soap and handle the wound 5% alcohol tincture of iodine. If you have a microtraum, scratch, scratching damaged plaster plaster.
6. According to the indications, extraction prevention of hepatitis and HIV infection is carried out.
7. Upon receipt of injuries, including microtrams (injections, cuts), dangerous in terms of infection, responsible for the prevention of parenteral infections in the LPU organizes the registration in the accounting journal and is an act in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
8. Sitting and protective creams, ensuring the elasticity and strength of the skin, are used to care for hands.
Disinfection
Disinfection is a system of measures aimed at the complete destruction of pathogenic microorganisms and the destruction of patrogen-based organisms to a safe level at the external environment.
In disinfection of a high level (two), only some types of microorganisms dispute remain viable (used for the final processing of flexible endoscopes).
Types of disinfection
1. Preventive - before the appearance of cases of infectious diseases (chlorination of tap water, cleaning of rooms with disinfecting solutions).
2. The focal - when the focus of the disease appears (in the apartment, hospital, etc.) is divided into:
1) the current - from the moment the infectious disease is detected until the patient is removed from the hearth;
2) Final - after removing the patient from the epide. focus.
Disinfection methods
1. Mechanical methods:
Wet cleaning of premises and furnishings;
Liberation of the premises from dust with the help of vacuum cleaners, whitewings, painting rooms;
Washing hands.
2. Physical agents and methods (thermal):
Sun rays;
Irradiation with ultraviolet radiation;
Stroking hot iron;
Burning garbage and items that are not valuable;
Processing boiling water or heating to boiling;
Pasteurization;
Boiling.
3. Chemical methods (chemical substance destroying microorganisms):
Irrigation;
Rubbing;
Full immersion;
Spraying (apply aqueous solutions, emulsions, powders).
Disinfection control methods:
1. Visual (art. M / s, ch. M / s, epidemiologist);
2. Chemical (indicator strips - determine the percentage concentration of the active substance in the working solution).
3. Bacteriological (washes).
Documentation for working with disinfectants:
1. "Journal of accounting and spending of disinfectants";
2. "Working instructions for the preparation of a disinfectant solution";
3. "Folder with the results of chemical control of the percentage concentration of the active substance in the working solution."
Precautions when working with disinfectants
1. Used for disinfection, pre-solidization processing, sterilization, disinfection. Chemical preparations have a varying degree local and common toxic effect.
2. Faces are allowed to work with disinfection drugs, persons not under the age of 18, which have passed the appropriate instruction on duties, safety techniques, precautionary measures and the prevention of random poisoning, set out in the "Rules for labor protection of workers of disinfectural departments, offices of preventive disinfection of sanitary and epidemic stations, separate Disinfection installations "approved by the USSR Ministry of Health 09.02.1979 No. 1963-79. Responsible for the instruction is the chief physician of the institution or a specially appointed person.
3. Persons with increased sensitivity to applicable chemicals and allergic diseases from working with them are removed.
4. During work, it is necessary to follow personal hygiene rules. Do not smoke, drink, eat. After working open areas of the body (face, hands) wash with water with soap.
5. Soaking underwear, dishes and other items in solutions of disinfectants, preservation processing and sterilization of medical products with chemicals are carried out in special rooms equipped with supply-exhaust ventilation.
6. Preparation of working solutions of disinfectants are carried out in well-ventilated premises. Stored solutions and withstand processed objects in tightly closing tanks. Stocks of drugs are stored in places inaccessible to common use, in dark dishes, in a dry, dark and cool premises. All disinfectants and solutions must have labels indicating the name, concentration, production dates and shelf life. In the departments, disinfectants and their solutions are stored under the lock in places inaccessible for children and disinfection individuals, separately from therapeutic drugs.
7. Strictly follows the sequence, and the stages of washing and disinfection are accurately performed, providing maximum removal from the processed objects of detergents and disinfectants.
8. All work with disinfectants, chemicals are carried out in accordance with the instructions.
9. When cleaning the spilled concentrate, it is necessary to use protective clothing, boots and personal protective equipment: respiratory organs by universal RPG-67 type respirators or RU-60M with brand in brand 9. eye - hermetic points; Skin hands - rubber gloves. The resulting concentrated remedy should be adsorbed by a moisture-holding substance (sand, sawdust) or rag and send to disposal. It is forbidden to merge the concentrated agent into the sewer.
First aid for random poisoning disinfection drugs.
1. In violation of the mode of operation, non-compliance with precautions and in emergency situations, personnel may have phenomena of general poisoning or local irritation with disinfection drugs. Characteristic for most applied chemical disinfection and sterilization chemicals is an irritant effect on the skin, mucous membranes of the eyes, respiratory tract.
2. If the drug gets into the skin immediately washed off this section with clean water. Lubricate the skin with a softening cream.
3. When signs of irritation of the respiratory organs should be discontinued with the means. Immediately remove the victim from the room on fresh air or in a well-ventilated room, mouth and the nasopharynk rinse with water, if necessary, consult a doctor.
4. If the drug gets into the eyes immediately rinse them under the jet of water for 10-15 minutes, drip a 30% sodium sulphacian solution. Urgently consult a doctor.
5. When means in the stomach, give the victim a few glasses of water with 10-20 crushed tablets of activated carbon. Stomach do not wash. If necessary, consult a doctor.
Before using any new disinfectant carefully examine instructions and precautions.
The technique of preparing disinfectants Goal: Use for disinfection, according to the order for compliance with the sanitary.
EQUIPMENT:
Overalls:
Long robe
Hood
An apron of glue
Medical gloves
Respirator (4 - layer gauze mask)
Protective glasses
Indoor shoes
Dz. means
- Capacity:
For water with labeling with lids
For a disinfecting solution with labeling with lids
For detergent with labeling with lids.
ATTENTION: See the instructions for cooking and use
| Stages | Justification |
| Preparation for the procedure | |
| 1. Return overalls. | Security M / s in the workplace |
| 2. Add equipment | Compliance with clarity in work |
| 3. Check marking (Description Tools, Concentration, Purpose, Cooking Date) | Providing personal responsibility |
| Procedure | |
| 1. Put in the water capacity up to the label | |
| 2, put the disinfectant in water tank | Compliance with the method of preparation of the percentage concentration solution |
| 3. Perform a solution with a wooden spatula | |
| 4. Close the lid. | |
| 5. By tag to put the date of preparation and signature M / s. | Ensuring continuity in working with Dz. solutions, personal responsibility. |